CC Chemokines
Related Symbol Search List
- CCL1
- CCL11
- CCL13
- CCL14
- CCL15
- CCL16
- CCL17
- CCL18
- CCL19
- CCL2
- CCL20
- CCL21
- CCL22
- CCL23
- CCL24
- CCL25
- CCL26
- CCL27
- CCL28
- CCL3
- CCL3L1
- CCL4
- CCL4L1
- CCL5
- CCL6
- CCL7
- CCL8
- CCL9
Immunology Background
Available Resources for CC Chemokines Research
Creative BioMart stands as your foremost destination for all your research needs related to CC chemokines. Our extensive selection of carefully developed products and personalized services is designed to steer your exploration into the realm of CC chemokines and their crucial roles in various physiological processes.
- Within our product range, you will find top-notch recombinant proteins, protein pre-coupled magnetic beads, cell and tissue lysates, and more.
- Additionally, we offer a comprehensive repository of resources on CC chemokines, covering essential topics such as associated pathways, protein functionalities, interacting proteins, relevant articles, and current research areas.
Our Featured Products
About CC Chemokines
CC chemokines, also known as C-C motif chemokines, are a subgroup of chemokines characterized by the presence of two adjacent cysteine residues near their amino terminus. Chemokines are small proteins that play a fundamental role in immune cell trafficking, inflammation, and the regulation of immune responses. CC chemokines specifically interact with CC chemokine receptors (CCRs) expressed on the surface of immune cells, guiding their migration and activation.
CC chemokines are involved in various physiological and pathological processes, including immune surveillance, infection, inflammation, tissue repair, and cancer progression. They are produced by a wide range of cells, including immune cells (such as macrophages, T cells, and dendritic cells), stromal cells, and epithelial cells, among others.
The CC chemokine family encompasses multiple members, each with unique functions and expression patterns. Some well-known CC chemokines include:
- CCL2 (also known as monocyte chemoattractant protein-1, MCP-1): It attracts monocytes and plays a key role in recruitment during inflammation.
- CCL3 (also known as macrophage inflammatory protein-1 alpha, MIP-1α): It attracts and activates various immune cells, including monocytes, T cells, and natural killer (NK) cells.
- CCL5 (also known as regulated upon activation, normal T-cell expressed, and secreted, RANTES): It attracts various immune cells, including T cells, eosinophils, and monocytes, and plays a role in allergic responses and inflammation.
- CCL19 and CCL21: These chemokines are involved in the organization of lymphoid tissues and the homing of immune cells to lymph nodes.
- CCL22: It is involved in attracting regulatory T cells and modulating immune responses.
CC chemokines exert their effects by binding to specific CCRs on target cells. This interaction triggers intracellular signaling pathways, leading to cell migration, activation, and various cellular responses associated with immune function.
The dynamic interplay between CC chemokines and their receptors is crucial for directing immune cell trafficking and orchestration of immune responses. Dysregulation of CC chemokines and their receptors has been implicated in various diseases, including chronic inflammation, autoimmune disorders, infectious diseases, and cancer. Therefore, understanding the function and regulation of CC chemokines is essential for unraveling the complexities of immune responses and developing targeted therapeutic strategies to modulate immune cell behavior in health and disease.
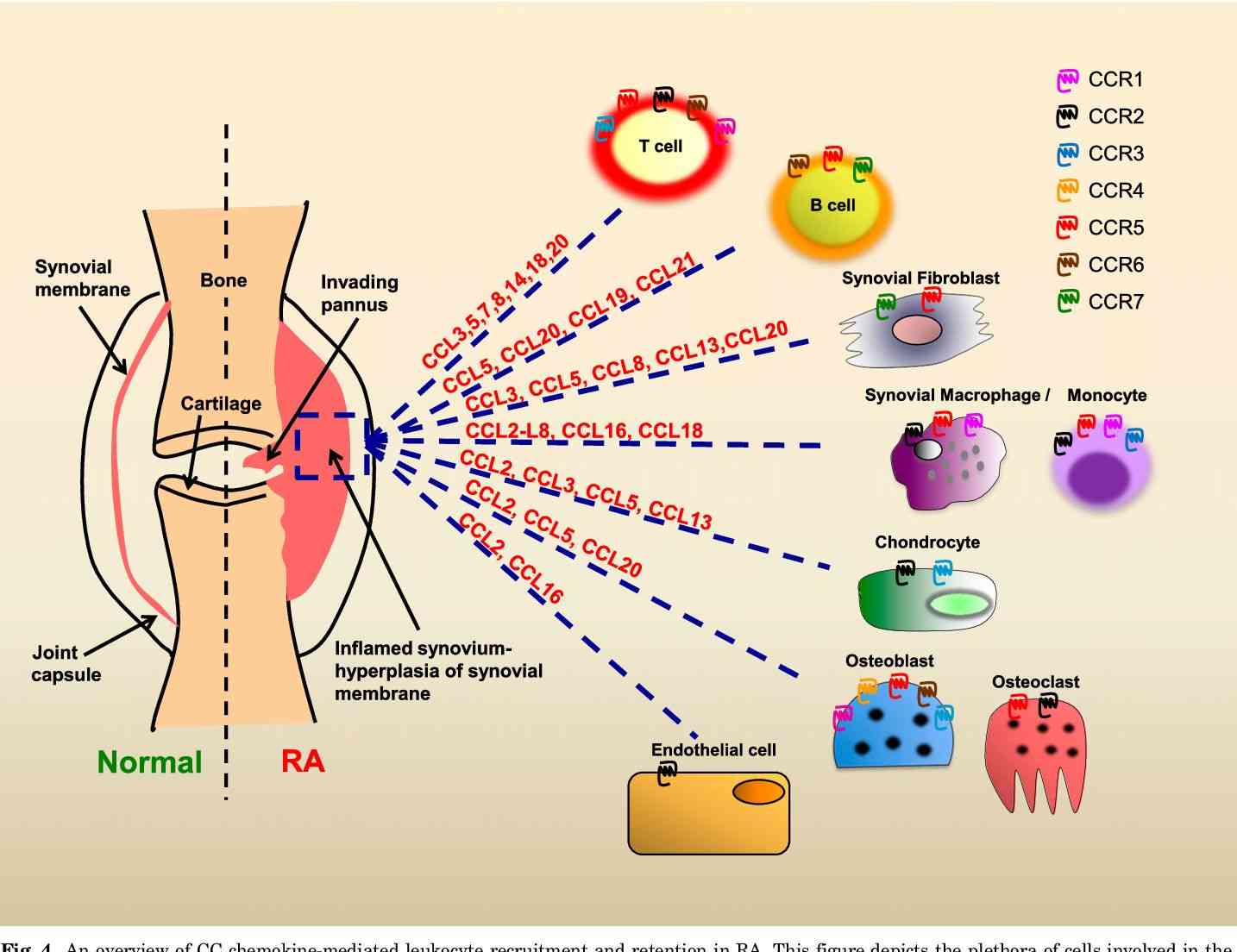 Fig.1 An overview of CC chemokine-mediated leukocyte recruitment and retention in RA. (White, G.E., et al., 2013)
Fig.1 An overview of CC chemokine-mediated leukocyte recruitment and retention in RA. (White, G.E., et al., 2013)
Research on CC Chemokines
Research on CC chemokines has been extensive and has contributed significantly to our understanding of immune responses, inflammation, and various disease processes. Here are some key areas of research on CC chemokines:
- Immune Cell Recruitment and Migration: CC chemokines play a crucial role in immune cell recruitment and migration to inflamed or infected tissues. Research has focused on elucidating the specific chemokine-receptor interactions and signaling pathways involved in immune cell trafficking. This knowledge helps in understanding how immune cells are recruited to sites of inflammation and infection, and how these processes can be modulated for therapeutic purposes.
- Inflammatory Disorders: CC chemokines have been implicated in various inflammatory disorders, including rheumatoid arthritis, asthma, and inflammatory bowel disease. Research aims to understand the contribution of specific CC chemokines and their receptors in disease pathogenesis, as well as their potential as therapeutic targets. This includes studying the expression patterns of CC chemokines in inflamed tissues, characterizing their effects on immune cell activation and migration, and developing strategies to intervene in their signaling pathways.
- Infectious Diseases: CC chemokines and their receptors play critical roles in host defense against infectious diseases. Research has focused on understanding how specific CC chemokines contribute to the recruitment and activation of immune cells during infections. For example, the role of CCL2 and CCL5 in attracting monocytes and T cells in response to viral or bacterial infections has been extensively studied. Additionally, CC chemokines have been investigated as potential targets for antiviral therapies, including HIV infection.
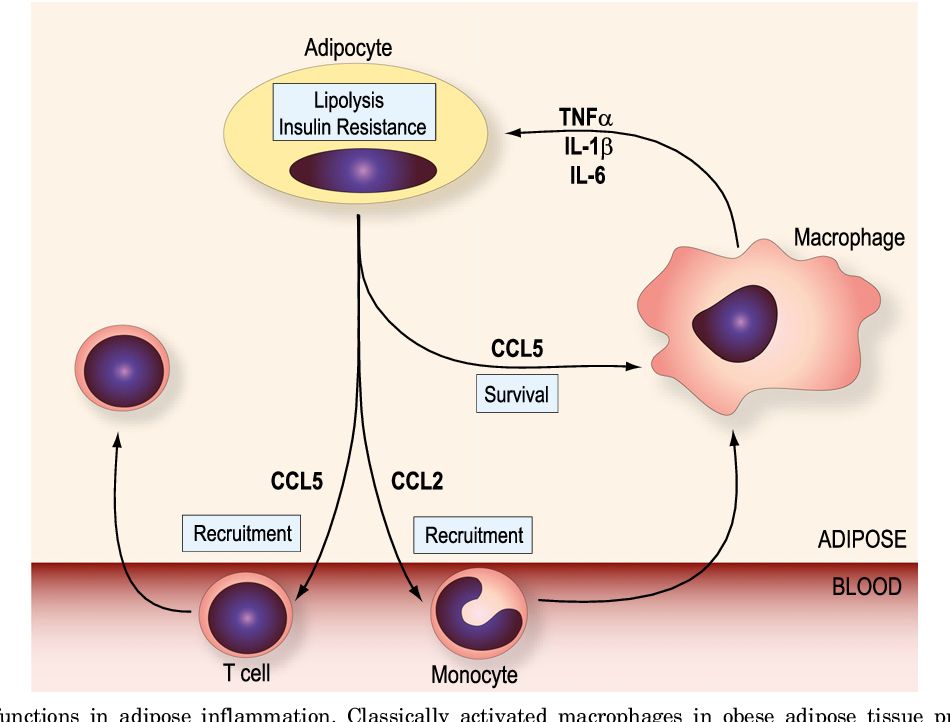 Fig.2 CC chemokine functions in adipose inflammation. (White, G.E., et al., 2013)
Fig.2 CC chemokine functions in adipose inflammation. (White, G.E., et al., 2013)
- Cancer Biology and Metastasis: CC chemokines have emerged as key players in cancer biology, particularly in tumor progression and metastasis. Research has focused on understanding how CC chemokines and their receptors influence tumor cell migration, invasion, and the recruitment of immune cells within the tumor microenvironment. This knowledge helps in identifying potential targets for cancer therapy and developing strategies to modulate immune responses against tumors.
- Therapeutic Interventions: Research has been conducted to explore the therapeutic potential of targeting CC chemokines and their receptors. This includes the development of small molecule inhibitors, antibodies, and chemokine-based therapies to modulate immune cell function, reduce inflammation, or interfere with disease progression. Such interventions aim to regulate immune responses in various diseases, including autoimmune disorders, chronic inflammatory conditions, and cancer.
- Biomarker Discovery: Researchers have investigated the utility of CC chemokines as biomarkers for disease diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment response. By measuring the levels of specific CC chemokines in patient samples, such as blood or tissue, researchers can gain insights into disease activity, predict treatment outcomes, and monitor therapeutic efficacy.
Overall, research on CC chemokines continues to advance our understanding of immune responses and their role in various diseases. The findings from these studies have the potential to lead to the development of novel therapeutic strategies and improve patient care in a wide range of conditions.
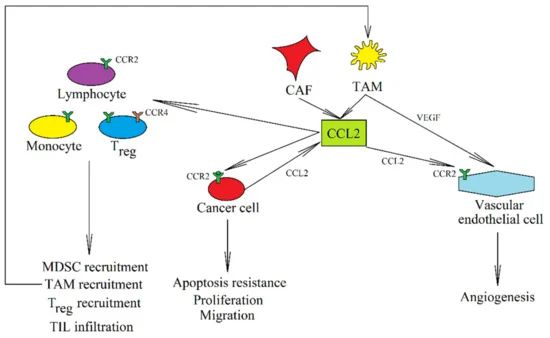 Fig.3 The role of CCL2 in caner. (Korbecki J, et al., 2020)
Fig.3 The role of CCL2 in caner. (Korbecki J, et al., 2020)
If you have any questions, requirements, or cooperation intentions, please feel free to contact us. We very much look forward to working with you and helping you achieve research and commercial success.
Related References
- White, G.E., Iqbal, A.J., & Greaves, D.R. (2013). CC Chemokine Receptors and Chronic Inflammation—Therapeutic Opportunities and Pharmacological Challenges. Pharmacological Reviews, 65, 47 - 89.
- Korbecki J, Kojder K, Simińska D, Bohatyrewicz R, Gutowska I, Chlubek D, Baranowska-Bosiacka I. CC Chemokines in a Tumor: A Review of Pro-Cancer and Anti-Cancer Properties of the Ligands of Receptors CCR1, CCR2, CCR3, and CCR4. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(21):8412.

