CCL1
-
Official Full Name
chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 1 -
Overview
Chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 1 (CXCL1) is a small cytokine belonging to the CXC chemokine family that was previously called GRO1 oncogene, GROα, KC, Neutrophil-activating protein 3 (NAP-3) and melanoma growth stimulating activity, alpha (MSGA-α). In humans, this protein is encoded by the CXCL1 gene. -
Synonyms
CCL1;chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 1;C-C motif chemokine 1;P500;TCA3;CCR8 ligand;SIS-epsilon;T-cell activation protein 3;small inducible cytokine A1;small-inducible cytokine A1;I-309;Scya1;Tca-3;BF534335;Ccl1
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Chicken
- Rhesus macaque
- Hamster
- Rat
- Human Cells
- Mammalian Cells
- E.coli
- HEK293
- CHO
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- Fc
- Non
- GST
- His
- Avi
- MBP
- Flag
Background
What is ccl1 protein?
CCL1, also known as chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 1, is a small cytokine belonging to the CC chemokine family that was previously called I-309. It is produced by activated T cells and has been identified as a potent chemoattractant for monocytes, T lymphocytes, and eosinophils. The chemokine CCL1 is also involved in immunoregulatory and inflammatory processes.
The discovery of CCL1 protein dates back to the earlier years of chemokine research in the 1990s. This small protein of about 8-14 kDa was initially termed I-309 due to its immune cell activity. The protein was re-designated later on as CCL1 under a systematic nomenclature following chemokine characterizations.
CCL1 protein consists of 74 amino acids, with four cysteine residues involved in the formation of two disulfide bonds that connect Cys11 to Cys50 and Cys12 to Cys34. The structure of the monomeric chemokine accommodates an extended N-terminus, a three-stranded beta sheet, and a C-terminal alpha helix, which are commonly found in most members of the chemokine family.
The structural consensus of CCL1 is juxtaposed by its unique receptor specificity. Among the 19 human CC chemokines, CCL1 is the only one that binds the receptor CCR8 selectively. This specific relationship between ligand and receptor prevents the interaction with other cell types expressing alternative receptors, making CCL1 signaling more precise and narrow in scope compared to many other chemokine signals.
CCL1 protein plays a significant role in T cell activation and inflammatory processes. Its abnormal signaling has been implicated in various pathologies like allergies, autoimmunity, and cancer, and it's often seen as a potential therapeutic target.
What is the function of ccl1 protein?
Chemoattraction - It acts as a chemoattractant for immune cells like T lymphocytes, monocytes, dendritic cells and eosinophils by binding to the CCR8 receptor.
Cell recruitment - CCL1 recruits these leukocytes to sites of inflammation, infection or injury by inducing directed migration/chemotaxis.
T cell trafficking - It plays an important role in trafficking T lymphocytes to lymph nodes and sites of antigen presentation.
Inflammation - CCL1 contributes to inflammatory responses by stimulating migration and infiltration of immune cells into tissues.
CCL1 related signaling pathway
CCR8 signaling pathway: Binding of CCL1 to its receptor CCR8 on immune cells activates downstream G-protein coupled signaling cascades.
JAK-STAT signaling pathway: CCL1 stimulation leads to phosphorylation of JAK kinases and STAT proteins, regulating gene expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines.
MAPK signaling pathway: CCL1 activates MAPKs like ERK, JNK and p38 kinases involved in cell migration, proliferation and inflammatory responses.
NF-κB signaling pathway: CCL1 stimulation activates NF-κB, a major pro-inflammatory transcription factor inducing chemokines and adhesion molecules.
CCL1 Related Diseases
Cancer: Upregulated in several cancers like breast, prostate and lung cancers. Promotes proliferation and metastasis via leukocyte recruitment.
Asthma: Increased levels in asthmatic airways contribute to eosinophilic inflammation.
Autoimmune diseases: Higher CCL1 levels seen in multiple sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease.
Atopic dermatitis: Plays a role in allergic skin inflammation by recruiting T cells and eosinophils.
Biomedical Application of CCL1 Protein
Cancer immunotherapy: CCL1 inhibitors may block tumor-promoting inflammation and metastasis.
Anti-angiogenic therapy: Targeting CCL1's pro-angiogenic role offers new avenues to cut off blood supply to tumors.
Anti-inflammatory drug development: Agents modulating CCL1 signaling could help treat inflammatory/autoimmune conditions.
Case Study
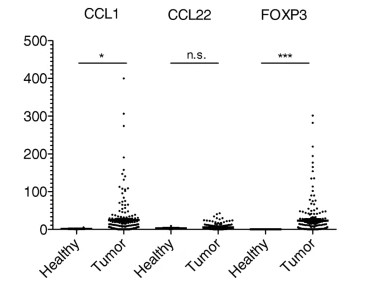
(Benjamin Kuehnemuth, 2018)
Fig2. TMAs of breast cancer and healthy breast tissue were analyzed for the number of positive cells/mm2. For statistical analysis the Mann-Whitney-U-Test was used
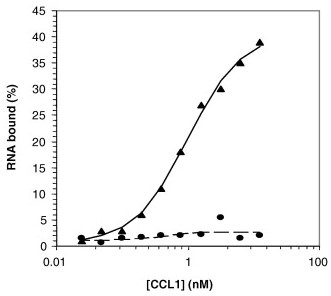
(Martin L. Marro, 2006)
Fig3.Binding studies of the T48 aptamer to hCCL1. Nitrocellulose binding studies of the T48 aptamer (▴, solid line) and a random control aptamer (•, dashed line).
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (Cat. No.: CCL1-605H)
Involved Pathway
CCL1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways CCL1 participated on our site, such as Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction,Chemokine signaling pathway, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with CCL1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction | TNFRSF1A,FLT1,CD40,EDAR,CXCR7,CCL21B,IL12RB2,AMH,IL11RA2,LEP |
| Chemokine signaling pathway | SHC4,CCL19,CXCL3,CCL6,XCL2,PIK3R3,ARRB2,PLCB1,PARD3,LOC100033925 |
Protein Function
CCL1 has several biochemical functions, for example, CCR chemokine receptor binding,chemokine activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by CCL1 itself. We selected most functions CCL1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with CCL1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| CCR chemokine receptor binding | CCL15,CCRL2,CCL34A.4,CCL11,XCL2,CCL34B.4,XCL1,CCL20B,CCL16,CCL22 |
| chemokine activity | Ccl21c,PF4V1,CXCL18B,CCL14,Ccl21a,CXCL20,CCL18,CCL34B.1,PPBP,CXCL12B |
Interacting Protein
CCL1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with CCL1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of CCL1.
Resources
Gene Families
Research Area
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Metcalf, TU; Baxter, VK; et al. Recruitment and Retention of B Cells in the Central Nervous System in Response to Alphavirus Encephalomyelitis. JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY 87:2420-2429(2013).
- Birkhauser, FD; Koya, RC; et al. Dendritic Cell-Based Immunotherapy in Prevention and Treatment of Renal Cell Carcinoma: Efficacy, Safety, and Activity of Ad-GM.CAIX in Immunocompetent Mouse Models. JOURNAL OF IMMUNOTHERAPY 36:102-111(2013).



