What is S100B Protein
The S100B protein, also known as S100 calcium-binding protein B, is a multifunctional protein encoded by the S100B gene. It is a member of the S100 family of proteins, a group of small, acidic proteins characterized by their calcium-binding properties. S100B is often referred to by its synonyms, such as S100β or S100-B, highlighting its association with diverse cellular processes.
S100B Protein Structural Characteristics and Classification
Structurally, S100B is composed of two calcium-binding EF-hand motifs, giving it the ability to bind calcium ions, a crucial aspect of its functionality. This protein is classified as a dimeric protein due to its tendency to form dimers in its active state. Recent research advances have shed light on the dynamic nature of S100B, revealing its involvement in various cellular activities and its potential significance in disease contexts.
S100B Biological Functions and Molecular Mechanisms
S100B plays a pivotal role in various biological functions within the cell. Its primary function revolves around its ability to modulate calcium homeostasis, thereby influencing cellular activities. One of the key molecular mechanisms involves the regulation of intracellular calcium levels, impacting processes such as cell cycle progression, differentiation, and apoptosis.
Beyond its role in calcium modulation, S100B is implicated in neurogenesis, neuronal differentiation, and synaptic plasticity within the nervous system. It interacts with numerous cellular targets, including enzymes, cytoskeletal proteins, and receptors, contributing to the intricate network of signaling pathways.
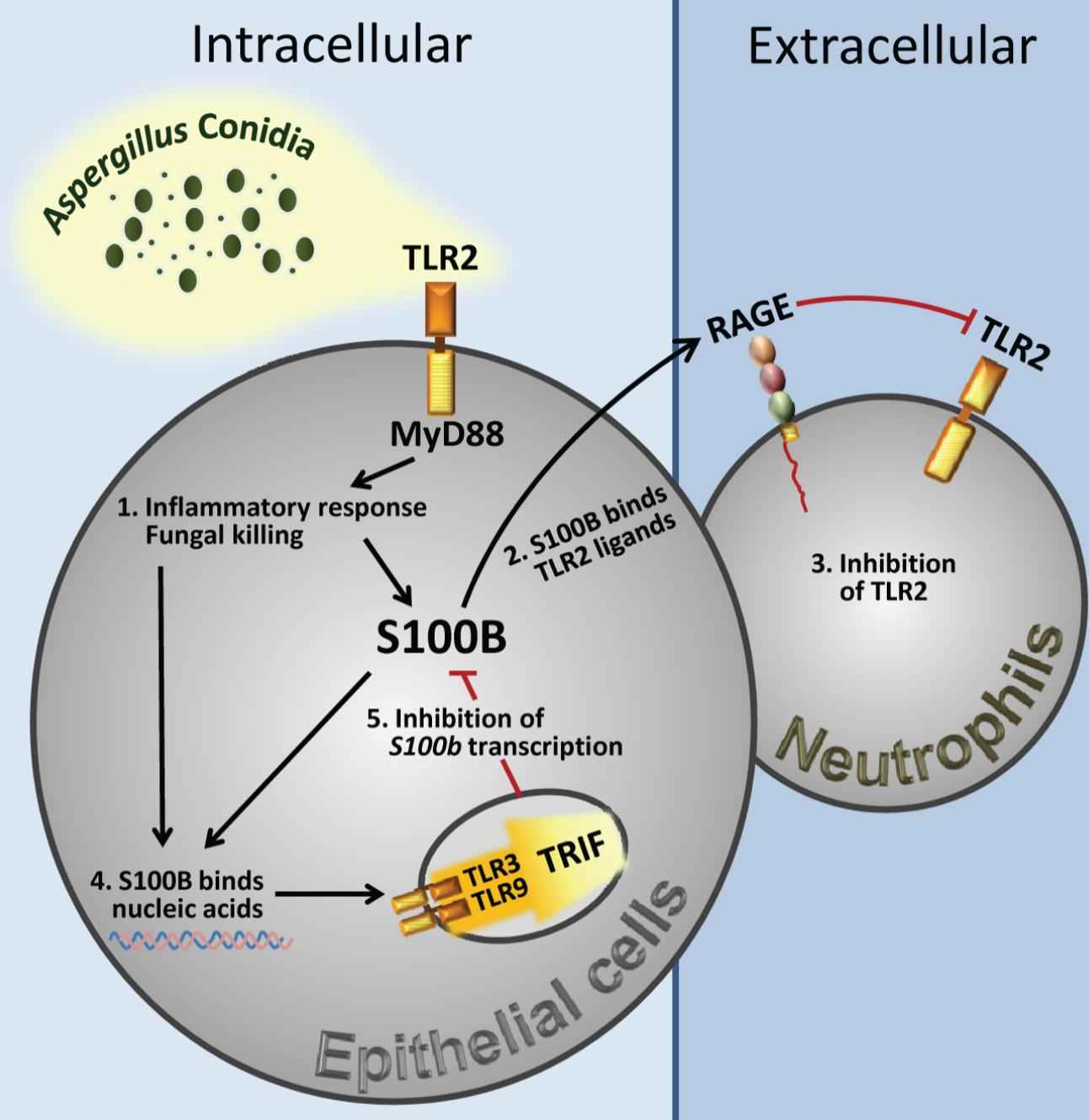
Figure 1. Spatiotemporal integration of signals from TLRs and RAGE by S100B limits pathogen– and danger–induced inflammation. (Sorci G, et al., 2011)
S100B Related Signaling Pathway
The signaling pathways associated with S100B are complex and context-dependent. In the nervous system, S100B modulates intracellular calcium levels, influencing the activation of kinases and transcription factors. Moreover, its interaction with receptors such as the receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) and toll-like receptors (TLRs) contributes to its role in inflammation and immune responses.
In cancer, S100B participates in pathways regulating cell proliferation, survival, and invasion. Its involvement in the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway and the phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt pathway underscores its significance in tumor progression.
S100B Related Diseases
While S100B is integral to normal cellular function, dysregulation of its expression or activity has been associated with several pathological conditions. Elevated levels of S100B in the bloodstream have been linked to neurological disorders, particularly those involving brain injury or neurodegeneration. It serves as a biomarker for conditions such as traumatic brain injury, Alzheimer's disease, and schizophrenia.
In cancer biology, aberrant expression of S100B has been observed in various malignancies, implicating its involvement in tumor progression and metastasis. The intricate balance of S100B in health and disease highlights its potential as a diagnostic marker and therapeutic target.
S100B's Applications in Biomedicine
The unique properties of S100B make it a valuable tool in biomedical research and applications. Its presence in the bloodstream serves as a diagnostic marker for neurological disorders, facilitating the development of diagnostic assays for conditions like traumatic brain injury. Additionally, the identification of S100B as a potential therapeutic target in cancer opens avenues for drug development.
In the realm of vaccine development, S100B's role in immune regulation suggests its potential as a target for immunotherapeutic interventions. Understanding its influence on immune responses could pave the way for innovative vaccine strategies.
In therapeutics, the modulation of S100B activity holds promise for the treatment of diseases where its dysregulation is implicated. Targeting S100B in neurodegenerative disorders or cancer could lead to the development of novel therapeutic approaches.
Recommended Products
| Cat.# | Product name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S100B-3633H | Recombinant Human S100B protein, GST-tagged | Human | E.coli | GST |
| S100B-68H | Recombinant Human S100B, Fc tagged | Human | Human Cell | Fc |
| S100B-2493H | Recombinant Human S100B, GST-tagged | Human | E.coli | GST |
| S100B-323H | Recombinant Human S100B protein, His/MBP-tagged | Human | E.coli | His/MBP |
| S100B-2724H | Recombinant Human S100 Calcium Binding Protein B, His-tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
| S100B-7016H | Recombinant Human S100B protein, His-tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
| S100B-0052H | Recombinant Human S100B Protein | Human | HEK293 cells | |
| S100B-31010TH | Recombinant Human S100B, His-tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
| S100B-374HFL | Recombinant Full Length Human S100B Protein, C-Flag-tagged | Human | Mammalian cells | Flag |
| S100B-042H | Recombinant Human S100B Protein, MYC/DDK-tagged, C13 and N15-labeled | Human | HEK293 | C-Myc/DDK |
Reference
- Sorci G, et al. The danger signal S100B integrates pathogen–and danger–sensing pathways to restrain inflammation. PLoS Pathogens. 2011, 7(3): e1001315.

