IL23A
-
Official Full Name
interleukin 23, alpha subunit p19 -
Overview
Interleukin-23 (IL-23) is a heterodimeric cytokine consisting of two subunits, one called p40, which is shared with another cytokine, IL-12, and another called p19 (the IL-23 alpha subunit). IL-23 is an important part of the inflammatory response against infection. It promotes upregulation of the matrix metalloprotease MMP9, increases angiogenesis and reduces CD8+ T-cell infiltration. Recently, IL-23 has been implicated in the development of cancerous tumors. In conjunction with IL-6 and TGF-β1, IL-23 stimulates naive CD4+ T cells to differentiate into a novel subset of cells called Th17 cells, which are distinct from the classical Th1 and Th2 cells. Th17 cells produce IL-17, a proinflammatory cytokine that enhances T cell priming and stimulates the production of proinflammatory molecules such as IL-1, IL-6, TNF-alpha, NOS-2, and chemokines resulting in inflammation. Knockout mice deficient in either p40 or p19, or in either subunit of the IL-23 receptor (IL-23R and IL12R-β1) develop less severe symptoms of multiple sclerosis and inflammatory bowel disease highlighting the importance of IL-23 in the inflammatory pathway. -
Synonyms
IL23A;interleukin 23, alpha subunit p19;P19;SGRF;IL-23;IL-23A;IL23P19;MGC79388;interleukin-23 subunit alpha;IL-23-A;IL-23p19;IL-23 subunit alpha;interleukin 23 p19 subunit;interleukin-23 subunit p19;JKA3 induced upon T-cell activation
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Bovine
- Mouse
- Marmoset
- Rhesus macaque
- Rat
- Cynomolgus
- Pig
- Guinea pig
- HEK293
- CHO
- Yeast
- S.frugiperda
- Hi-5 Insect Cells
- Insect Cells
- E.coli
- Sf21 Cells
- Human Cells
- Sf9 Cells
- Wheat Germ
- Mammalian Cells
- Avi
- Fc
- His
- Non
- GST
- Flag
- DDK
- Myc
- SUMO
- mFc
- MBP
- TRxA
Background
What is IL23A protein?
IL23A (interleukin 23 subunit alpha) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 12 at locus 12q13. This gene encodes a subunit of the heterodimeric cytokine interleukin 23 (IL23). IL23 is composed of this protein and the p40 subunit of interleukin 12 (IL12B). The receptor of IL23 is formed by the beta 1 subunit of IL12 (IL12RB1) and an IL23 specific subunit, IL23R. Both IL23 and IL12 can activate the transcription activator STAT4, and stimulate the production of interferon-gamma (IFNG). The IL23A protein is consisted of 189 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 20.7 kDa.
What is the function of IL23A protein?
The IL23A protein binds to the IL12B protein to form the pro-inflammatory cytokine IL-23, a heterodimer factor that plays different roles in innate and adaptive immunity. IL-23 specifically acts on memory CD4(+) T cells, promoting the expansion and survival of helper T cells 17 (Th17), a CD4-positive subpopulation of helper T cells that produce IL-17. IL-23 plays a key role in the inflammatory process by promoting the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as interleukin 17A (IL17A), which in turn is involved in the regulation of inflammatory responses. Because of its role in a variety of inflammatory and autoimmune diseases, IL-23 has emerged as a potential drug target for the treatment of these conditions.
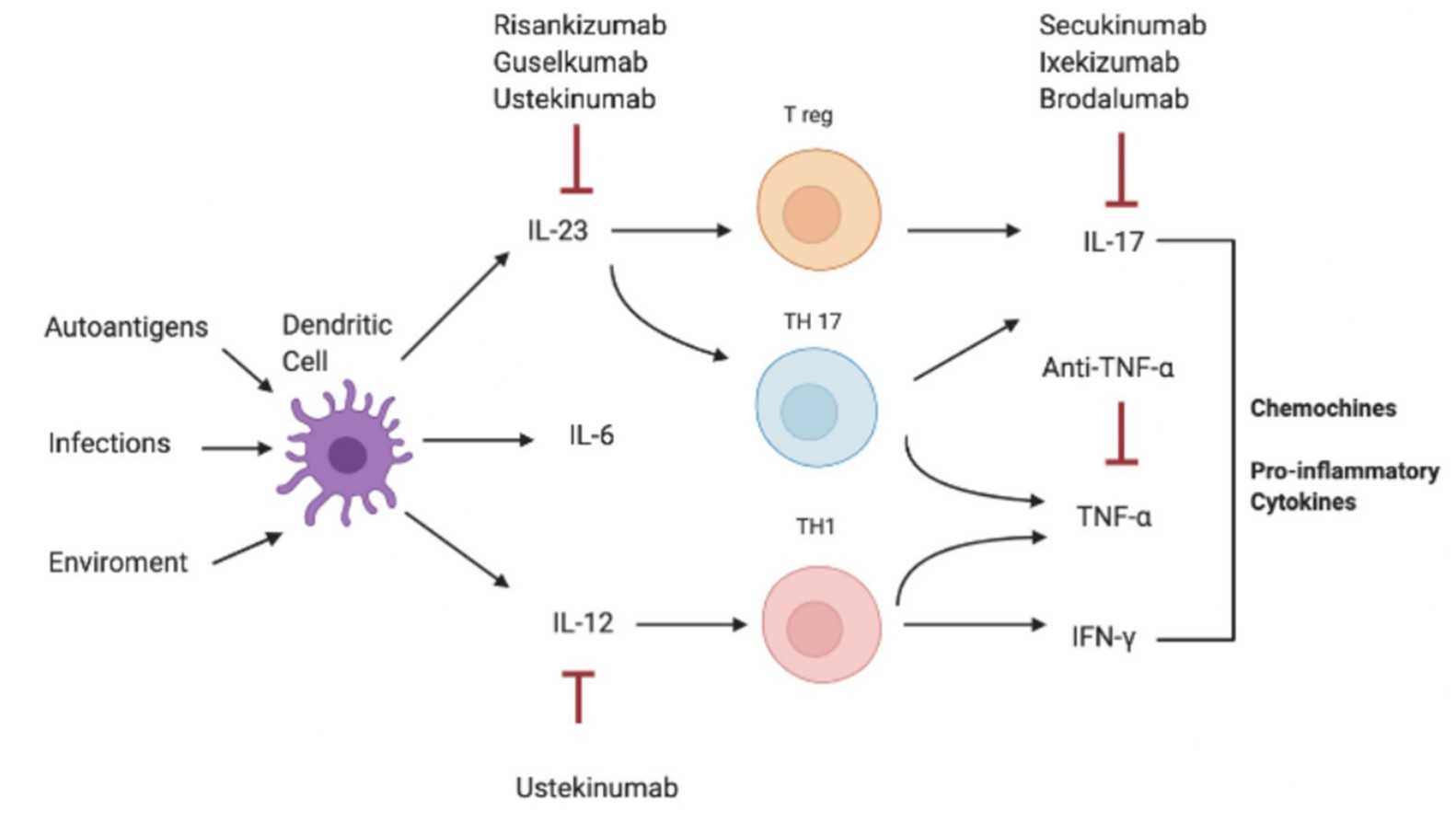
Fig1. Pathogenesis of IL-17-correlated disease and different targets of therapy. (Claudia Schinocca, 2021)
IL23A Related Signaling Pathway
When IL-23 binds to its receptor, it activates the JAK family of kinases, including JAK2 and TYK2, which in turn activates STAT3 and STAT4, leading to the activation of various signaling pathways, such as p38 MAPK or NF-κB. The IL-23 receptor consists of two subunits of the IL-12 receptor β1 (IL-12Rβ1) and the IL-23 receptor, a transmembrane protein whose extracellular region contains multiple functional domains. IL23A binds to IL12B to form the pro-inflammatory cytokine IL-23, a heterodimer factor that plays different roles in innate and adaptive immunity. IL-23 promotes the production of IL-17 by activating Th17 cells, which is involved in the amplification of inflammatory response and the regulation of autoimmune response.
IL23A Related Diseases
IL-23A is involved in the pathogenesis of psoriasis, especially in the activation of T cells and the inflammatory response in psoriasis. IL-23A is also involved in the inflammatory process of psoriatic arthritis, affecting pathological changes in the joints and skin. IL-23A plays a role in the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease, specifically associated with Th17 cell activation and intestinal inflammatory response. The role of IL-23A in autoimmune diseases is receiving increasing attention because it plays a key role in regulating the immune response and promoting inflammation. IL-23A may be involved in the occurrence and development of a variety of other inflammatory diseases by affecting the activation of immune cells and the release of inflammatory mediators. IL-23A in the tumor microenvironment may promote tumor growth by affecting the activity of T cells and other immune cells.
Bioapplications of IL23A
IL23A is a potential target for drug development. Drugs have been developed that target IL23A or its receptors to treat diseases in which the IL23A signaling pathway is abnormal. IL23A acts as a cytokine and may be used to regulate immune responses, for example in immune deficiencies or autoimmune diseases. Studies have shown that IL23 cytokines can specifically act on activated CAR T cells and improve their proliferation after recognizing tumor antigens and anti-cancer function in multiple solid tumor models.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Shan He, 2022
As a vital problem in reproductive health, recurrent spontaneous abortion (RSA) affects about 1% of women. The researchers performed this study with an aim to explore the molecular mechanism of interleukin-23 (IL-23) and find optimal or effective methods to improve RSA. First, ELISA was applied to evaluate the expressions of IL-23 and its receptor in HTR-8/SVneo cells after IL-23 treatment. CCK-8, TUNEL, wound healing and transwell assays were employed to assess the proliferation, apoptosis, migration and invasion of HTR-8/SVneo cells, respectively. Additionally, the expressions of apoptosis-, migration-, epithelial-mesenchymal transition- (EMT-) and p38 MAPK signaling pathway-related proteins were measured by western blotting. To further investigate the relationship between IL-23 and p38 MAPK signaling pathway, HTR-8/SVneo cells were treated for 1 h with p38 MAPK inhibitor SB239063, followed by a series of cellular experiments on proliferation, apoptosis, migration and invasion, as aforementioned. The results showed that IL-23 and its receptors were greatly elevated in IL-23-treated HTR-8/SVneo cells. Additionally, IL-23 demonstrated suppressive effects on the proliferation, apoptosis, migration, invasion and EMT of IL-23-treated HTR-8/SVneo cells. More importantly, the molecular mechanism of IL-23 was revealed in this study; that is to say, IL-23 inhibited the proliferation, apoptosis, migration, invasion and EMT of IL-23-treated HTR-8/SVneo cells via activating p38 MAPK signaling pathway.
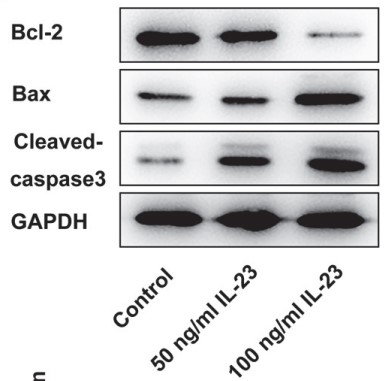
Fig1. The expressions of apoptosis-related proteins in IL-23-treated HTR-8/SVneo cells.
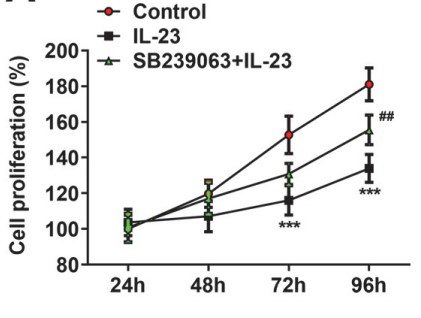
Fig2. The cell proliferation of IL-23-treated HTR-8/SVneo cells.
Case Study 2: Susanne Meier, 2019
The functionality of most secreted proteins depends on their assembly into a defined quaternary structure. Despite this, it remains unclear how cells discriminate unassembled proteins en route to the native state from misfolded ones that need to be degraded. Here the researchers show how chaperones can regulate and control assembly of heterodimeric proteins, using interleukin 23 (IL-23) as a model. They find that the IL-23 α-subunit remains partially unstructured until assembly with its β-subunit occurs and identify a major site of incomplete folding. Incomplete folding is recognized by different chaperones along the secretory pathway, realizing reliable assembly control by sequential checkpoints. Structural optimization of the chaperone recognition site allows it to bypass quality control checkpoints and provides a secretion-competent IL-23α subunit, which can still form functional heterodimeric IL-23.
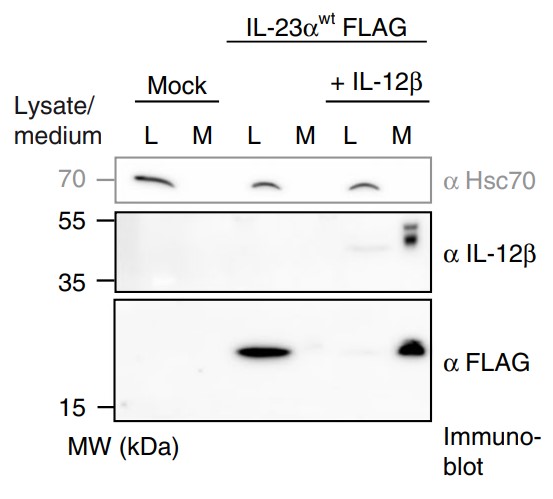
Fig3. Secretion behavior of FLAG-tagged wild type IL-23α.
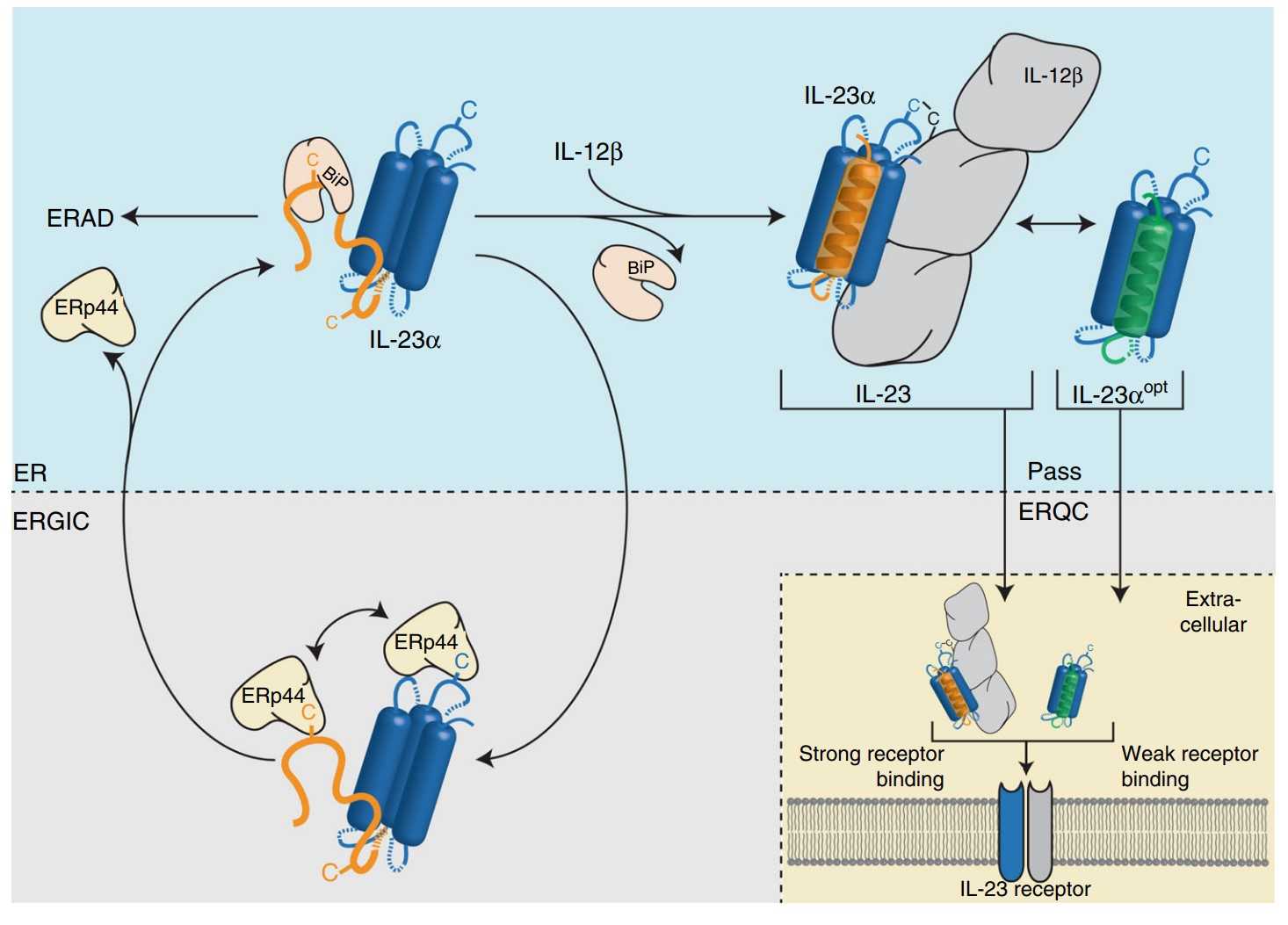
Fig4. A model for IL-23 assembly control in the cell.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (IL23A-1823H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (IL23A-02H)
Involved Pathway
IL23A involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways IL23A participated on our site, such as Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction,Jak-STAT signaling pathway,Pertussis, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with IL23A were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Jak-STAT signaling pathway | LEPA,CSH2,CTF1,STAM2,CRFB4,HRAS,PTPN11B,PTPN2A,GFAP,MCL1 |
| Pertussis | C4A,PYCARD,GNAI3,GNAI1,CALM1,TNF,Casp3,ITGAM,IRF1,Il23a; Il12b |
| Rheumatoid arthritis | TNFRSF11A,TLR2,ATP6V0E2,ATP6V1G2,H2-AA,IL6,ATP6V1C1,IL11,ATP6AP1,CXCL12 |
| Tuberculosis | CALM1,PIK3C3,cgr2b,HLA-DRB4,BAX,NFYB,TNFRSF1A,MAPK3,TRADD,CD209A |
| Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction | TGFB2,FLT4,IFNA10,CSF1,ACVR1BA,Kitl,TGFBR2,FASLG,TNFRSF9A,CXCR3 |
| Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) | SMAD3,HLA-DOB,IL13,HLA-DQA1,MAF,IL4R,TGFB3,IFNGR1,IL5,RORC |
Protein Function
IL23A has several biochemical functions, for example, . Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by IL23A itself. We selected most functions IL23A had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with IL23A. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|
Interacting Protein
IL23A has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with IL23A here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of IL23A.
Resources
Gene Families
Research Area
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Masaki, K; Suzuki, Y; et al. Dual Role of Interleukin-23 in Epicutaneously-Sensitized Asthma in Mice. ALLERGOLOGY INTERNATIONAL 63:13-22(2014).
- Britze, A; Palmfeldt, J; et al. 44-plex cytokine profile of cholesteatoma. ACTA OTO-LARYNGOLOGICA 134:41-50(2014).
Reviews
In the past, we have ordered IL23A from your company. As it works very well for our assay, we would like to order some more. - Customer from @umcg.nl

