USP2
-
Official Full Name
ubiquitin specific peptidase 2 -
Overview
This gene encodes a member of the family of de-ubiquitinating enzymes, which belongs to the peptidase C19 superfamily. The encoded protein is a ubiquitin-specific protease which is required for TNF-alpha (tumor necrosis factor alpha) -induced NF-kB (nuclear factor kB) signaling. This protein deubiquitinates polyubiquitinated target proteins such as fatty acid synthase, murine double minute 2 (MDM2), MDM4/MDMX and cyclin D1. MDM2 and MDM4 are negative regulators of the p53 tumor suppressor and cyclin D1 is required for cell cycle G1/S transition. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been identified. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2011] -
Synonyms
USP2;ubiquitin specific peptidase 2;USP9;UBP41;ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase 2;ubiquitin thioesterase 2;deubiquitinating enzyme 2;ubiquitin specific protease 9;ubiquitin specific protease 12;41 kDa ubiquitin-specific protease;ubiquitin-specific-processing protease 2
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Rhesus macaque
- Rat
- Chicken
- E.coli
- Sf9 Cells
- Mammalian Cells
- HEK293
- Non
- GST
- Flag
- His
- Avi
- Fc
- DDK
- Myc
Background
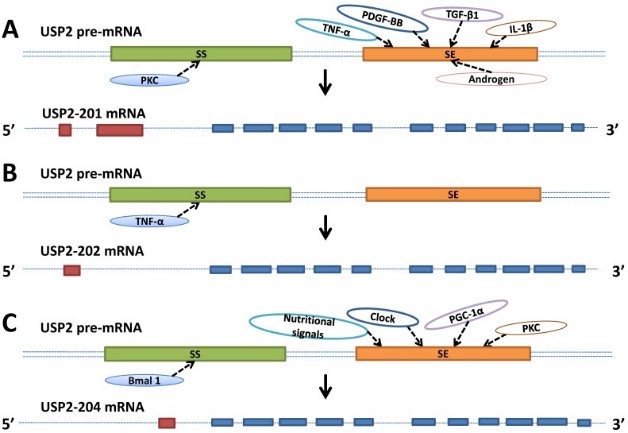
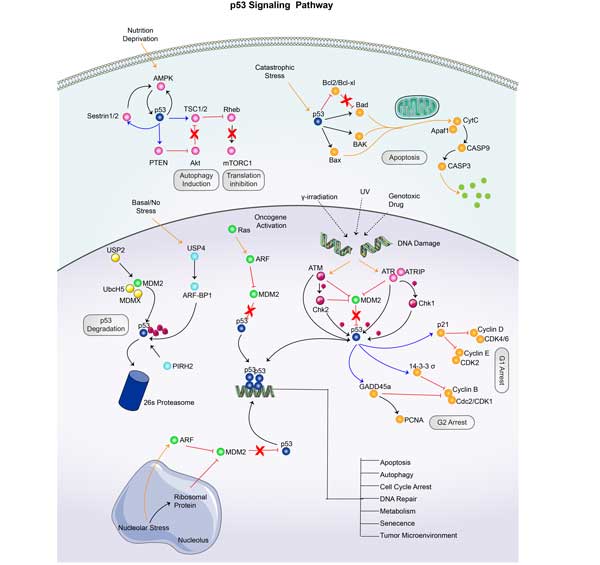
Fig1. Schematic represents the factors involved in the USP2's alternative splicing. (Han-Qing Zhu, 2017)
What is USP2 protein?
USP2 (ubiquitin specific peptidase 2) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 11 at locus 11q23. This gene encodes a member of the family of de-ubiquitinating enzymes, which belongs to the peptidase C19 superfamily. The encoded protein is a ubiquitin-specific protease which is required for TNF-alpha (tumor necrosis factor alpha) -induced NF-kB (nuclear factor kB) signaling. This protein deubiquitinates polyubiquitinated target proteins such as fatty acid synthase, murine double minute 2 (MDM2), MDM4/MDMX and cyclin D1. MDM2 and MDM4 are negative regulators of the p53 tumor suppressor and cyclin D1 is required for cell cycle G1/S transition. The USP2 protein is consisted of 605 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 68.1 kDa.
What is the function of USP2 protein?
USP2 is a deubiquitinating enzyme (DUB) that removes ubiquitin chains from target proteins, thereby preventing their degradation by the proteasome. This function is crucial for controlling the stability and levels of various proteins within the cell. USP2 has been implicated in the regulation of the cell cycle. It can deubiquitinate and stabilize proteins involved in cell cycle progression, such as cyclin D1 and cyclin A1, which are important for the G1 to S phase transition and the S to G2 phase transition, respectively. USP2 may also influence metabolism, particularly fatty acid synthesis, through its interaction with the enzyme fatty acid synthase (FASN), which is overexpressed in several cancers and contributes to tumor growth. USP2 has been identified as a deubiquitinase that stabilizes S-phase kinase-associated protein 2 (SKP2), an F-box protein that targets tumor suppressor substrates for ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation.
USP2 Related Signaling Pathway
USP2 has been shown to interact with IDOL, an E3 ubiquitin ligase that targets the LDL receptor (LDLR) for degradation. USP2 can deubiquitinate and stabilize IDOL, which in turn affects the degradation of LDLR. This interaction forms a trimeric complex that regulates the ubiquitination and degradation of LDLR, impacting cholesterol homeostasis. USP2 is implicated in cell cycle regulation by stabilizing proteins such as cyclin D1 and cyclin A1 through deubiquitination, which are crucial for cell cycle progression. USP2 has been reported to play a role in the regulation of apoptosis, particularly in the context of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) signaling, where it can influence the stability of proteins involved in this process.
USP2 Related Diseases
USP2 is involved in the regulation of cell cycle progression and apoptosis, and its overexpression has been linked to several types of cancer, including breast, liver, ovarian, colorectal, bladder, prostate, and glioblastoma. USP2's role in stabilizing proteins involved in cholesterol homeostasis, such as the LDL receptor (LDLR), suggests a potential involvement in metabolic disorders like hypercholesterolemia. The involvement of USP2 in regulating proteins that are part of immune responses, such as TNF receptor-associated factors, could indirectly link it to autoimmune diseases where immune regulation is disrupted. USP2's role in modulating immune responses may also have implications for infectious diseases, particularly in the context of viral infections where the immune system plays a critical role in controlling the infection.
Bioapplications of USP2
USP2 plays an important role in a variety of tumors and is a potential target for the treatment of malignant tumors. Drug development targeting USP2 could be used to treat a wide range of cancers, including breast, liver, ovarian, colorectal, bladder, prostate, and glioblastoma. Different splicing variants of USP2 play different roles in tumorigenesis and metabolic diseases, so it has the potential to become a biomarker of related diseases and contribute to the early diagnosis and prognosis assessment of diseases. The interaction between USP2 and the biological clock system provides a new perspective for studying the influence of biorhythm and its role in disease.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Jiachen Duan, 2022
Clear cell renal cell carcinoma, the most common type of renal cancer, is associated with poor survival. Ubiquitin-specific peptidase 2 regulates the molecular mechanisms of cancer cells. However, its mechanism in clear cell renal cell carcinoma remains unclear. Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, and immunohistochemistry were performed to assess ubiquitin-specific peptidase 2 expression in human clear cell renal cell carcinoma samples. Ubiquitin-specific peptidase 2 was weakly expressed in clear cell renal cell carcinoma samples and associated with poor patient outcomes. Ubiquitin-specific peptidase 2 inhibition promoted clear cell renal cell carcinoma cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. Ubiquitin-specific peptidase 2 overexpression inhibited clear cell renal cell carcinoma cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in vitro and in vivo. Expression of p-nuclear factor-κB p65, N-cadherin, Vimentin, and Snail, which were markedly increased, as well as E-cadherin, which was decreased following ubiquitin-specific peptidase 2 knockdown. Rescue experiments using the nuclear factor-κB inhibitor BAY 11-7082 revealed that the migration and invasion abilities and the expression of epithelial-mesenchymal transition pathway proteins were inhibited in both the short hairpin RNA (shRNA) for ubiquitin-specific peptidase 2 and shRNA for negative control groups. Ubiquitin-specific peptidase 2 is a potential biomarker to distinguish clear cell renal cell carcinoma patients from healthy individuals. Ubiquitin-specific peptidase 2-mediated inhibition of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in clear cell renal cell carcinoma cells is dependent on the nuclear factor-κB pathway.
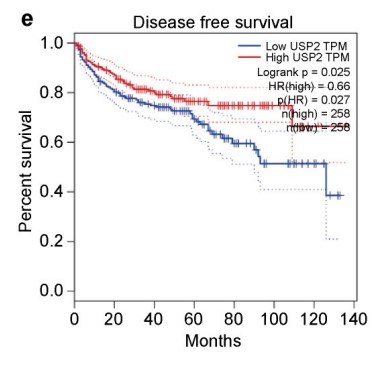
Fig1. Gene Expression Profiling Interactive Analysis revealed that higher expression of ubiquitin-specific peptidase 2 was positively correlated with a better clinical clear cell renal cell carcinoma prognosis.
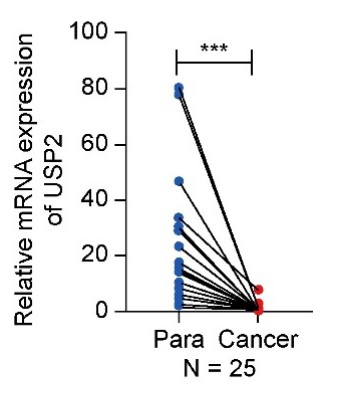
Fig2. The expression of ubiquitin-specific peptidase 2 was low in clear cell renal cell carcinoma tissues.
Case Study 2: Jiayu Wang, 2021
An appropriate development of the placenta consisting of trophoblast cell migration, invasion, proliferation, and apoptosis, is essential to establishing and maintaining a successful pregnancy. Ubiquitin-specific protease 2a (USP2a) regulates the processes of metastasis in multiple tumor cells. Yet, no known research has focused on exploring the effect of USP2a on trophoblasts and its possible mechanism in the pathogenies of recurrent miscarriage (RM). In this study, the researchers first detected the decreased mRNA levels and the protein levels of USP2a in placental villous tissue samples from the RM patients. In vitro assays verified that overexpression of USP2a promoted human trophoblast proliferation, migration, invasion, whereas knockdown of USP2a inhibited these processes. Mechanistically, USP2a activated PI3K/Akt/GSK3β signaling pathway to promote nuclear translocation of β-catenin and further activated epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in the trophoblasts. Moreover, transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β) up-regulated USP2a expression in trophoblasts. Interestingly, M2 macrophage secreted TGF-β induced trophoblast migration and invasion, and an anti-TGF-β antibody alleviated this effect.
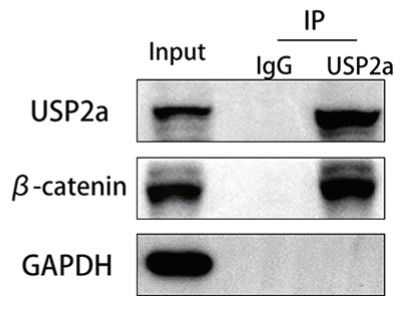
Fig3. Co-IP assays of the interaction between USP2a and β-catenin in HTR8.
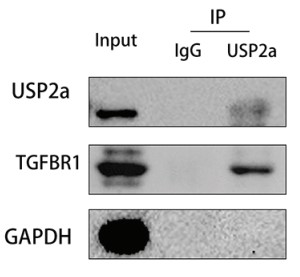
Fig4. co-IP assays of the interaction between USP2a and TGFBR1 in p-USP2a/HTR8.
Quality Guarantee
High Bioactivity
.jpg)
Fig1. Activity Data (USP2-092H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. Activity Data (USP2-320H)
Involved Pathway
USP2 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways USP2 participated on our site, such as Death Receptor Signalling,Regulation of TNFR1 signaling,Signal Transduction, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with USP2 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| TNF-alpha/NF-kB Signaling Pathway | DAP,CAPN3,UNC5CL,G3BP2,MCC,SMARCC2,CRADD,COPS3,MARK2,NR2C2 |
| Signal Transduction | PPY,GDI1,OR2AP1,QRFP,RHOT1A,LGR4,NTS,CCL35.2,NEDD8L,RNF146 |
| TNF signaling | SHRPRBCK1R,SHARPIN,CLIP3,TAX1BP1,OTULINB,FAM105B,OTUD7B,RNF31,USP4,TAX1BP1B |
| Death Receptor Signalling | TAB1,OTULINB,GNB2L1,USP4,RBCK1,TAX1BP1B,OTUD7B,CLIP3,FAM105B,SHARPIN |
| TNFR1-induced proapoptotic signaling | USP4,OTUD7B |
| TNFR1-induced NFkappaB signaling pathway | SHARPIN,RNF31,USP4,OTUD7B,SHRPRBCK1R |
| Regulation of TNFR1 signaling | CLIP3,RBCK1,FAM105B,SHARPIN,TAX1BP1,OTULIN,RNF31,OTULINB,OTUD7B,TAX1BP1B |
Protein Function
USP2 has several biochemical functions, for example, cyclin binding,cysteine-type endopeptidase activity,identical protein binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by USP2 itself. We selected most functions USP2 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with USP2. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| identical protein binding | EPOR,MRI1,INHBA,CLDN20,SIAH1,ERN1,PLK4,AMOTL2,CPT1A,RAD52 |
| ubiquitin protein ligase binding | RIPK1,UBE2H,C10orf46,WFS1,TUBB,PDE4D,CUL1B,HSPA1B,PINK1,PACRG |
| cyclin binding | CDK2,CUL3,FBXW7,CDK14,CDK5RAP3,CDK4,CDK12,INCA1,PFTK1,CDK6 |
| protein binding | PUM1,ATXN3,S100A4,CUTC,DCAF12L1,C19orf40,RCN3,CD300LG,RPL36AL,PPP1R15A |
| cysteine-type endopeptidase activity | CTSL2,CASP6L2,CTSS,Casp3,MALT1A,ATG4A,CTSBB,CASP9,CTSSB.1,CTSW |
| metal ion binding | GNA14,MUSK,RPE65A,ADAL,ZNF490,TCN2,PARP12B,ZNF507,WT1B,CYP2F2 |
| ubiquitin-specific protease activity | USP43A,USP24,OTUB2,OTUD7A,OTUD1,USP30,FAM105B,USP14,OTUD7B,TNFAIP3 |
Interacting Protein
USP2 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with USP2 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of USP2.
KRT15;TRAF2;HOMER3;NEFL;TRIM27;GOLGA2
USP2 Related Signal Pathway
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Stes, E; Laga, M; et al. A COFRADIC Protocol To Study Protein Ubiquitination. JOURNAL OF PROTEOME RESEARCH 13:3107-3113(2014).
- Husted, RF; Lu, HY; et al. Oxygen regulation of the epithelial Na channel in the collecting duct. AMERICAN JOURNAL OF PHYSIOLOGY-RENAL PHYSIOLOGY 300:F412-F424(2011).