Recombinant Human Glutathione Peroxidase 1, His-tagged
| Cat.No. : | GPX1-1273H |
| Product Overview : | Recombinant human GPX1(U49C) protein, fused to His-tag at N-terminus, was expressed in E.coli and purified by using conventional chromatography techniques. |
- Specification
- Gene Information
- Related Products
- Citation
- Download
| Species : | Human |
| Source : | Human |
| Tag : | His |
| Description : | GPX1 belongs to the glutathione peroxidase family, consisting of eight known glutathione peroxidases (Gpx1-8) in humans. GPX1 functions in the detoxification of hydrogen peroxide, and is one of the most important antioxidant enzymes in humans. The GPX1 is part of the enzymatic antioxidant defence, preventing oxidative damage to DNA, proteins and lipids by detoxifying hydrogen and lipid peroxides that may contribute to prostate cancer development. This protein is one of only a few proteins known in higher vertebrates to contain selenocysteine, which occurs at the active site of glutathione peroxidase and is coded by the nonsense (stop) codon TGA. |
| Form : | Liquid. In 20mM Tris-HCl buffer (pH 8.0) containing 2mM DTT, 30% glycerol, 100mM NaCl |
| Molecular Weight : | 24.2kDa (223aa), confirmed by MALDI-TOF |
| Purity : | > 90% by SDS - PAGE |
| Concentration : | 0.5mg/ml (determined by Bradford assay) |
| Sequences of amino acids : | MGSSHHHHHH SSGLVPRGSH MCAARLAAAA AAAQSVYAFS ARPLAGGEPV SLGSLRGKVL LIENVASLCG TTVRDYTQMN ELQRRLGPRG LVVLGFPCNQ FGHQENAKNE EILNSLKYVR PGGGFEPNFM LFEKCEVNGA GAHPLFAFLR EALPAPSDDA TALMTDPKLI TWSPVCRNDV AWNFEKFLVG PDGVPLRRYS RRFQTIDIEP DIEALLSQGP SCA |
| Storage : | Can be stored at +4C short term (1-2 weeks). For long term storage, aliquot and store at -20C or -70C. Avoid repeated freezing and thawing cycles. |
| Pathways : | Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS); Arachidonic acid metabolism; Direct p53 effectors; Folate Metabolism; Glutathione metabolism; Huntington"s disease; Metabolism of nucleotides; Oxidative Stress; Purine catabolism; Selenium Metabolism and Selenoproteins; Selenium Pathway; glutathione redox reactions I |
| Publications : |
| Gene Name | GPX1 glutathione peroxidase 1 [ Homo sapiens ] |
| Official Symbol | GPX1 |
| Synonyms | GPX1; glutathione peroxidase 1; GSHPX1; MGC14399; MGC88245; GPX1; Cellular glutathione peroxidase; MGC14399; GPx-1; MGC88245; GSHPx-1; OTTHUMP00000210766; OTTHUMP00000210765; EC 1.11.1.9; EC 1.11.1 |
| Gene ID | 2876 |
| mRNA Refseq | NM_000581 |
| Protein Refseq | NP_000572 |
| MIM | 138320 |
| UniProt ID | P07203 |
| Chromosome Location | 3p21.3 |
| Function | SH3 domain binding; endopeptidase inhibitor activity; glutathione peroxidase activity; oxidoreductase activity |
| ◆ Recombinant Proteins | ||
| GPX1-5307H | Recombinant Human GPX1 Protein, His-tagged | +Inquiry |
| GPX1-29074TH | Recombinant Human GPX1, His-tagged | +Inquiry |
| Gpx1-1585R | Recombinant Rat Gpx1 Protein, His-tagged | +Inquiry |
| GPX1-5579HF | Recombinant Full Length Human GPX1 Protein, GST-tagged | +Inquiry |
| GPX1-2469H | Recombinant Human GPX1 Protein (Thr50-Ala202), N-His tagged | +Inquiry |
| ◆ Native Proteins | ||
| GPX1-8429H | Native Human GPX1 | +Inquiry |
| ◆ Cell & Tissue Lysates | ||
| GPX1-348HKCL | Human GPX1 Knockdown Cell Lysate | +Inquiry |
| GPX1-5763HCL | Recombinant Human GPX1 293 Cell Lysate | +Inquiry |
Impact of carbonylation on glutathione peroxidase-1 activity in human hyperglycemic endothelial cells
Journal: Redox Biology PubMed ID: 29499564 Data: 2018/3/1
Authors: Cheryl S. Sultan, Andrea Saackel, Andreas H. Wagner
Article Snippet:For some approaches in vitro metal catalyzed oxidation of recombinant GPx1 protein was performed as previously published elsewhere followed by activity measurements or mass spectrometry analysis.For some approaches in vitro metal catalyzed oxidation of recombinant GPx1 protein was performed as previously published elsewhere followed by activity measurements or mass spectrometry analysis.. For this purpose recombinant GPx1 (Creative BioMart, #GPX1-1273H) was dissolved at 0.5 mg/ml in sample buffer (50 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.6, containing 5 mM EDTA).. Oxidation was accomplished by supplementing 10–20 μl of protein solution (5 μg) with a freshly prepared FeSO4 with a final concentration of 1.2 mmol/L and incubating for 10–30 min at room temperature after addition of 0.05% (w/w) cumene hydroperoxide (Sigma-Aldrich, #247502) or 0.3% (w/w) hydrogen peroxide (Merck Millipore, #107209).Oxidation was accomplished by supplementing 10–20 μl of protein solution (5 μg) with a freshly prepared FeSO4 with a final concentration of 1.2 mmol/L and incubating for 10–30 min at room temperature after addition of 0.05% (w/w) cumene hydroperoxide (Sigma-Aldrich, #247502) or 0.3% (w/w) hydrogen peroxide (Merck Millipore, #107209).
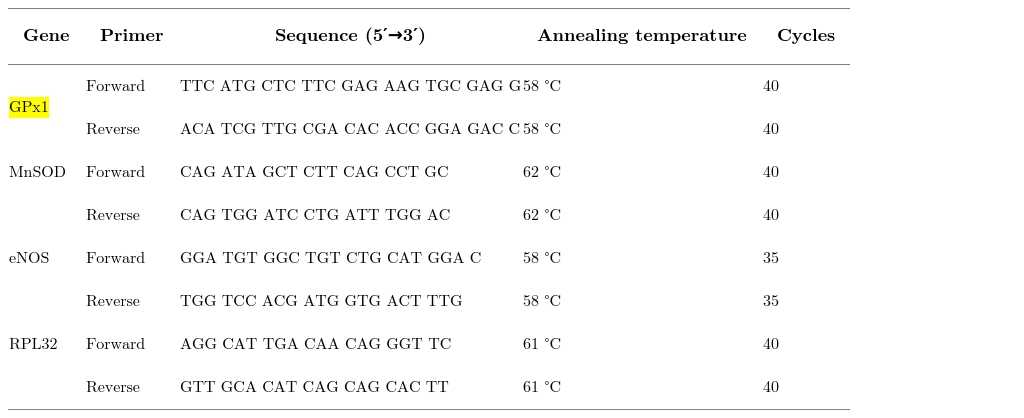
Primers used for qPCR.
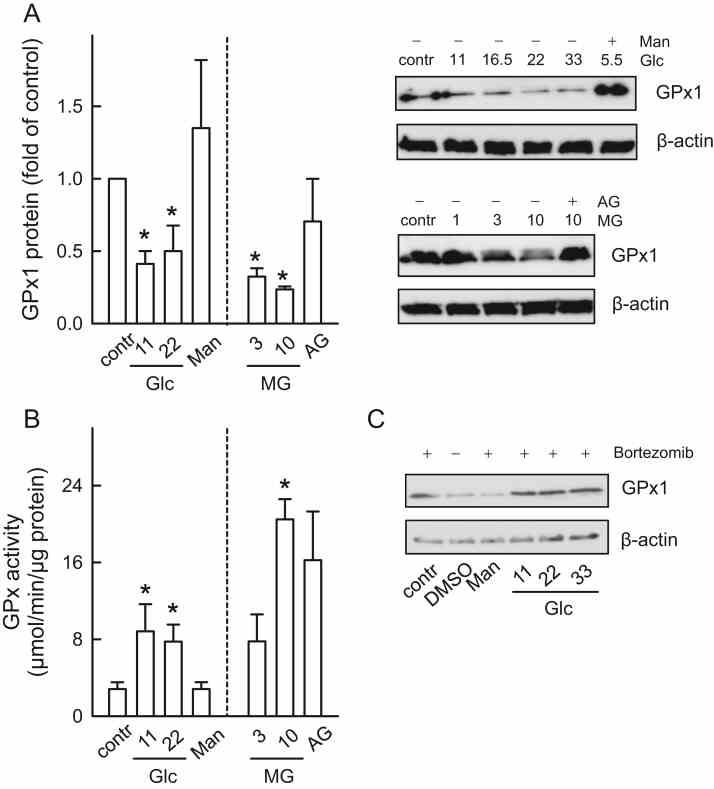
Enhanced GPx activity compensates for the decreased
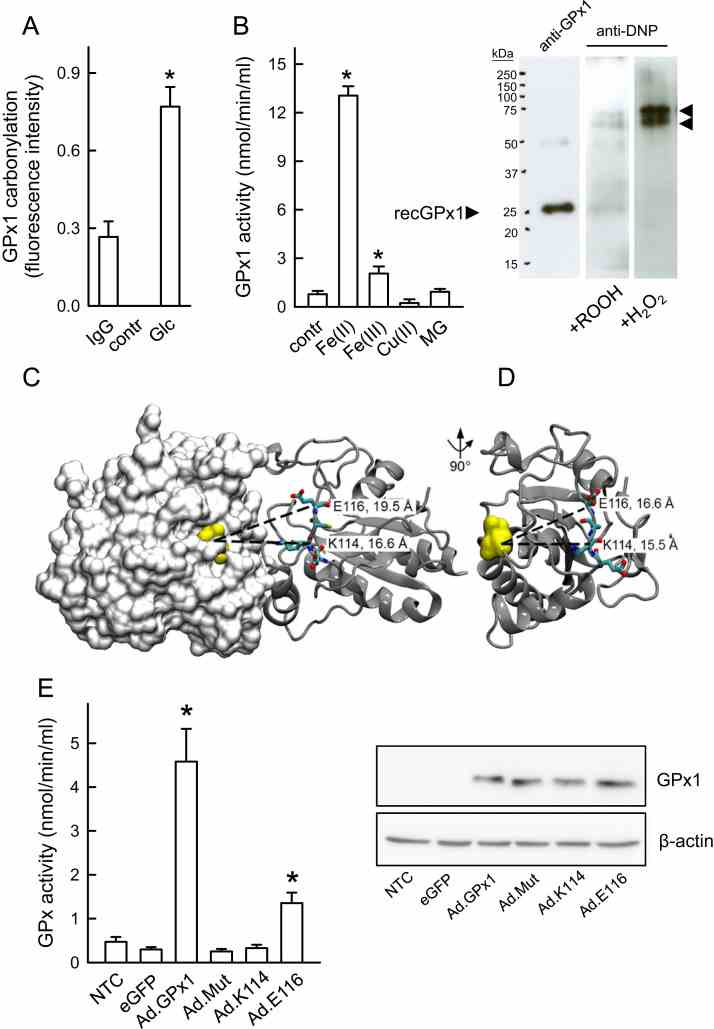
Carbonylation-associated increase in GPx activity. ( A ) Specific quantification of
Not For Human Consumption!
Inquiry
- Reviews (0)
- Q&As (0)
Ask a Question for All GPX1 Products
Required fields are marked with *
My Review for All GPX1 Products
Required fields are marked with *



