Active Recombinant Human Iinterleukin 23, Alpha Subunit P19
| Cat.No. : | L23A-269H |
| Product Overview : | Recombinant Human IL23A is expressed inHuman 293 cellsas a heterodimeric glycoprotein composed of two disulfide-linked subunits (p40 cystine linked to p19). |
- Specification
- Gene Information
- Related Products
- Citation
- Download
| Species : | Human |
| Source : | HEK293 |
| Tag : | Non |
| Description : | Production in Human 293 cells offers authentic glycosylation. Cytokines produced in Sf9 or Sf21 cells have posttranslational modifications which are not humanlike. This gene encodes a subunit of the heterodimeric cytokine interleukin 23 (IL23). IL23 is composed of this protein and the p40 subunit of interleukin 12 (IL12B). The receptor of IL23 is formed by the beta 1 subunit of IL12 (IL12RB1) and an IL23 specific subunit, IL23R. Both IL23 and IL12 can activate the transcription activator STAT4, and stimulate the production of interferon-gamma (IFNG). In contrast to IL12, which acts mainly on naive CD4 (+) T cells, IL23 preferentially acts on memory CD4 (+) T cells. |
| Endotoxin : | Endotoxin-free. |
| Purity : | >95%. The protein was resolved by SDS polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and the gelwas stained with Coomassie blue. |
| Activity : | The specific activity was determined by the dose-dependent secretion of IL-17 from mouse splenocytes activated with 10ng/mL PMA. |
| Solubility : | It is recommended to reconstitute the lyophilized Bone Morphogenetic Protein-6 in sterile 20mM AcOH (acetic Acid) not less than 100µg/ml, which can then be further diluted to other aqueous solutions. |
| Storage : | -20℃. |
| Gene Name | IL23A interleukin 23, alpha subunit p19 [Homo sapiens] |
| Synonyms | P19; SGRF; IL-23; IL-23A; IL23P19; MGC79388; IL23A ;interleukin-23 subunit alpha ; IL-23-A ; IL-23p19 ; IL-23 subunit alpha ; interleukin 23 p19 subunit ; interleukin-23 subunit p19 ; JKA3 induced upon T-cell activation |
| Gene ID | 51561 |
| mRNA Refseq | NM_ 016584 |
| Protein Refseq | NP_057668 |
| MIM | 605580 |
| UniProt ID | Q9NPF7 |
| Chromosome Location | 12q13.3 |
| Pathway | Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction; Jak-STAT signaling pathway |
| Function | cytokine activity; protein binding |
| ◆ Recombinant Proteins | ||
| IL23A-2358H | Recombinant Human IL23A protein(Met1-Pro189), mFc-tagged | +Inquiry |
| IL23A-1172H | Recombinant Human IL23A Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | +Inquiry |
| IL23A-179H | Recombinant Active Human IL23A Protein, His-tagged(N-ter) | +Inquiry |
| IL23A-1173H | Recombinant Human IL23A Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | +Inquiry |
| Il23a-2461M | Recombinant Mouse Il23a protein, His-tagged | +Inquiry |
| ◆ Cell & Tissue Lysates | ||
| IL23A-5231HCL | Recombinant Human IL23A 293 Cell Lysate | +Inquiry |
A Role for RUNX3 in Inflammation-Induced Expression of IL23A in Gastric Epithelial Cells
Journal: Cell reports PubMed ID: 25008775 Data: 2015/1/20
Authors: Yit Teng Hor, Dominic Chih-Cheng Voon, Yoshiaki Ito
Article Snippet:For measurement of IL-23 in the supernatants harvested from cultured cells, ELISA was performed using the Human IL-23 Ready-SET-Go! kit (eBioscience) and the Human IL23A/p19 ELISA kit (Creative BioMart) as per the manufacturer’s instructions.. To induce the secretion of IL-23, gastric epithelial cell lines and the monocytic cell line THP-1 were stimulated with TNF-α, H. pylori , or LPS for 24 hr.To induce the secretion of IL-23, gastric epithelial cell lines and the monocytic cell line THP-1 were stimulated with TNF-α, H. pylori , or LPS for 24 hr.
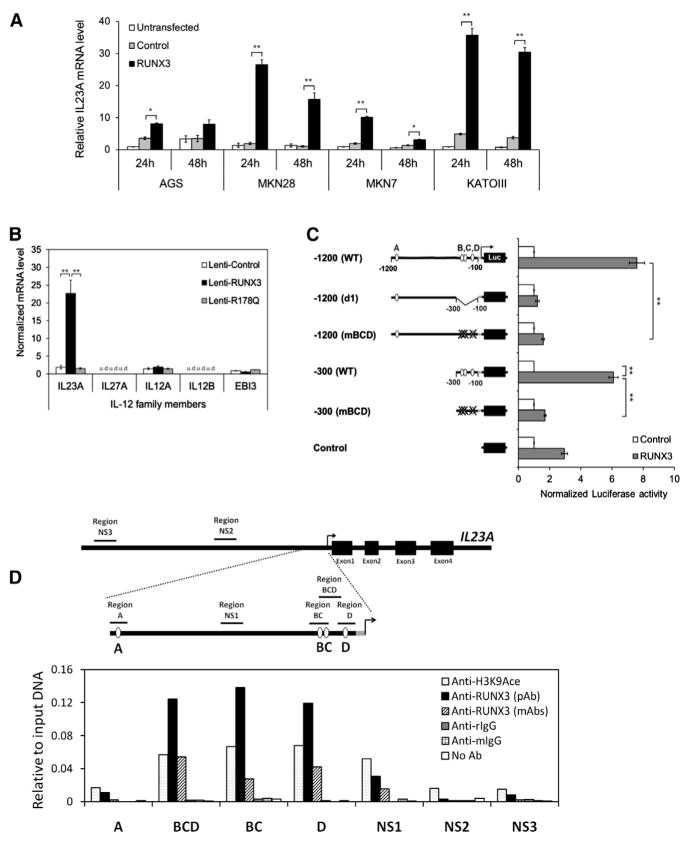
(A)
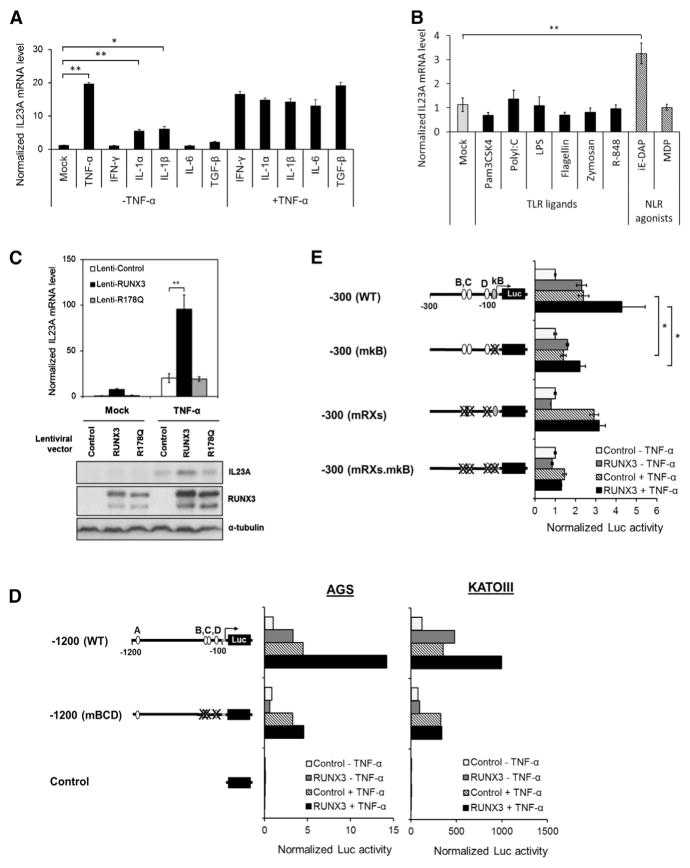
(A and B) The effects of various proinflammatory stimuli on the expression of
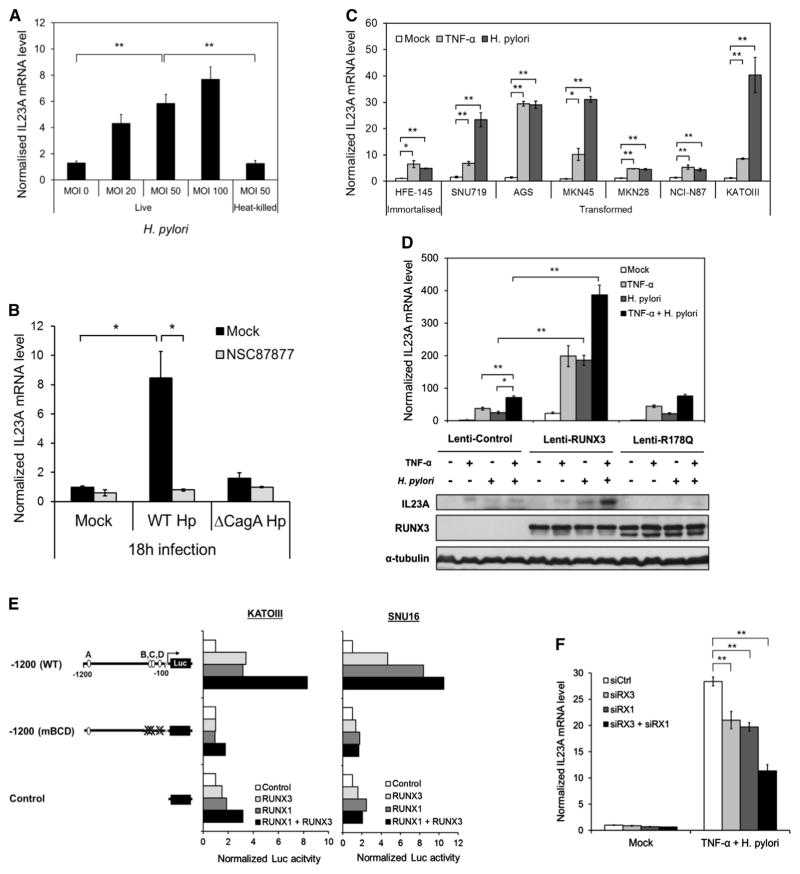
(A) H. pylori activates
Not For Human Consumption!
Inquiry
- Reviews (0)
- Q&As (1)
Ask a Question for All IL23A Products
Required fields are marked with *
My Review for All IL23A Products
Required fields are marked with *


