CFH
-
Official Full Name
complement factor H -
Overview
Factor H is a member of the regulators of complement activation family and is a complement control protein. It is a large (155 kilodaltons), soluble glycoprotein that circulates in human plasma (at a concentration of 500–800 micrograms per milliliter). Its principal function is to regulate the Alternative Pathway of the complement system, ensuring that the complement system is directed towards pathogens and does not damage host tissue. Factor H regulates complement activation on self cells by possessing both cofactor activity for the Factor I mediated C3b cleavage, and decay accelerating activity against the alternative pathway C3 convertase, C3bBb. Factor H protects self cells from complement activation but not bacteria/viruses, in that it binds to glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) that are present on host cells but not pathogen cell surfaces. -
Synonyms
CFH;complement factor H;beta-1H;factor H-like 1;beta-1-H-globulin;OTTHUMP00000033598;OTTHUMP00000034106;H factor 1 (complement);H factor 2 (complement);adrenomedullin binding protein;isoform b ag;e-related maculopathy susceptibility 1;FH;HF;HF1;HF2;HUS;FHL1;AHUS1;AMBP1;ARMD4;ARMS1;CFHL3;MGC88246;age-related maculopathy susceptibility 1
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Cattle
- Rat
- Zebrafish
- HEK293
- Mammalian Cells
- Human Serum
- Wheat Germ
- E.coli
- Human Cells
- Mouse
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- His
- Non
- GST
- Fc
- T7
- Avi
- rFc
Background
What is CFH protein?
CFH (complement factor H) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 1 at locus 1q31. CFH, also known as H-factor (HF), is a key regulatory protein in the complement system. The complement system is part of the body's immune system and consists of a series of plasma proteins that, when activated, can work together to clear pathogens, promote inflammatory responses, and participate in the clearance of immune complexes. The primary function of CFH is to regulate the activity of the complement system to prevent damage to healthy cells and tissues. The CFH protein is consisted of 1231 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 139.1 kDa.
What is the function of CFH protein?
CFH inhibits C3 convertase activity by binding to complement component C3b, thereby reducing further C3 conversion and activation of the complement activation pathway. CFH is expressed on the surface of vascular endothelial cells and helps protect these cells from complement-mediated damage by acting as a "guardian" of the complement system. CFH is involved in promoting the clearance of immune complexes and reducing inflammatory damage in autoimmune responses. CFH is also involved in regulating cell-cell interactions, including cell adhesion and migration. CFH plays an anti-inflammatory role by inhibiting the overactivation of the complement system.
CFH Related Signaling Pathway
CFH, as a regulatory protein of the complement system, binds to C3b, thereby inhibiting the activity of C3 invertase, reducing further hydrolysis of C3 and the production of C3a and C5a, which are key inflammatory mediators in the complement activation pathway. CFH promotes the degradation of C3b to iC3b, an important step in the complement replacement pathway that helps stop the chain reaction of complement activation. CFH is expressed on vascular endothelial cells and glomeruli and helps protect these cells from complement-mediated damage by preventing the complement activation pathway from progressing on the surface of host cells.
CFH Related Diseases
Mutations in the CFH gene have been linked to an increased risk of age-related macular degeneration (AMD), a common cause of vision loss in older adults. Abnormal function of CFH can lead to uncontrolled activation of the complement system, resulting in atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome (aHUS), a rare but serious disorder characterized by microvascular hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia, and acute kidney injury. Mutations in the CFH gene or its abnormal localization in the glomeruli are associated with the development of membranous nephropathy (MN), a common primary glomerular disease characterized by membranous transformation of the glomerular basement membrane. The role of CFH in host defense may lead to increased susceptibility to certain infections, especially when CFH function is impaired.
Bioapplications of CFH
Determination of CFH protein activity and levels can be used as biomarkers for the diagnosis of certain complement-mediated diseases, such as age-related macular degeneration (AMD), atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome (aHUS), and membranous nephropathy (MN). CFH or its functional mimicry molecules may serve as potential drugs for the treatment of diseases associated with the complement system, particularly in the treatment of AMD and aHUS. CFH is a key regulator of the complement pathway, and its related drug screening and evaluation are crucial for the development of new complement inhibitors.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Rayne R Lim, 2024
Complement dysregulation is a key component in the pathogenesis of age-related macular degeneration (AMD) and related diseases such as early-onset macular drusen (EOMD). Although genetic variants of complement factor H (CFH) are associated with AMD risk, the impact of CFH and factor H-like protein 1 (FHL-1) expression on local complement activity in human retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) remains unclear. The researchers identified a novel CFH variant in a family with EOMD and generated patient induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC)-derived RPE cells. They assessed CFH and FHL-1 co-factor activity through C3b breakdown assays and measured complement activation by immunostaining for membrane attack complex (MAC) formation. Expression of CFH, FHL-1, local alternative pathway (AP) components, and regulators of complement activation (RCA) in EOMD RPE cells was determined by quantitative PCR, western blot, and immunostaining. Isogenic EOMD (cEOMD) RPE was generated using CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing. The CFH variant (c.351-2A>G) resulted in loss of CFH and FHL-1 expression and significantly reduced CFH and FHL-1 protein expression (∼50%) in EOMD iPSC RPE cells. CRISPR/Cas9 correction restored CFH/FHL-1 expression and mitigated alternative pathway complement activity in cEOMD RPE cells.
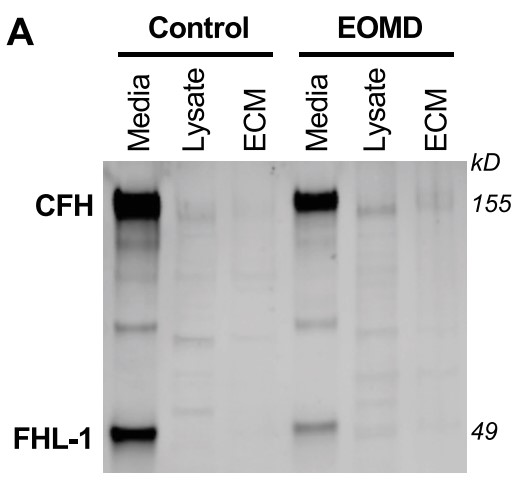
Fig1. CFH and FHL-1 proteins were largely secreted, with slight retention in the ECM.
EOMD RPE cells.jpg)
Fig2. Protein expression of CFH and FHL-1 secretion from CRISPR-corrected (c)EOMD RPE cells.
Case Study 2: Aimiao Bian, 2018
Circular RNAs (circRNAs) are widely expressed in mammals and can regulate the development and progression of human tumors. has_circ_0015758 (circ-CFH) is an exon circRNA transcript from the GRCh37/hg19 fragment of chromosome 1 and is homologous to the protein-coding gene complement factor H (CFH). Currently, the function of circ-CFH in glioma remains unclear. In this study, circ-CFH, miR-149, and Akt1 mRNA expression levels were analyzed by qRT-PCR assays. To investigate the function of circ-CFH in cell proliferation, circ-CFH knockdown models were established by using circ-CFH siRNAs. Cell proliferation abilities were measured by CCK-8 and colony formation assays and in vivo experiments. In addition, the interaction between circ-CFH and miR-149 was assessed by luciferase reporter assays. Circ-CFH expression was significantly upregulated in glioma tissue and was correlated with tumor grade. Circ-CFH expression levels were also markedly higher in U251 and U373 glioma cell lines. Circ-CFH knockdown inhibited cell proliferation and colony formation abilities. Luciferase assays indicated that circ-CFH functions as a miR-149 sponge and inhibits its function in U251 and U373 cells.
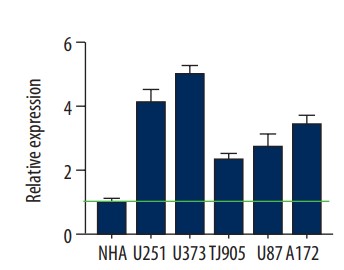
Fig3. Expression of circ-CFH in different glioma cell lines.
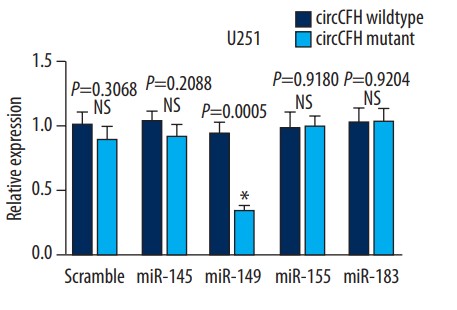
Fig4. The luciferase intensity was measured.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (CFH-641H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (CFH-763H)
Involved Pathway
CFH involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways CFH participated on our site, such as Complement and coagulation cascades,Staphylococcus aureus infection, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with CFH were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Complement and coagulation cascades | CFD,FGB,C4BP,PLAU,SERPING1,SERPINA1D,PLG,PLAUR,FGA,C9 |
| Staphylococcus aureus infection | H2-AA,HLA-DRB4,DSG1,C1RA,Itgam&Itgb2,SELP,HLA-DRA,ITGAL,MBL2,HLA-DQA1 |
Protein Function
CFH has several biochemical functions, for example, heparan sulfate proteoglycan binding,heparin binding,protein binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by CFH itself. We selected most functions CFH had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with CFH. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| protein binding | BBS10,YWHAE,CDKN1A,STRA13,BCL3,WFS1,EIF4H,PRPSAP1,FNTA,URI1 |
| heparin binding | CECR1,CYR61L1,SERPIND1,OGN,WISP1B,FGFR2,ELANE,VEGFA,WISP3,LPL |
| heparan sulfate proteoglycan binding | PLA2G2D,GPC1B,GPC1A,GPC3,Gpc2,GPC5,ITGAM,COMP,GPC6A,GPC1 |
Interacting Protein
CFH has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with CFH here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of CFH.
C3;C3;ennX;TFAP2A;VDR;GRB2;SMAD3;ZBTB16;EP300;q81p70_bacan;colA;TFAP2C;YTHDC1;q99ib8-pro_0000045596;d-mannose;ALB
Resources
Research Area
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Cortina, G; Trojer, R; et al. De novo tacrolimus-induced thrombotic microangiopathy in the early stage after renal transplantation successfully treated with conversion to everolimus. PEDIATRIC NEPHROLOGY 30:693-697(2015).
- Khandelwal, P; Gupta, A; et al. Effect of plasma exchange and immunosuppressive medications on antibody titers and outcome in anti-complement factor H antibody-associated hemolytic uremic syndrome. PEDIATRIC NEPHROLOGY 30:451-457(2015).



