Wnt Inhibitors
Related Symbol Search List
Immunology Background
Available Resources for Wnt Inhibitors Research
At Creative BioMart you can find a wide range of products related to Wnt inhibitors, including recombinant proteins and other key products. In addition, we offer customized services to meet your specific requirements, ensuring you get the product you need.
In addition to our products and services, we offer a wealth of resources for your reference. Our resources cover all aspects of Wnt inhibitors, including the involved pathways, protein function, interacting proteins, related articles, research areas, and other relevant topics. These resources will be invaluable to researchers wishing to deepen their understanding of Wnt inhibitors and their role in physiological processes.
Our Featured Products
About Wnt Inhibitors
Wnt inhibitors are a class of molecules that modulate the Wnt signaling pathway, which plays a crucial role in various biological processes, including embryonic development, tissue regeneration, and homeostasis. The Wnt signaling pathway is highly conserved and involved in cell proliferation, differentiation, and cell fate determination.
The Wnt pathway is initiated by the binding of Wnt ligands to cell surface receptors known as Frizzled (FZD) receptors, along with co-receptors such as LRP5/6. This binding triggers a cascade of intracellular events, leading to the activation of various downstream signaling pathways, including the canonical Wnt/β-catenin pathway and non-canonical pathways such as the Wnt/Ca2+ pathway and the planar cell polarity pathway.
Aberrant activation of the Wnt signaling pathway has been implicated in the development and progression of various diseases, including cancer. In some cancers, mutations in key components of the pathway, such as APC (adenomatous polyposis coli) or β-catenin, lead to constitutive activation of the pathway, resulting in uncontrolled cell growth and tumor formation.
Wnt inhibitors are designed to target and modulate the Wnt signaling pathway to restore its normal function or inhibit its hyperactivation. These inhibitors can act at different levels of the pathway, including blocking the interaction between Wnt ligands and their receptors, inhibiting downstream signaling events, or promoting the degradation of key components involved in the pathway.
Several classes of Wnt inhibitors have been developed, including small molecule inhibitors, antibodies, peptides, and RNA-based therapeutics. Small molecule inhibitors often target specific enzymes or proteins involved in Wnt signaling, such as tankyrase inhibitors that interfere with the stabilization of β-catenin. Antibodies and peptides can target Wnt ligands or receptors, blocking their interaction and preventing pathway activation. RNA-based therapeutics, such as small interfering RNA (siRNA) or antisense oligonucleotides, can specifically target and degrade RNA molecules encoding key components of the Wnt pathway.
Research into Wnt inhibitors is actively ongoing, and their potential applications extend beyond cancer. They hold promise for the treatment of other diseases, including fibrosis, neurodegenerative disorders, and regenerative medicine, where the modulation of Wnt signaling can influence tissue repair and regeneration.
It's important to note that while Wnt inhibitors show therapeutic potential, their development and application in clinical settings are still in progress, and further research is needed to fully understand their efficacy, safety, and potential side effects.
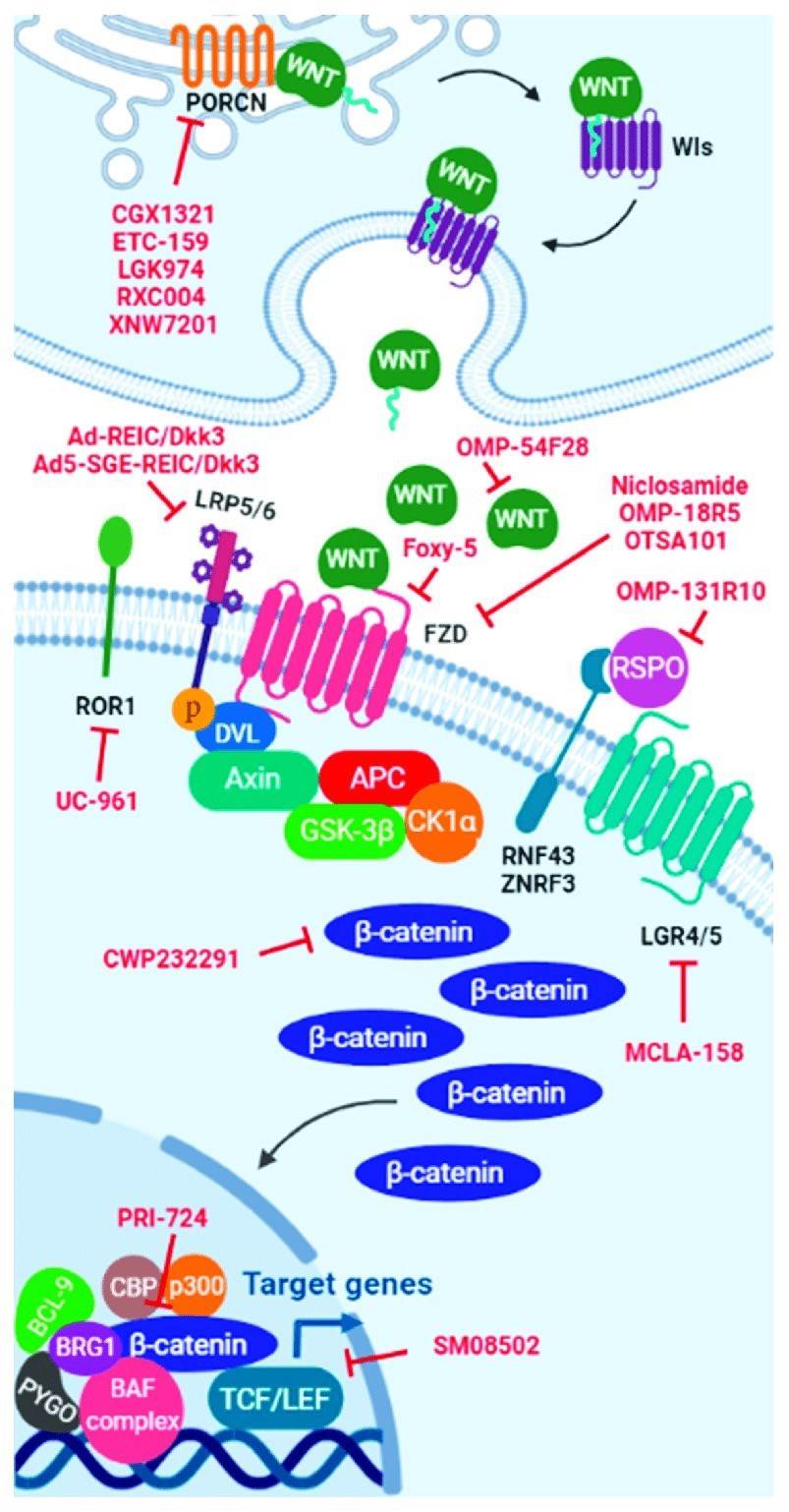 Fig.1 WNT signaling pathway inhibitors. Scheme of the WNT signaling pathway showing the interaction site of each WNT inhibitor include in clinical trials. (Martinez-Font E, et al., 2021)
Fig.1 WNT signaling pathway inhibitors. Scheme of the WNT signaling pathway showing the interaction site of each WNT inhibitor include in clinical trials. (Martinez-Font E, et al., 2021)
Functions of Wnt Inhibitors
Wnt inhibitors serve a variety of functions based on their ability to modulate the Wnt signaling pathway. Here are some of the key functions of Wnt inhibitors:
- Downregulation of Wnt signaling: The primary function of Wnt inhibitors is to suppress or downregulate the Wnt signaling pathway. By inhibiting the interaction between Wnt ligands and their receptors or interfering with downstream signaling events, these inhibitors can reduce the activation of the pathway and restore normal cellular processes.
- Cancer therapy: Aberrant activation of the Wnt signaling pathway is often observed in various types of cancer. Wnt inhibitors have shown potential in cancer therapy by targeting the dysregulated pathway. By blocking the signaling cascade, these inhibitors can impede tumor growth, induce apoptosis (cell death) in cancer cells, and inhibit metastasis.
- Stem cell regulation: Wnt signaling plays a crucial role in the self-renewal and differentiation of stem cells. Wnt inhibitors can modulate this pathway to regulate stem cell behavior. By controlling the activation of Wnt signaling, inhibitors can influence the fate determination of stem cells, promoting their differentiation into specific cell types or maintaining their undifferentiated state.
- Tissue regeneration: Wnt signaling is involved in tissue regeneration and repair processes. Wnt inhibitors can be used to modulate this pathway to promote tissue regeneration in cases of injury or disease. By manipulating the Wnt signaling levels and dynamics, inhibitors can influence cell proliferation, migration, and differentiation, facilitating tissue regeneration and healing.
- Developmental biology: Wnt signaling is crucial for embryonic development and organogenesis. Wnt inhibitors have been used in developmental biology research to study the role of Wnt signaling in various developmental processes. By blocking specific components of the pathway, researchers can investigate the effects on embryonic development and gain insights into the underlying mechanisms.
- Disease modulation: Besides cancer, dysregulated Wnt signaling has been implicated in other diseases, including fibrosis, neurodegenerative disorders, and metabolic disorders. Wnt inhibitors hold promise for therapeutic interventions in these conditions by targeting the underlying Wnt pathway abnormalities and restoring normal cellular functions.
It's important to note that the functions of Wnt inhibitors can vary depending on the specific inhibitor and the context in which it is applied. Ongoing research is expanding our understanding of Wnt signaling and the potential applications of Wnt inhibitors in various fields of medicine and biology.
If you have any questions, requirements, or cooperation intentions, please feel free to contact us. We very much look forward to working with you and helping you achieve research and commercial success.
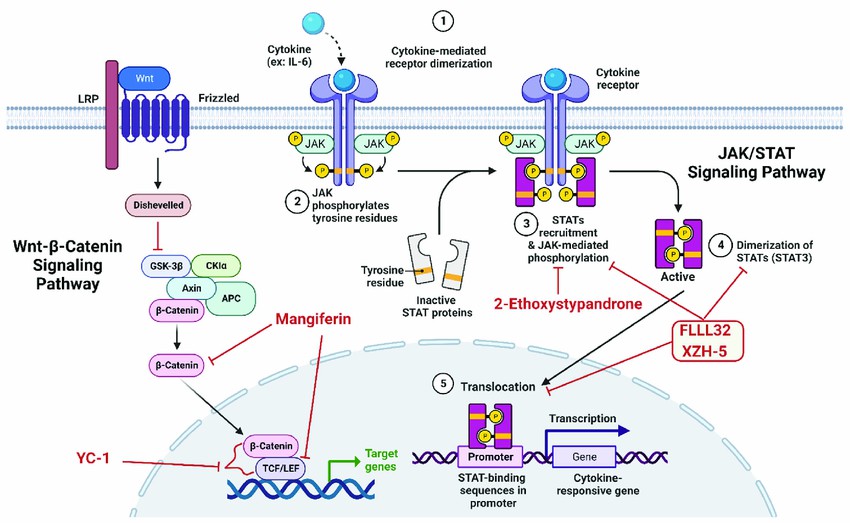 Fig.2 Schematic representations of emerging small molecule inhibitors of Wnt signaling pathway and STAT3 signaling pathway. (Kamal MA, et al., 2022)
Fig.2 Schematic representations of emerging small molecule inhibitors of Wnt signaling pathway and STAT3 signaling pathway. (Kamal MA, et al., 2022)
This figure was generated by biorender. Wnt, Wingless and Int-1; TCF/LEF, T-cell factor/lymphoid enhancer-binding factor; GSK-3β, glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta; APC, Adenomatous Polyposis Coli; LRP, lipoprotein receptor-related protein; JAK, Janus Kinase.
References:
- Martinez-Font E, Pérez-Capó M, Vögler O, Martín-Broto J, Alemany R, Obrador-Hevia A. WNT/β-Catenin Pathway in Soft Tissue Sarcomas: New Therapeutic Opportunities? Cancers (Basel). 2021;13(21):5521. Published 2021 Nov 3.
- Kamal MA, Mandour YM, Abd El-Aziz MK, Stein U, El Tayebi HM. Small Molecule Inhibitors for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Advances and Challenges. Molecules. 2022;27(17):5537. Published 2022 Aug 28.

