Recombinant Human GSTM4, GST-tagged
| Cat.No. : | GSTM4-13577H |
| Product Overview : | Recombinant Human GSTM4 protein, fused to GST-tag, was expressed in E.coli and purified by GSH-sepharose. |
| Availability | February 02, 2026 |
| Unit | |
| Price | |
| Qty |
- Specification
- Gene Information
- Related Products
- Citation
- Download
| Species : | Human |
| Source : | E.coli |
| Tag : | GST |
| Protein Length : | 1-218a.a. |
| Description : | This gene encodes a member of the GRB2/Sem5/Drk family and functions as a cytoplasmic signaling protein which contains an SH2 domain flanked by two SH3 domains. The SH2 domain interacts with ligand-activated receptors for stem cell factor and erythropoietin, and facilitates the formation of a stable complex with the BCR-ABL oncoprotein. This protein also associates with the Ras guanine nucleotide exchange factor SOS1 (son of sevenless homolog 1) through its N-terminal SH3 domain. In general, it couples signals from receptor and cytoplasmic tyrosine kinases to the Ras signaling pathway. |
| Storage : | The protein is stored in PBS buffer at -20℃. Avoid repeated freezing and thawing cycles. |
| Storage Buffer : | 1M PBS (58mM Na2HPO4,17mM NaH2PO4, 68mM NaCl, pH8. ) added with 100mM GSH and 1% Triton X-100,15%glycerol. |
| Gene Name | GSTM4 glutathione S-transferase mu 4 [ Homo sapiens ] |
| Official Symbol | GSTM4 |
| Synonyms | GSTM4; glutathione S-transferase mu 4; glutathione S transferase M4; glutathione S-transferase Mu 4; GST-Mu2; GTS-Mu2; GST class-mu 4; glutathione S-transferase M4; glutathione S-aryltransferase M4; glutathione S-alkyltransferase M4; glutathione S-aralkyltransferase M4; S-(hydroxyalkyl)glutathione lyase M4; GTM4; GSTM4-4; MGC9247; MGC131945; |
| Gene ID | 2948 |
| mRNA Refseq | NM_000850 |
| Protein Refseq | NP_000841 |
| MIM | 138333 |
| UniProt ID | Q03013 |
| Chromosome Location | 1p13 |
| Pathway | Biological oxidations, organism-specific biosystem; Drug metabolism - cytochrome P450, organism-specific biosystem; Drug metabolism - cytochrome P450, conserved biosystem; Glutathione conjugation, organism-specific biosystem; Glutathione metabolism, organism-specific biosystem; Glutathione metabolism, conserved biosystem; Metabolism, organism-specific biosystem; |
| Function | glutathione transferase activity; transferase activity; |
| ◆ Recombinant Proteins | ||
| GSTM4-27545TH | Recombinant Human GSTM4, His-tagged | +Inquiry |
| GSTM4-1994R | Recombinant Rhesus monkey GSTM4 Protein, His-tagged | +Inquiry |
| Gstm4-1604M | Recombinant Mouse Gstm4 Protein, His-tagged | +Inquiry |
| GSTM4-4420H | Recombinant Human GSTM4 Protein, GST-tagged | +Inquiry |
| Gstm4-652R | Recombinant Rat Gstm4 protein, His & T7-tagged | +Inquiry |
| ◆ Cell & Tissue Lysates | ||
| GSTM4-5711HCL | Recombinant Human GSTM4 293 Cell Lysate | +Inquiry |
Biosynthetic metabolomes of cysteinyl-containing immunoresolvents
Journal: The FASEB Journal PubMed ID: 31589826 Data: 2020/10/5
Authors: Charlotte C. Jouvene, Ashley E. Shay, Charles N. Serhan
Article Snippet:Recombinant human LTA 4 hydrolase (LTA 4 H), LTC 4 S, mGST2, and mGST3 were prepared as previously described in refs. 30 , 33 , and 34 , and TK05 (LTC 4 S inhibitor) was earlier identified through high-throughput screening ( 35 ).Recombinant human LTA 4 hydrolase (LTA 4 H), LTC 4 S, mGST2, and mGST3 were prepared as previously described in refs. 30 , 33 , and 34 , and TK05 (LTC 4 S inhibitor) was earlier identified through high-throughput screening ( 35 ).. Recombinant human GSTM4 was purchased from Creative BioMart (Shirley, NY, USA).. Synthetic eMaR, ePD, [ 13 C] 2 15 N-MCTR1, [ 13 C] 2 15 N-MCTR2, and [ 13 C] 2 15 N-MCTR3 were prepared by the lab of Dr. N. A. Petasis (University of Southern California, Los Angeles, CA, USA); their total organic synthesis will be reported separately.Synthetic eMaR, ePD, [ 13 C] 2 15 N-MCTR1, [ 13 C] 2 15 N-MCTR2, and [ 13 C] 2 15 N-MCTR3 were prepared by the lab of Dr. N. A. Petasis (University of Southern California, Los Angeles, CA, USA); their total organic synthesis will be reported separately.
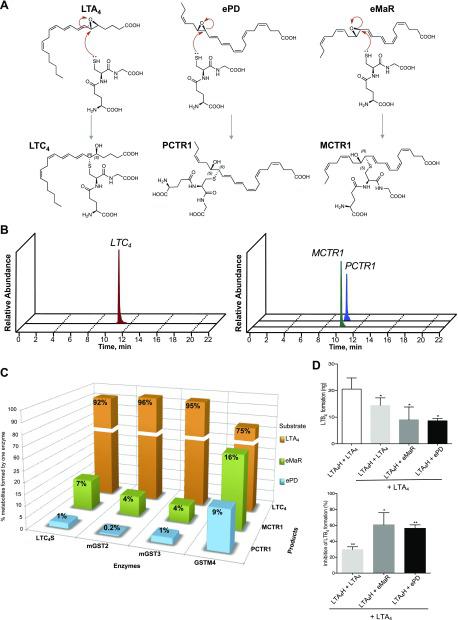
Selective conversion of ePD and eMaR to PCTR1 and MCTR1 by specific human GST. Each human recombinant enzyme (LTC4S, mGST2, mGST3, and
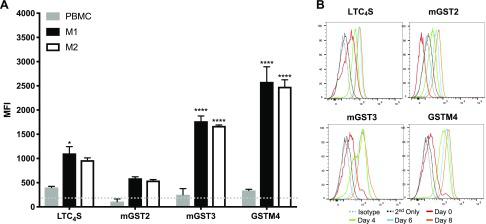
Human M1- and M2-like macrophages express the enzymes involved in the biosynthesis of the CTRs. Human PBMCs were isolated from the whole blood of 3 individual donors and differentiated into M1-like and M2-like phenotypes. A) MFI of LTC4S, mGST2, mGST3, and
Not For Human Consumption!
Inquiry
- Reviews (0)
- Q&As (0)
Ask a Question for All GSTM4 Products
Required fields are marked with *
My Review for All GSTM4 Products
Required fields are marked with *



