CD Antigen (Dendritic Cell Co-stimulatory Molecules)
Related Symbol Search List
Immunology Background
Available Resources for CD Antigen (Dendritic Cell Co-stimulatory Molecules) Research
Creative BioMart is a leading provider of resources and services dedicated to CD antigens (dendritic cell co-stimulatory molecules). Our platform offers researchers a wide range of high-quality products, tailored services, and technical support to advance scientific knowledge and contribute to the development of novel therapies
Our comprehensive list of CD antigens (dendritic cell co-stimulatory molecules) includes well-known markers such as CD28, CD80, TNFRSF8, TNFRSF9, TNFSF9, BAFF, and many more. These antigens are essential for understanding the mechanisms of immune cell communication and immune responses.
- We offer a diverse range of products to support CD antigens (dendritic cell co-stimulatory molecules) research, including antibodies, recombinant proteins, protein pre-coupled magnetic beads, cell and tissue lysates, chromatography reagents, and other kits.
- We also provide customized services tailored to meet specific research needs. Our team of experienced scientists offers custom antibody development, protein engineering, recombinant antigen production, and assay development services.
- In addition to our products and services, we provide a wealth of resources to support CD antigens (dendritic cell co-stimulatory molecules) research. Our platform includes information on involved pathways, protein functions, interacting proteins, related articles, research areas, and other relevant topics.
Our Featured Products
| Cat.# | Product name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD28-321H | Recombinant Human CD28 Protein | Human | HEK293 | N/A |
| CD80-581H | Active Recombinant Human CD80, His-tagged, Biotinylated | Human | Human Cell | His |
| TNFRSF8-563H | Recombinant Human TNFRSF8, His tagged | Human | Human Cell | His |
| TNFRSF9-550H | Recombinant Human TNFRSF9, His tagged | Human | Human Cell | His |
| TNFSF9-3323H | Recombinant Human TNFSF9, GST-tagged | Human | E.coli | GST |
About CD Antigen (Dendritic Cell Co-stimulatory Molecules)
CD antigens, also known as cluster of differentiation antigens, encompass a diverse group of cell surface molecules that are used to classify and characterize different cell types in the immune system. Among these CD antigens, certain molecules serve as dendritic cell co-stimulatory molecules, playing a vital role in the activation and regulation of dendritic cells (DCs).
Dendritic cells are professional antigen-presenting cells that capture, process, and present antigens to T cells, initiating immune responses. Co-stimulatory molecules expressed on the surface of dendritic cells provide essential signals to T cells, influencing their activation, proliferation, and differentiation into effector cells. These interactions are crucial for the initiation and coordination of immune responses.
- One prominent example of a dendritic cell co-stimulatory molecule is CD40. CD40 is a cell surface receptor expressed on DCs and other antigen-presenting cells. It interacts with its ligand, CD40L (CD154), which is predominantly expressed on activated T cells. The binding of CD40 to CD40L provides a co-stimulatory signal that enhances antigen presentation, promotes the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, and supports T cell activation and effector functions. This interaction is essential for the development of effective immune responses against pathogens and the generation of memory T cells.
- Another essential dendritic cell co-stimulatory molecule is CD80 (B7-1) and its counterpart, CD86 (B7-2). CD80 and CD86 are cell surface molecules expressed on dendritic cells and other antigen-presenting cells. They interact with CD28 and CTLA-4 receptors on T cells. Engagement of CD80 or CD86 with CD28 provides a co-stimulatory signal that promotes T cell activation, cytokine production, and effector functions. Conversely, interaction with CTLA-4 can inhibit T cell responses, contributing to immune regulation and tolerance. These interactions play a critical role in determining the balance between immune activation and immune tolerance.
- Other CD antigens, such as OX40L (CD252), ICOSL (CD275), and 4-1BBL (CD137L), also function as dendritic cell co-stimulatory molecules, providing signals that influence T cell activation, survival, and effector functions.
Understanding the role of CD antigens as dendritic cell co-stimulatory molecules is crucial for elucidating the mechanisms of immune cell communication and immune system regulation. These molecules serve as key targets for therapeutic interventions aimed at modulating immune responses, such as immunotherapy, vaccine development, and immune tolerance induction.
In summary, CD antigens that function as dendritic cell co-stimulatory molecules, including CD40, CD80, CD86, OX40L, ICOSL, and 4-1BBL, play a pivotal role in the activation, regulation, and coordination of immune responses. Their interactions with T cells are vital for the initiation of effective immune reactions and the maintenance of immune homeostasis.
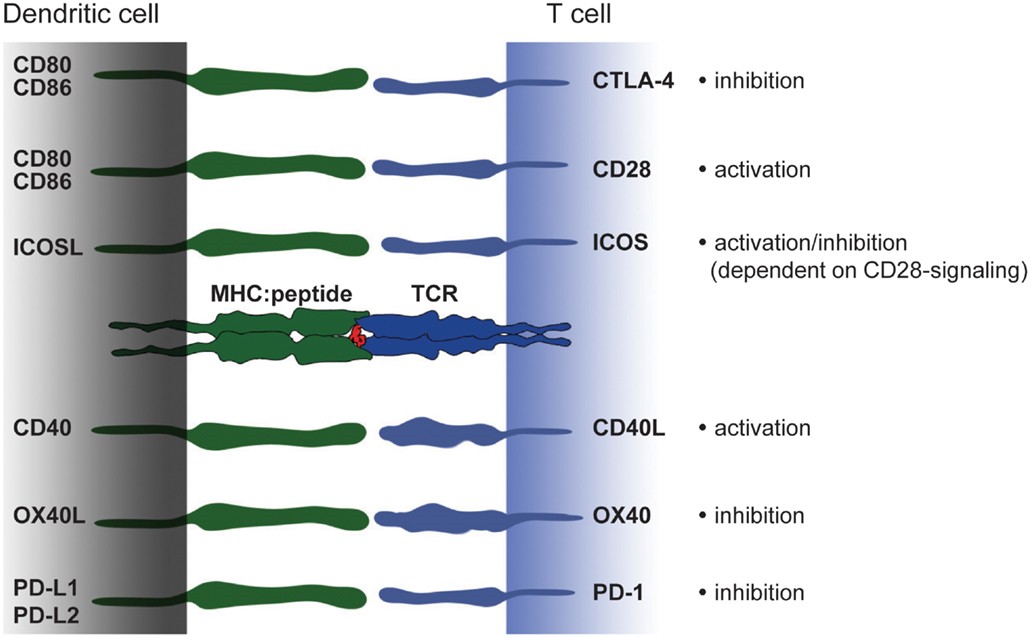 Fig.1 Costimulatory molecules and their ligands – a brief overview. (Hubo M, et al., 2013)
Fig.1 Costimulatory molecules and their ligands – a brief overview. (Hubo M, et al., 2013)
Role of CD Antigens as Dendritic Cell Co-stimulatory Molecule in the Immune Response
CD antigens serve as dendritic cell co-stimulatory molecules, playing a crucial role in the immune response by providing essential signals for the activation and regulation of dendritic cells (DCs). These interactions between CD antigens and their corresponding receptors on T cells are critical for the initiation, modulation, and coordination of immune responses. Here are a few examples of CD antigens as dendritic cell co-stimulatory molecules and their roles in the immune response:
- CD40-CD40L Interaction: CD40 is expressed on the surface of DCs, while its ligand, CD40L (CD154), is predominantly expressed on activated T cells. The binding of CD40 to CD40L provides a co-stimulatory signal that enhances antigen presentation, promotes the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, and supports T cell activation and proliferation. This interaction is important for the development of effective immune responses against pathogens. For example, in the context of T cell-dependent B cell activation, CD40-CD40L interaction is crucial for germinal center formation, antibody class switching, and the generation of memory B cells.
- CD80 (B7-1) and CD86 (B7-2) Interactions: CD80 and CD86 are co-stimulatory molecules expressed on DCs and other antigen-presenting cells. They interact with CD28 and CTLA-4 receptors on T cells. Engagement of CD80 or CD86 with CD28 provides a co-stimulatory signal that promotes T cell activation, cytokine production, and effector functions. This interaction is essential for the initiation and amplification of immune responses. For example, during T cell activation, CD80 and CD86 on DCs bind to CD28 on T cells, leading to T cell proliferation, enhanced cytokine production, and differentiation into effector cells. Conversely, the interaction of CD80 and CD86 with CTLA-4 on T cells can inhibit T cell activation, contributing to immune regulation and tolerance.
- OX40L (CD252) and OX40 (CD134) Interaction: OX40L is expressed on the surface of DCs and other antigen-presenting cells, while its receptor, OX40, is predominantly expressed on activated T cells. The engagement of OX40L with OX40 provides a co-stimulatory signal that enhances T cell survival, proliferation, and cytokine production. This interaction is particularly important for the development of memory T cells and the amplification of immune responses. For example, OX40-OX40L signaling promotes the survival of activated T cells, facilitates the generation of long-lived memory T cells, and enhances effector functions.
These examples highlight the role of CD antigens as dendritic cell co-stimulatory molecules in shaping immune responses. The interactions between these molecules and their receptors on T cells provide crucial signals for T cell activation, proliferation, cytokine production, and differentiation. These co-stimulatory signals are instrumental in determining the magnitude, duration, and quality of immune responses, aiding in the clearance of pathogens, the generation of memory cells, and immune regulation.
If you have any questions, requirements, or cooperation intentions, please feel free to contact us. We very much look forward to working with you and helping you achieve research and commercial success.
Related References
- Hubo M, Trinschek B, Kryczanowsky F, Tuettenberg A, Steinbrink K, Jonuleit H. Costimulatory molecules on immunogenic versus tolerogenic human dendritic cells. Front Immunol. 2013;4:82.
- Gaurav R, Agrawal DK. Clinical view on the importance of dendritic cells in asthma. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2013;9(10):899-919.

