Other T Cell CD Antigen
Related Symbol Search List
Immunology Background
Resources Available for the Study of Other T Cell CD Antigens
Creative BioMart commitment to offering exceptional products and personalized assistance ensures that you have everything necessary to explore the complexities of other T cell CD antigens (In addition to the CD antigens associated with helper T cells, regulatory T cells, T cell antigen recognition, and T cell migration/adhesion).
- Our diverse product selection includes recombinant proteins, native proteins, protein-coupled magnetic beads, cell and tissue lysates, chromatography reagents, GMP proteins, assay kits, and more. Each product is meticulously designed to meet your specific research requirements with unparalleled precision and expertise.
- Beyond our extensive product offerings, we provide a wealth of resources on other T cell CD antigens. Our in-depth insights encompass relevant pathways, protein functionalities, interacting proteins, literature reviews, and other valuable information. These resources serve as a valuable asset in gaining a deeper comprehension of the molecular mechanisms and biological importance of other T cell CD antigens.
Our Featured Products
| Cat.# | Product name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD74-2227H | Active Recombinant Human CD74 protein, His-tagged | Human | HEK293 | His |
| DPP4-270H | Active Recombinant Human DPP4 protein | Human | HEK293 | N/A |
| BMPR1A-771H | Recombinant Human BMPR1A, Fc-His tagged | Human | Human Cell | Fc/His |
| Il6ra-2297M | Recombinant Mouse Il6ra, His tagged | Mouse | HEK293 | His |
| ITGA5-4116H | Recombinant Human ITGA5, flag & His tagged | Human | Human Cell | Flag/His |
About Other T Cell CD Antigens
In addition to the CD antigens associated with helper T cells, regulatory T cells, T cell antigen recognition, and T cell migration/adhesion, there are several other CD antigens that play important roles in various aspects of T cell biology. These antigens include CD74, DPP4, CXCR1, CXCR2, BMPR1A, Il6ra, ITGA5, and others. Here's a brief introduction to these CD antigens:
- CD74: CD74, also known as the invariant chain (Ii), is involved in antigen presentation. It functions as a chaperone protein, guiding the assembly and transport of major histocompatibility complex class II (MHC-II) molecules. CD74 is primarily expressed on antigen-presenting cells (APCs) and is crucial for efficient loading of antigenic peptides onto MHC-II molecules, enabling their presentation to CD4+ T cells.
- DPP4 (CD26): DPP4 is a cell surface peptidase expressed on various cell types, including T cells. It has multiple functions, including enzymatic activity, costimulation, and adhesion. DPP4 can cleave certain chemokines, modulating their function and affecting T cell migration. It also acts as a costimulatory molecule, promoting T cell activation. Additionally, DPP4 has been implicated in T cell adhesion to endothelial cells and extracellular matrix components.
- CXCR1 and CXCR2: CXCR1 and CXCR2 are chemokine receptors expressed on T cells, among other cell types. They specifically bind to and respond to chemokines of the interleukin-8 (IL-8) family. These receptors play a role in T cell chemotaxis and recruitment to sites of inflammation or infection. CXCR1 and CXCR2 engagement by their ligands regulates T cell migration and positioning within different tissues.
- BMPR1A: BMPR1A (Bone Morphogenetic Protein Receptor Type 1A) is a receptor for the bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) family. It is involved in T cell development and differentiation. BMPR1A signaling influences the balance between effector and regulatory T cell populations, contributing to immune homeostasis and immune responses.
- Il6ra (CD126): Il6ra is a subunit of the interleukin-6 (IL-6) receptor complex. It is expressed on various immune cells, including T cells. IL-6 signaling through Il6ra plays a role in T cell activation, differentiation, and survival. It influences T cell responses in various immune contexts, such as inflammation, infection, and autoimmunity.
- ITGA5: ITGA5 (Integrin alpha-5) is a subunit of integrin receptors expressed on T cells and other cell types. It forms integrin heterodimers, such as α5β1, which interact with extracellular matrix proteins, including fibronectin. ITGA5-mediated adhesion and signaling contribute to T cell migration, homing, and interaction with the extracellular matrix.
These additional CD antigens mentioned above play diverse roles in T cell biology, including antigen presentation, enzymatic activity, chemotaxis, receptor signaling, adhesion, and modulation of T cell responses. Understanding their functions and interactions provides insights into the complex regulation of T cell behavior and immune responses. These CD antigens represent potential targets for therapeutic interventions aimed at modulating T cell function in various diseases and immune-related disorders.
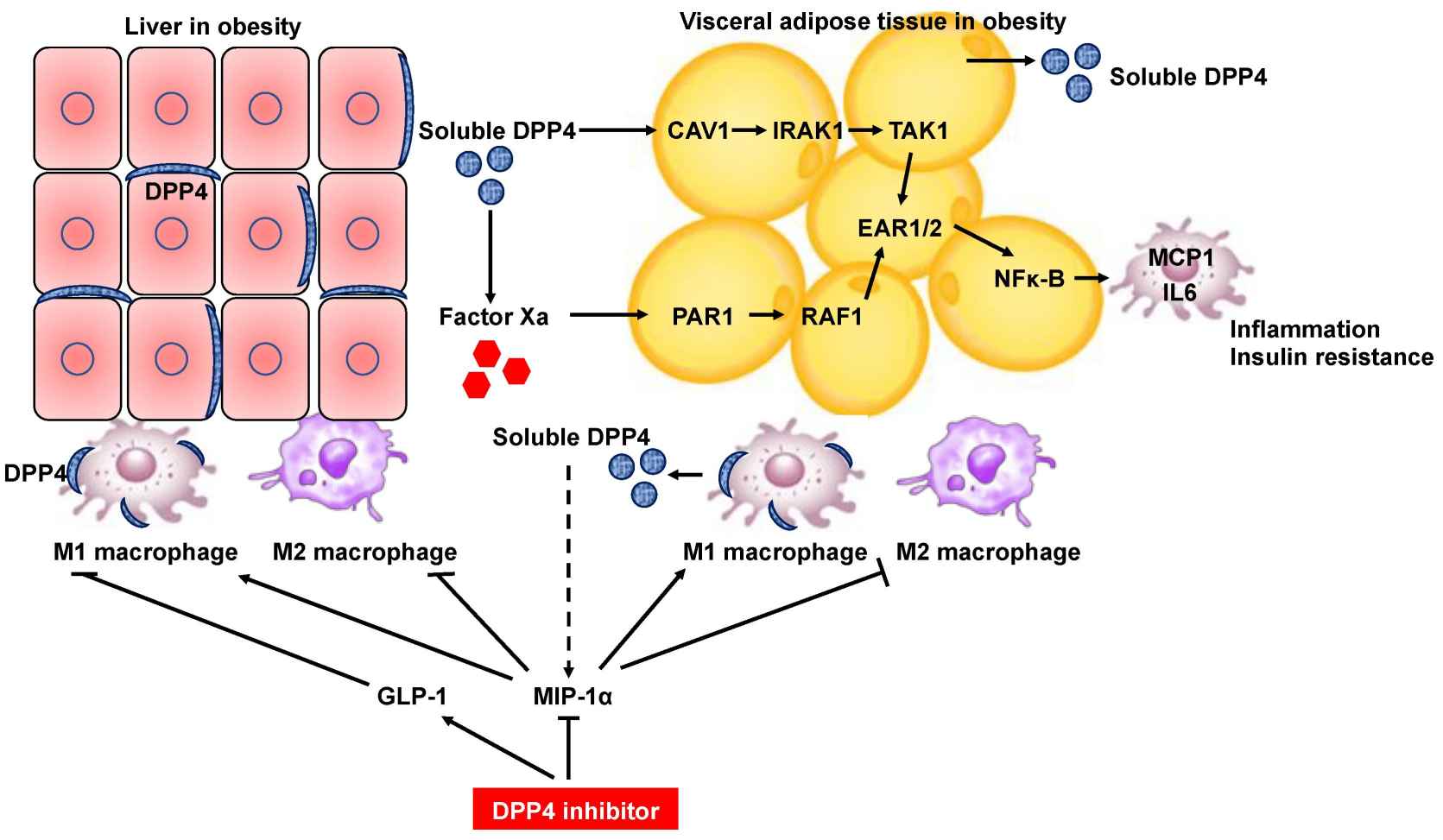 Fig.1 Schematic diagram depicting DPP4 inhibitor-mediated inhibition of inflammation in the liver and adipose tissues through amelioration of dysregulated M1/M2 polarization of macrophages. (Nishina S, et al., 2022)
Fig.1 Schematic diagram depicting DPP4 inhibitor-mediated inhibition of inflammation in the liver and adipose tissues through amelioration of dysregulated M1/M2 polarization of macrophages. (Nishina S, et al., 2022)
Other T Cell CD Antigens in Various Diseases
Autoimmune Diseases
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE): CD74 is upregulated on B cells, promoting the presentation of self-antigens and contributing to autoantibody production. This leads to immune complex formation and tissue damage, affecting multiple organs.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): CD74 is involved in synovial inflammation and joint destruction. Dysregulated CD74 signaling contributes to the recruitment and activation of inflammatory cells, leading to chronic inflammation and progressive joint damage.
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS): CD74 plays a role in antigen presentation and T cell activation. In MS, CD74-mediated presentation of myelin-derived antigens to autoreactive T cells leads to an immune attack on myelin sheaths in the central nervous system, resulting in demyelination and neurodegeneration.
Metabolic Diseases
- Type 2 Diabetes: DPP4 is involved in the degradation of incretin hormones, such as glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1), which regulate insulin secretion and glucose homeostasis. Inhibition of DPP4 enhances incretin hormone activity, leading to improved glycemic control.
Inflammatory Diseases
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD): CXCR1 and CXCR2 are chemokine receptors involved in neutrophil recruitment and activation. Dysregulation of CXCR1 and CXCR2 signaling leads to excessive neutrophil infiltration, chronic inflammation, and tissue damage in the lungs.
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD): Il6ra is the receptor for IL-6, a pro-inflammatory cytokine implicated in IBD. Dysregulated IL-6 signaling through Il6ra contributes to chronic intestinal inflammation, mucosal damage, and altered immune responses.
Vascular Disorders
- Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia (HHT): BMPR1A is a receptor for bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs) involved in vascular development. Mutations in BMPR1A disrupt normal blood vessel formation, leading to the development of telangiectasias (dilated blood vessels) and arteriovenous malformations (AVMs) in various organs.
Cancer
- Breast Cancer: ITGA5 is a cell adhesion molecule involved in tumor cell migration, invasion, and angiogenesis. Increased ITGA5 expression is associated with aggressive tumor behavior and poor prognosis in breast cancer.
- Lung Cancer: CXCR1 and CXCR2 play a role in tumor progression and metastasis by promoting tumor cell migration, invasion, and angiogenesis. Dysregulated CXCR1 and CXCR2 signaling contribute to the invasive potential and poor prognosis of lung cancer.
- Pancreatic Cancer: ITGA5 mediates tumor cell adhesion to the extracellular matrix and promotes tumor cell invasion and metastasis. In pancreatic cancer, increased ITGA5 expression is associated with enhanced tumor aggressiveness and metastatic potential.
These examples illustrate how CD74, DPP4, CXCR1, CXCR2, BMPR1A, Il6ra, and ITGA5 are involved in various diseases across different categories, shedding light on their roles in disease pathogenesis and potential therapeutic targets for intervention.
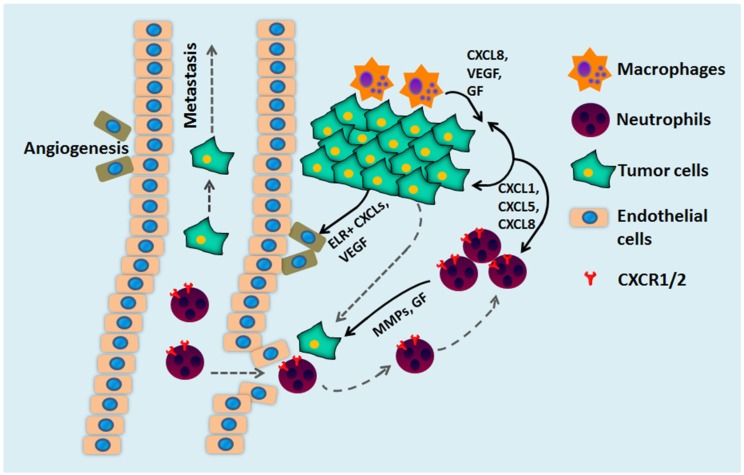 Fig.2 The multiple roles of CXCL chemokines and CXCR1/2 during tumor development. (Ha H, et al., 2017)
Fig.2 The multiple roles of CXCL chemokines and CXCR1/2 during tumor development. (Ha H, et al., 2017)
Choose Creative BioMart as your trusted partner, and embark on a journey of scientific exploration with confidence and precision. If you have any questions, requirements, or cooperation intentions, please feel free to contact us. We very much look forward to working with you and helping you achieve research and commercial success.
Related References
- Sánchez-Zuno GA, Bucala R, Hernández-Bello J, et al. Canonical (CD74/CD44) and Non-Canonical (CXCR2, 4 and 7) MIF Receptors Are Differentially Expressed in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients Evaluated by DAS28-ESR. J Clin Med. 2021;11(1):120.
- Ha H, Debnath B, Neamati N. Role of the CXCL8-CXCR1/2 Axis in Cancer and Inflammatory Diseases. Theranostics. 2017;7(6):1543-1588.
- Narazaki M, Kishimoto T. The Two-Faced Cytokine IL-6 in Host Defense and Diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(11):3528.
- Nishina S, Hino K. CD26/DPP4 as a Therapeutic Target in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis Associated Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers. 2022; 14(2):454.

