MERTK
-
Official Full Name
c-mer proto-oncogene tyrosine kinase -
Overview
In case of filovirus infection, seems to function as a cell entry factor. -
Synonyms
MERTK;c-mer proto-oncogene tyrosine kinase;Eyk;Mer;Nyk;nmf12;tyrosine-protein kinase Mer;Tyro 12;proto-oncogene c-Mer;receptor tyrosine kinase MerTK;proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Mer
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Rat
- Chicken
- Dog
- Cynomolgus
- HEK293
- Insect Cells
- E.coli
- Sf9 Cells
- Mammalian Cells
- Human Cells
- Baculovirus
- Wheat Germ
- HT-1080
- Fc
- His
- Non
- GST
- T7
- Flag
- Avi
- mFc
- DDK
- Myc
Background
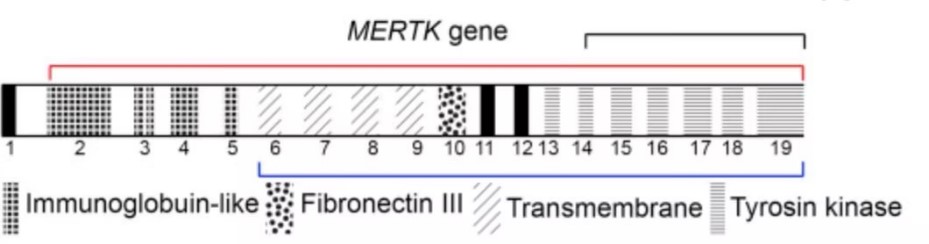
Fig1. An illustration of the MERTK gene showing the different exons coding for the different protein domains of the receptor. Exons are labeled 1 to 19. (Almedawar, 2020)
What is MERTK protein?
MERTK (MER proto-oncogene, tyrosine kinase) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 2 at locus 2q13. This gene is a member of the MER/AXL/TYRO3 receptor kinase family and encodes a transmembrane protein with two fibronectin type-III domains, two Ig-like C2-type (immunoglobulin-like) domains, and one tyrosine kinase domain. The MERTK protein is consisted of 999 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 110.2 kDa.
What is the function of MERTK protein?
Following activation by ligand, interacts with GRB2 or PLCG2 and induces phosphorylation of MAPK1, MAPK2, FAK/PTK2 or RAC1. MERTK signaling plays a role in various processes such as macrophage clearance of apoptotic cells, platelet aggregation, cytoskeleton reorganization and engulfment. Functions in the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) as a regulator of rod outer segments fragments phagocytosis. Plays also an important role in inhibition of Toll-like receptors (TLRs)-mediated innate immune response by activating STAT1, which selectively induces production of suppressors of cytokine signaling SOCS1 and SOCS3.
MERTK Related Signaling Pathway
MERTK proteins are involved in several signaling pathways, the most important of which are the MERK-PI3K-Akt and MERK-STAT3 signaling pathways. In the MERK-PI3K-Akt pathway, MERTK further activates protein kinase B (Akt) by activating phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase (PI3K), thereby promoting cell survival and proliferation. In the MERK-STAT3 pathway, MERTK regulates cell proliferation, aging and immune response by activating signal transduction and transcriptional activator 3 (STAT3).
MERTK Related Diseases
Diseases associated with MERTK dysfunction include hereditary retinal dystrophy, hemostatic disorders, and some types of leukemia. Second, MERTK is also closely associated with the development of tumors, including breast cancer, lung cancer, ovarian cancer and glioma. In addition, MERTK has been linked to autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. MERTK is also involved in the development of cardiovascular diseases, such as atherosclerosis, and neurological diseases, such as Parkinson's disease and cerebral ischemia.
Bioapplications of MERTK
In the aspect of tumor therapy, MERTK, as an important target, is being studied as the targeted therapy of new anticancer drugs. In addition, MERTK has important applications in the field of ophthalmology, especially in diseases related to macular degeneration, where MERTK is considered a potential therapeutic target.
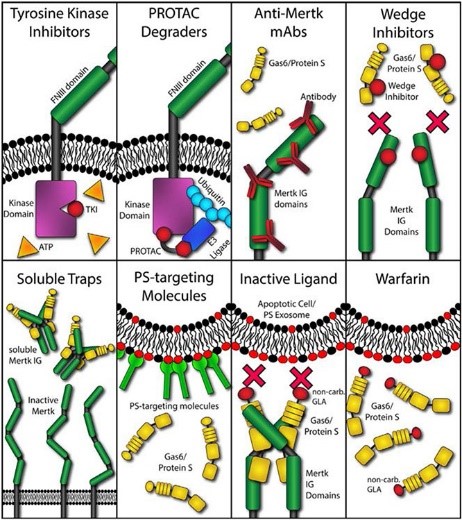
Fig2. Strategies for anti-Mertk therapeutics. A variety of strategies are possible for targeting Mertk therapeutically. (Kevin C Lahey, 2022)
Case Study
Case study 1: Seba Almedawar, 2020
Maintenance of a healthy photoreceptor-retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) interface is essential for vision. At the center of this interface, apical membrane protrusions stemming from the RPE ensheath photoreceptor outer segments (POS), and are possibly involved in the recycling of POS through phagocytosis. The molecules that regulate POS ensheathment and its relationship to phagocytosis remain to be deciphered.
By means of ultrastructural analysis, the researchers revealed that MERTK ligands, GAS6 and PROS1, rather than αVβ5 integrin receptor ligands, triggered POS ensheathment by human embryonic stem cell (hESC)-derived RPE. Consistently, POS ensheathment, fragmentation, and internalization were abolished in MERTK mutant RPE, and rescue of MERTK expression in retinitis pigmentosa (RP38) patient RPE counteracted these defects. The results suggest that loss of ensheathment due to MERTK dysfunction might contribute to vision impairment in RP38 patients.
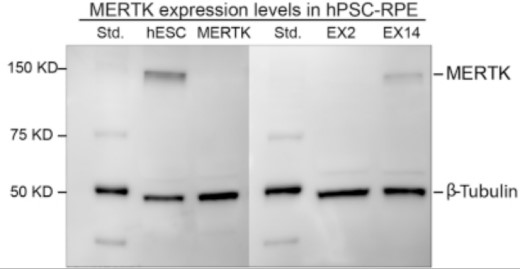
Fig1. Immunoblot (western blot) analysis of MERTK using total protein extracts from wild-type and MERTK mutant RPE.
Case study 2: Frank C Cackowski, 2017
Many prostate cancer (PCa) recurrences are thought to be due to reactivation of disseminated tumor cells (DTCs). The researchers previously found a role of the TAM family of receptor tyrosine kinases TYRO3, AXL, and MERTK in PCa dormancy regulation. However, the mechanism and contributions of the individual TAM receptors is largely unknown.
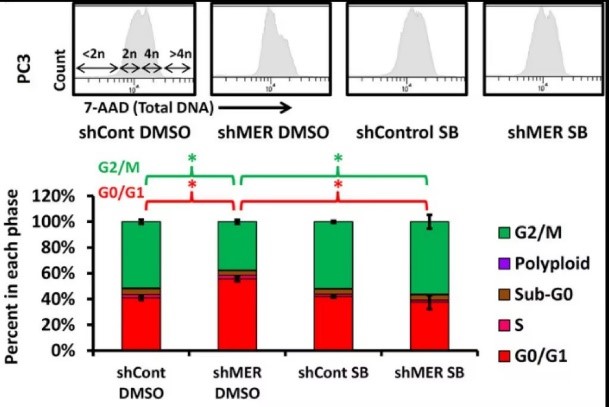
Knockdown of MERTK, but not AXL or TYRO3 by shRNA in PCa cells induced a decreased ratio of P-Erk1/2 to P-p38, increased expression of p27, NR2F1, SOX2, and NANOG, induced higher levels of histone H3K9me3 and H3K27me3, and induced a G1/G0 arrest, all of which are associated with dormancy. Also knockdown of MERTK in PCa cells increased metastasis free survival in an intra-cardiac injection mouse xenograft model. MERTK knockdown also failed to inhibit PCa growth in vitro and subcutaneous growth in vivo. Overall, this study shows that MERTK stimulates PCa dormancy escape through a MAP kinase dependent mechanism, also involving p27, pluripotency transcription factors, and histone methylation.
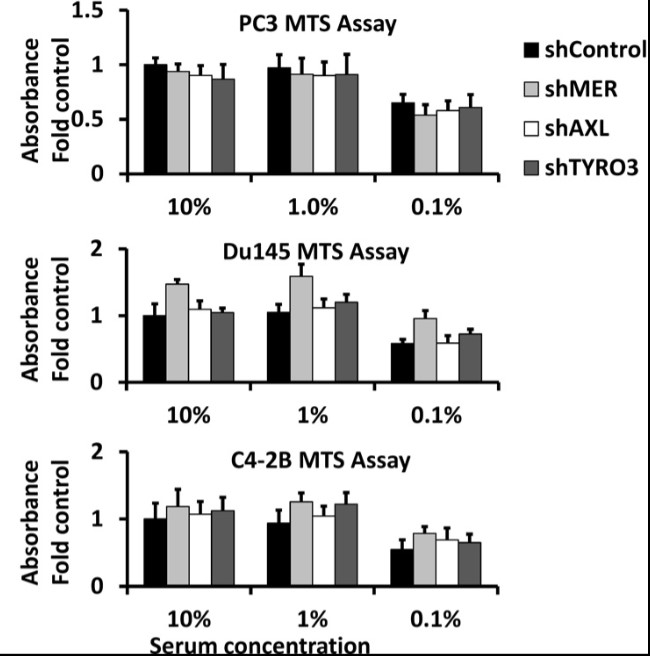
Fig3. Effect of MERTK knockdown on growth of prostate cancer cells in culture and in subcutaneous tumors.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
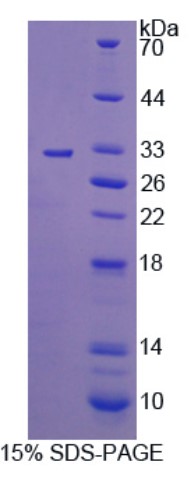
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (MERTK-1183H) (PROTOCOL for western blot)
.
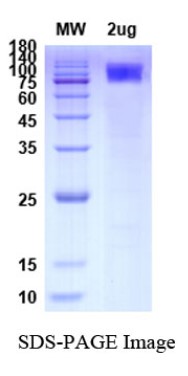
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (MERTK-3902H) (PROTOCOL for western blot)
Involved Pathway
MERTK involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways MERTK participated on our site, such as Cell surface interactions at the vascular wall,Hemostasis, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with MERTK were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Cell surface interactions at the vascular wall | CXADR,TREM1,CEACAM6,JAM2B,GRB7,SLC7A6,GAS6,DOK2,PROCR,GRB14 |
| Hemostasis | F9A,ESAMA,KIF2B,KIF22,C6orf25,DOK2,DOCK11,AKAP10,DOCK2,KIFAP3 |
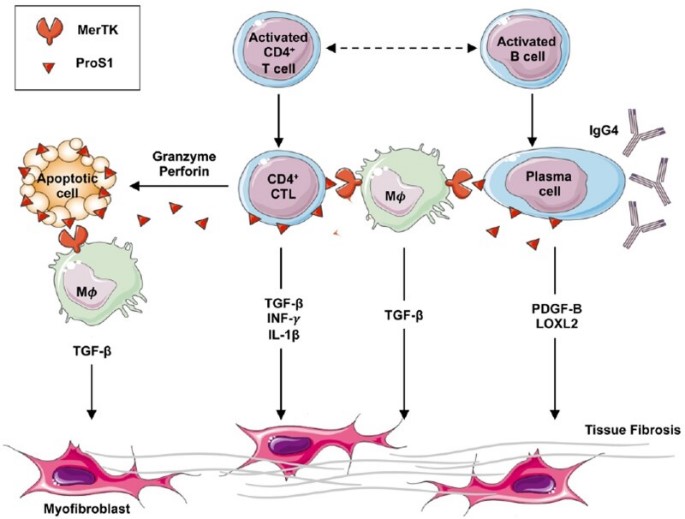
Fig1. Updated pathogenetic model of IgG4-RD Apoptotic phenomena triggered by CD4+ CTLs activate scavenger MerTK+ macrophages through ProS1 ligation. (Lucrezia Rovati, 2021)
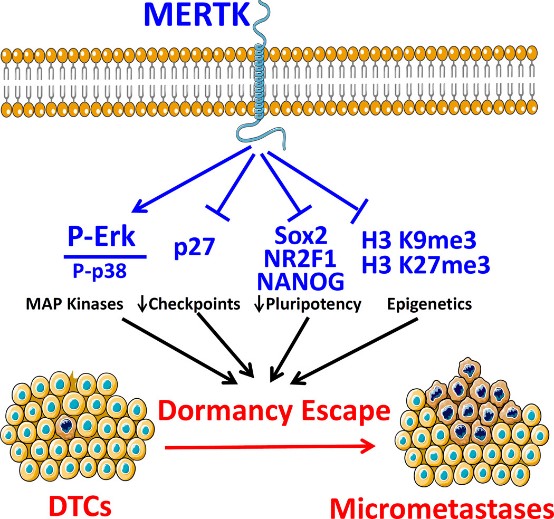
Fig2. MERTK stimulates PCa dormancy escape through a MAP kinase dependent mechanism, also involving p27, pluripotency transcription factors, and histone methylation. (Frank C Cackowski, 2017)
Protein Function
MERTK has several biochemical functions, for example, ATP binding,protein binding,transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by MERTK itself. We selected most functions MERTK had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with MERTK. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| protein binding | SVIP,AVPR2,OS9,ETV6,ZBTB22,CLU,ATN1,ALOX5AP,IFIT3,GM885 |
| ATP binding | SGK3,SMC4,TDRD12,IGF1R,GALK2,NMRK1,BMP2K,PKDCCA,KATNAL1,ADCY3 |
| transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase activity | ERBB3A,EK1,EPHA4A,FLT4,EPHB4,LTK,KDRL,NTRK1,IGF1RB,ERBB4A |
Interacting Protein
MERTK has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with MERTK here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of MERTK.
saicar;PKM;abl-tide;HSP90AB1;q5nhh0_fratt;mpl;crizotinib
Resources
Research Area
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Albert, R; Kristof, E; et al. Triamcinolone regulated apopto-phagocytic gene expression patterns in the clearance of dying retinal pigment epithelial cells. A key role of Mertk in the enhanced phagocytosis. BIOCHIMICA ET BIOPHYSICA ACTA-GENERAL SUBJECTS 1850:435-446(2015).
- Ginisty, A; Gely-Pernot, A; et al. Evidence for a Subventricular Zone Neural Stem Cell Phagocytic Activity Stimulated by the Vitamin K-Dependent Factor Protein S. STEM CELLS 33:515-525(2015).



