Receptor Tyrosine Kinases (RTKs) in the Akt Pathway
Related Symbol Search List
- ABL1
- AXL
- CSF1R
- DDR1
- EphA1
- Her2
- ERBB2
- HER3
- ERBB3
- ErbB4
- FGF1
- FLT1
- FLT4
- IGF1R
- INSR
- Kdr
- KIT
- MERTK
- Mst1r
- TrkA
- TrkB
- TrkC
- PDGFRA
- PPP2CB
- RET
- ROR1
- ROR2
- RYK
- STYK1
- TIE2
Immunology Background
About Receptor Tyrosine Kinases (RTKs) in the Akt Pathway
Receptor Tyrosine Kinases (RTKs) are a family of cell surface receptors involved in key cellular processes, including cell growth, differentiation, and survival.
RTKs are cell surface receptors that activate the Akt pathway. Upon ligand binding, RTKs dimerize and autophosphorylate, creating docking sites for proteins with Src homology 2 (SH2) domains. This leads to the recruitment and activation of phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K), which generates phosphatidylinositol (3,4,5)-trisphosphate (PIP3). PIP3 recruits Akt to the cell membrane, where it is phosphorylated and subsequently activated by phosphoinositide-dependent kinase 1 (PDK1) and the mammalian target of rapamycin complex 2 (mTORC2). This activation triggers downstream signaling affecting cell survival, proliferation, and metabolism. RTKs in the Akt Pathway include but are not limited to:
- Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR)
EGFR is a well-studied RTK involved in cell proliferation, survival, and migration.
Relationship with Akt: Activation of EGFR leads to the activation of PI3K, which in turn activates Akt, promoting cell survival and growth.
- Insulin Receptor (INSR)
INSR plays a crucial role in regulating glucose homeostasis and metabolism.
Relationship with Akt: Insulin binding to INSR activates the PI3K/Akt pathway, leading to the regulation of glucose uptake, metabolism, and cell survival.
- Platelet-Derived Growth Factor Receptor (PDGFR)
PDGFR is involved in cell growth, migration, and wound healing.
Relationship with Akt: PDGFR activation triggers PI3K/Akt signaling, promoting cell survival, proliferation, and migration.
- Hepatocyte Growth Factor Receptor (HGFR, also known as c-Met)
HGFR is a receptor for hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) involved in cell motility and proliferation.
Relationship with Akt: Activation of HGFR triggers PI3K/Akt signaling, influencing cell survival, growth, and metastasis.
- Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor (VEGFR)
VEGFR plays a crucial role in angiogenesis and vascular permeability.
Relationship with Akt: VEGFR activation leads to the activation of PI3K/Akt signaling, promoting endothelial cell survival, proliferation, and angiogenesis.
Understanding the complex mechanisms and interactions within the Akt pathway is critical to elucidating its importance in normal physiology and disease states, particularly cancer and metabolic disorders.
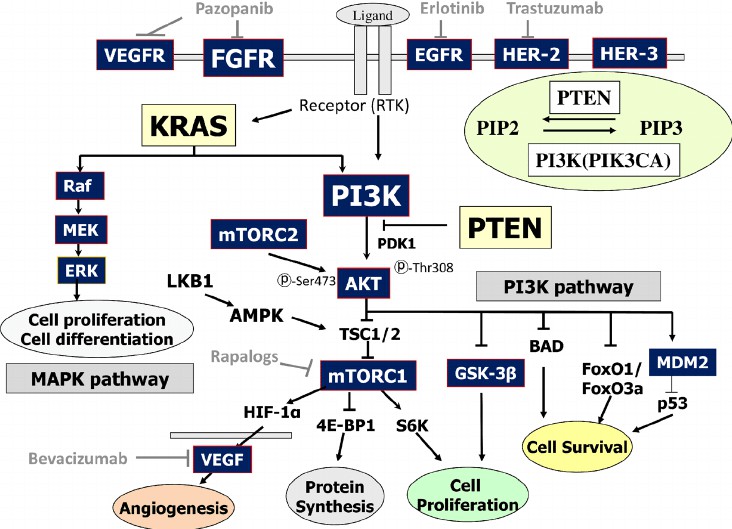 Fig.1 RTK (Receptor tyrosine kinases)/RAS/PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. (Oda K, et al., 2015)
Fig.1 RTK (Receptor tyrosine kinases)/RAS/PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. (Oda K, et al., 2015)
The Role of Receptor Tyrosine Kinases (RTKs) in the Akt Pathway
Here is a breakdown of the role of RTKs in the Akt pathway and their importance in cellular signal transduction:
Activation of RTKs: Ligand binding to RTKs induces receptor dimerization and autophosphorylation of tyrosine residues in the intracellular domain. This autophosphorylation creates docking sites for downstream signaling molecules and initiates the activation of intracellular signaling pathways.
Recruitment of PI3K: Phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) is recruited to the activated RTK through its interaction with phosphorylated tyrosine residues on the receptor. PI3K phosphorylates phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) to generate phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate (PIP3) at the plasma membrane.
Akt Activation: PIP3 acts as a second messenger to recruit Akt (also known as protein kinase B) to the plasma membrane. Once recruited, Akt is phosphorylated by phosphoinositide-dependent kinase 1 (PDK1) at threonine 308, leading to partial activation. Full activation of Akt requires phosphorylation at serine 473 by the mammalian target of rapamycin complex 2 (mTORC2).
Downstream Signaling: Activated Akt phosphorylates and regulates numerous downstream targets involved in cell survival, growth, and metabolism. These targets include:
- Bad: Phosphorylation of Bad by Akt prevents its pro-apoptotic function, promoting cell survival.
- Forkhead Box O (FOXO) transcription factors: Akt phosphorylates and inhibits FOXO transcription factors, suppressing their ability to induce apoptosis and promoting cell survival.
- Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3 (GSK-3): Akt phosphorylates and inhibits GSK-3, regulating glycogen synthesis, cell cycle progression, and gene expression.
- Mammalian Target of Rapamycin (mTOR): Akt activates mTOR, which plays a crucial role in cell growth, protein synthesis, and metabolism.
- Nuclear Factor-kappa B (NF-κB): Akt activates NF-κB, a transcription factor involved in inflammation, immune responses, and cell survival.
Role in Cellular Signal Transduction: The Akt pathway, driven by RTK activation, integrates extracellular signals and regulates key cellular processes. It promotes cell survival by inhibiting apoptosis and enhances cell growth and proliferation by stimulating protein synthesis and cell cycle progression. Additionally, the Akt pathway regulates glucose metabolism, lipid synthesis, and angiogenesis, contributing to overall cellular homeostasis.
Importance in Disease: Dysregulation of RTKs and the Akt pathway is associated with various diseases, including cancer, diabetes, cardiovascular disorders, and neurodegenerative diseases. Aberrant activation of RTKs and Akt signaling can lead to uncontrolled cell growth, resistance to apoptosis, and metabolic abnormalities, contributing to disease development and progression. Targeting RTKs and the Akt pathway has emerged as a promising therapeutic strategy for these diseases.
In summary, RTKs play a crucial role in activating the Akt pathway, which regulates diverse cellular processes. The activation of RTKs initiates a signaling cascade that ultimately controls cell survival, growth, metabolism, and proliferation. Understanding the role of RTKs in the Akt pathway is essential for unraveling the complexities of cellular signal transduction and developing targeted therapies for various diseases.
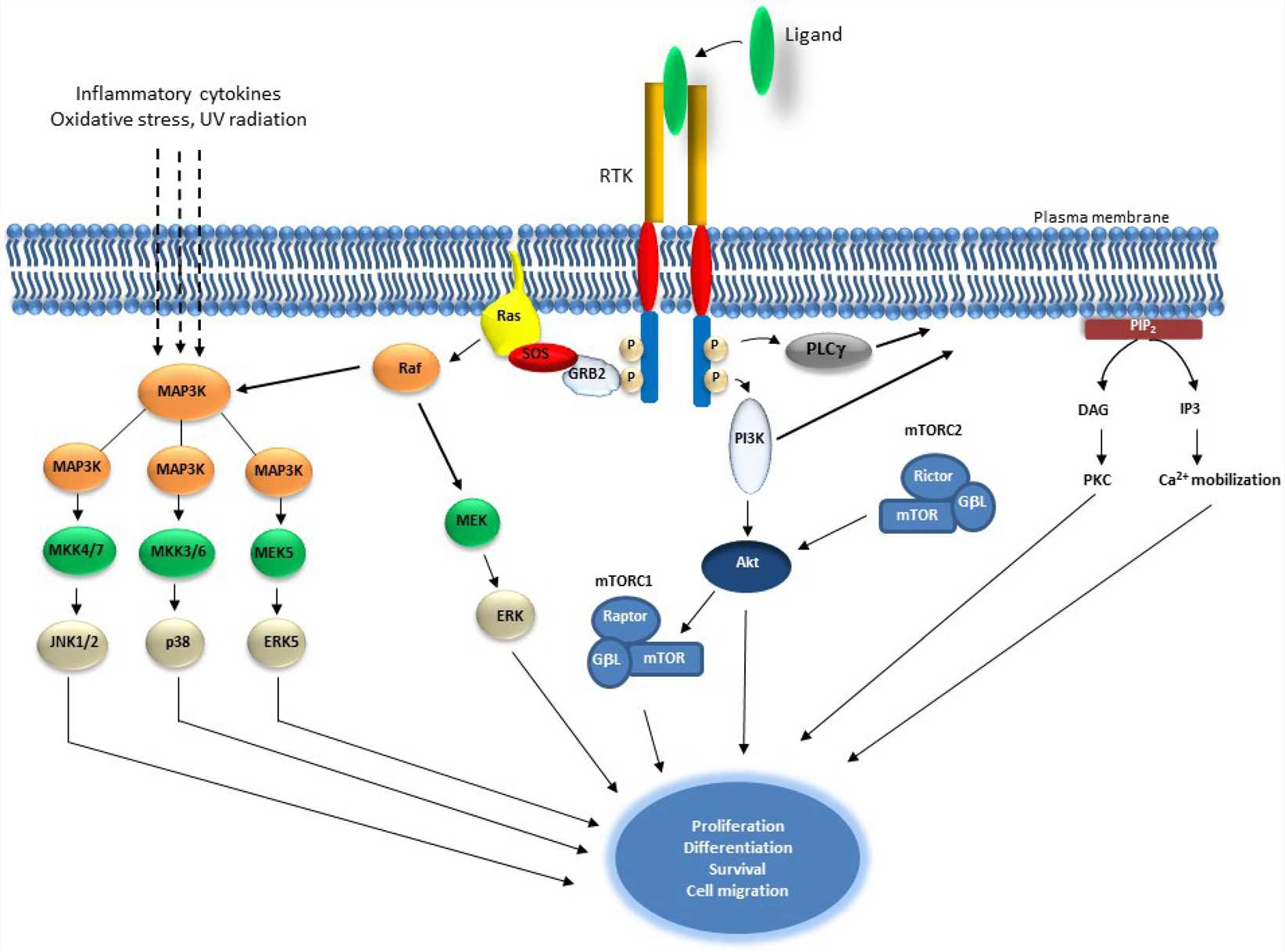 Fig.2 Schematic representation of Receptor Tyrosine Kinase and downstream signaling pathways. (Regad T, 2015)
Fig.2 Schematic representation of Receptor Tyrosine Kinase and downstream signaling pathways. (Regad T, 2015)
Receptor Tyrosine Kinases are auto-phosphorylated upon ligand binding, which results in the activation of Ras and induction of serine/threonine kinase Raf. Raf phosphorylates Mek1/2 which in turn phosphorylate and activate Erk1/2. Raf also activates MAP3 kinases that activate MKK4/7, MKKK3/6 and MEK5, which activates JNK1/2, p38 and ERK5, consecutively. MAP3Ks are also activated by inflammatory cytokines, oxidative stress and UV radiation. PI3K is activated by RTK autophosphorylation and results in the activation of Akt which also induces mTOR within the mTORC1 complex. Akt is also regulated by mTORC2 complex. PLCγ activation leads to Ca2+ mobilization and to the activation of PKC. These events play an essential role in proliferation, differentiation, survival and cell migration.
Available Resources for Receptor Tyrosine Kinases (RTKs) in the Akt Pathway
Understanding the RTKs in the Akt pathway is critical to elucidating its role in cellular processes and disease mechanisms, and Creative BioMart offers a wide range of resources to support researchers studying the Akt pathway and its associated molecules. By utilizing these resources, researchers can deepen their understanding of Akt signaling and potentially develop new therapeutic strategies for a variety of diseases.
Related Products
Creative BioMart is proud to offer a comprehensive range of products related to Receptor Tyrosine Kinases (RTKs). These products are designed to support researchers in their studies of RTKs and their involvement in various cellular processes. Some of the RTK-related products provided by Creative BioMart include:
Recombinant Proteins: Creative BioMart offers a wide selection of recombinant RTK proteins. These proteins are produced using advanced expression systems and undergo rigorous quality control to ensure their authenticity and functionality. Recombinant RTK proteins are valuable tools for studying protein-protein interactions, enzymatic activities, and downstream signaling pathways.
Cell & Tissue Lysates: Creative BioMart provides RTK-related cell and tissue lysates, which are prepared from various cell lines or tissues expressing specific RTKs. These lysates serve as valuable positive controls for Western blotting, immunoprecipitation, and other analytical techniques. They allow researchers to examine the expression levels and post-translational modifications of RTKs in different cellular contexts.
Protein Pre-coupled Magnetic Beads: Creative BioMart offers protein pre-coupled magnetic beads, providing a convenient and efficient solution for immunoprecipitation and protein purification. These magnetic beads are conjugated with antibodies specific to RTKs, enabling the isolation and enrichment of RTKs and their associated proteins from complex biological samples.
Native Proteins: In addition to recombinant proteins, Creative BioMart also provides native RTK proteins derived from natural sources. Native proteins maintain their native conformation and post-translational modifications, making them suitable for functional studies and drug discovery efforts targeting RTKs.
These RTK-related products from Creative BioMart are designed to meet the diverse needs of researchers studying RTKs and their involvement in cellular signaling pathways. By offering high-quality products, Creative BioMart aims to empower researchers with the necessary tools to advance their understanding of RTK biology and develop innovative therapeutic strategies.
Below are the molecules/targets related to receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) in the Akt pathway, click on them for product details.
Customized Services
Creative BioMart offers customized services to meet the specific needs of researchers. For example, for proteins of interest for specific research needs, as well as assay development and data analysis, we can tailor our services to provide personalized solutions for the study of complex signaling pathways associated with RTK and Akt pathways.
Technical Support
Creative BioMart emphasizes customer satisfaction and provides efficient customer support throughout the research process. Our dedicated customer service team is always available to answer inquiries, provide technical assistance, and address any concerns or questions researchers may have. We also provide application notes, protocol guides, and more to help customers make the most of our products and services.
If you have any questions or requests, please feel free to contact us.
References:
- Oda K, Ikeda Y, Kawana K, et al. mTOR signaling in endometrial cancer: from a molecular and therapeutic point of view[J]. Current Obstetrics and Gynecology Reports, 2015,4:1-10.
- Regad T. Targeting RTK Signaling Pathways in Cancer[J]. Cancers, 2015, 7(3).DOI:10.3390/cancers7030860.

