What is IL1RN Protein
The interleukin-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1RA) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IL1RN gene. IL-1RA was initially called the IL-1 inhibitor and was discovered separately in 1984 by two independent laboratories.
Discovery and Background of IL1RN Protein
The discovery of the IL1RN protein dates back to the late 1980s and early 1990s. During this period, researchers identified two types of Interleukins - IL-1α and IL-1β, both promoting inflammatory responses in the body. In the quest to explain the control mechanisms of these inflammatory responses, they discovered the IL1RN, a naturally occurring Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist.
Gene Locus and Protein Structure of IL1RN
The IL1RN, also known as IL1RA, exists within the IL1 cluster on chromosome 2q14.2 in humans. It is a member of the Interleukin-1 cytokine family, which consists of three genes: Interleukin 1 alpha (IL-1α), Interleukin 1 beta (IL-1β), and Interleukin 1 receptor antagonist (IL1RN).
The protein structure of IL1RN bears resemblance to the structure of Interleukin 1 - a structurally similar protein to the IL1 family's agonists but has no agonist capability. Its primary function is to bind IL-1R1 and prevent the binding of IL-1β or IL-1α, thereby negating their inflammatory action. The molecule's structure is such that it inhibits the receptor's activation rather than blocking the cytokine's signal.
Function of IL1RN Protein
The primary function of the IL1RN protein is to sustain the balance within our immune system by regulating inflammation. It accomplishes this by inhibiting the activities of IL-1α and IL-1β. It binds competitively to the same receptors as IL-1, without initiating a signal cascade, hence effectively serving as a biological 'off switch' to the IL-1 mediated pro-inflammatory response.
IL1RN Protein Related Signaling Pathway
The IL1RN loop of action is a part of the Interleukin-1 (IL-1) signaling pathway. This process starts when a immune or an inflammatory response is triggered in the body, causing the release of IL-1α or IL-1β, which bind to the IL-1R1 receptor. Under normal circumstances, this would signal further pro-inflammatory response. However, IL1RN's binding to the same receptor, in essence, 'blocks' this signal and obstructs the whole IL-1 inflammatory signaling pathway.
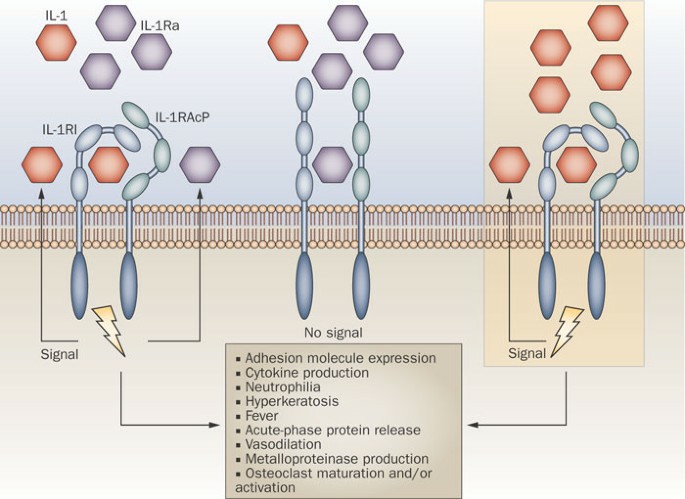
Fig1. Mutations in the IL1RN locus lead to autoinflammation (Gabay, C., et al. 2009)
IL1RN Protein Related Diseases
Disturbances in the IL1RN gene can contribute to various disorders. Too much IL1RN can lead to immune deficiencies, and too little can lead to excessive inflammation. Examples of diseases linked to IL1RN imbalance include Rheumatoid Arthritis, Systemic Lupus Erythematosus, Alzheimer's disease, cancer, and periodontal diseases. Recurrent IL1RN gene mutations can also lead to severe auto-inflammatory syndromes, like Deficiency of Interleukin-1 Receptor Antagonist (DIRA).
IL1RN Protein's Applications in Biomedical Research
Given its critical role in regulating inflammation, IL1RN continues to be of substantial biomedical interest. Its physiology has been targeted for therapeutic interventions in diseases with overactive inflammatory responses. For instance, Anakinra - a recombinant version of IL1RN, is already formulated for the treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis, Neonatal Onset Multisystem Inflammatory Disease (NOMID), and other autoinflammatory syndromes.
In conclusion, the IL1RN protein acts as a critical balancing factor in immune regulation by inhibiting the inflammatory actions of IL-1. Unraveling its complex interplays and signal pathways aids our understanding of diseases linked to inflammation and immune response. As genomic and proteomic technologies continue to advance, illuminating a clearer picture of the IL1RN and its role within the immune system might present unprecedented approaches to diagnose, prevent, and treat a broad range of diseases.
Our Featured Products
| Cat.No. | Product Name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IL1RN-05H | Recombinant Human IL1RN protein | Human | E.coli | N/A |
| IL1RN-314H | Recombinant Human IL1RN protein, hFc-tagged | Human | HEK293 | hFc |
| IL1RN-495H | Recombinant Human IL1RN protein, His-tagged | Human | HEK293F | His |
| IL1RN-1171H | Recombinant Human IL1RN Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | Human | HEK293 | His (Fc)-Avi |
| IL1RN-1893HFL | Recombinant Full Length Human IL1RN Protein, C-Flag-tagged | Human | Mammalian cells | Flag |
| IL1RN-115H | Active Recombinant Human Interleukin 1 Receptor Antagonist | Human | HEK293 | N/A |
Reference
- Gabay, C., & Palmer, G. (2009). Mutations in the IL1RN locus lead to autoinflammation. Nature Reviews Rheumatology, 5(9), 480-482. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrrheum.2009.177

