MMP13
-
Official Full Name
matrix metallopeptidase 13 (collagenase 3) -
Overview
Proteins of the matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) family are involved in the breakdown of extracellular matrix in normal physiological processes, such as embryonic development, reproduction, and tissue remodeling, as well as in disease processes, such as arthritis and metastasis. Most MMPs are secreted as inactive proproteins which are activated when cleaved by extracellular proteinases. The protein encoded by this gene cleaves type II collagen more efficiently than types I and III. It may be involved in articular cartilage turnover and cartilage pathophysiology associated with osteoarthritis. The gene is part of a cluster of MMP genes which localize to chromosome 11q22.3. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] -
Synonyms
MMP13;matrix metallopeptidase 13 (collagenase 3);CLG3;MANDP1;MMP-13;collagenase 3;matrix metalloproteinase 13 (collagenase 3)
Recombinant Proteins
- Mouse
- Human
- Rat
- Chicken
- Pig
- Rabbit
- Cattle
- Dog
- Mammalian Cells
- E.coli
- Sf9 Cells
- S.frugiperda
- HEK293
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- E. coli
- His
- Non
- T7
- SUMO
- Flag
- Avi
- Fc
- GST
Background
What is mmp13 protein?
MMP13 is mainly produced by chondrocytes, cells within cartilage, and plays an important role in cartilage remodeling and breakdown during development and growth. It is involved in endochondral ossification, the process by which bones are formed from cartilage templates. MMP13 action breaks down cartilage to allow its replacement with bone. Increased MMP13 expression/activity has been implicated in diseases involving cartilage degradation like osteoarthritis. It is a Marker of disease progression.MMP13 can also degrade other matrix proteins apart from collagens like aggrecan and pericellular matrix. Its activity is regulated at multiple levels including transcription, activation of zymogen, and inhibition by tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases (TIMPs).
What are the functions of MMP13 protein?
Cartilage breakdown: MMP13 is specialized in degrading type II collagen, which is the most abundant collagen in cartilage. It breaks down the collagen network in cartilage.
Bone development: MMP13 plays an important role in endochondral ossification by degrading cartilage templates to allow their replacement with bone. This allows for proper bone growth and modeling.
Tissue remodeling: Along with collagen degradation, MMP13 can also cleave other extracellular matrix proteins like aggrecan. This allows for tissue remodeling during development, growth and wound healing.
Arthritis: Increased MMP13 expression and activity leads to excess cartilage breakdown in arthritic conditions like osteoarthritis. It contributes to disease pathogenesis.
MMP13 related signaling pathway
MAPK pathway: MMP13 expression is regulated by the MAPK signaling cascade, especially the ERK1/2 and p38 pathways. Factors like IL-1β and TGF-β induce MMP13 via MAPKs.
NF-κB pathway: Inflammatory cytokines like IL-1β activate NF-κB signaling to upregulate MMP13 transcription. NF-κB binds to MMP13 promoter region.
Wnt/β-catenin pathway: Wnt ligands induce β-catenin nuclear translocation and transcriptional activation of MMP13. This pathway mediates MMP13 expression in arthritis.
Notch pathway: Notch intracellular domain binds to RBP-Jκ and induces MMP13 expression in chondrocytes and osteoblasts during skeletal development.
MMP13 Related Diseases
- Osteoarthritis: Increased MMP13 expression contributes to cartilage degradation in osteoarthritis. It is a marker for disease progression.
- Rheumatoid arthritis: MMP13 levels correlate with joint damage in RA. Inhibiting it may help slow disease progression.
- Developmental skeletal diseases: Mutations affecting MMP13 cause polymorphic chondrodysplasias due to impaired endochondral ossification.
- Cancer metastasis: Many cancers like gastric, breast and prostate show elevated MMP13. It promotes tumor cell invasion and metastasis.
- Periodontitis: MMP13 levels increase in gingival crevicular fluid of periodontitis patients, destroying ligament and bone tissues.
- Disease biomarker: MMP13 levels can serve as an indicator of disease progression in osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis and cancer metastasis.
- Drug target: Developing selective MMP13 inhibitors is a promising approach for arthritis and cancer therapeutic intervention.
- Tissue engineering: Regulations of MMP13 activity could promote cartilage regeneration for treating osteoarthritis and other joint disorders.
- Disease biomarker: MMP13 levels can serve as an indicator of disease progression in osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis and cancer metastasis.
- Drug target: Developing selective MMP13 inhibitors is a promising approach for arthritis and cancer therapeutic intervention.
- Tissue engineering: Regulations of MMP13 activity could promote cartilage regeneration for treating osteoarthritis and other joint disorders.
Case Study

(Jing Ma, 2014)
Fig2. The expression of MMP13 mRNA and protein was gradually and significantly increased from 1 to 7 days after the alkali burns.
(Jing Ma, 2014)
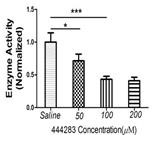
Fig3.The inhibitory effect of 444283 on MMP13 activity in alkali-burned rat corneas at day 7. Fifty μM of 444283 inhibited approximately 30% of MMP13 activity, but 100 and 200 μM of 444283 caused approximately a 60% reduction in MMP13 activity compared with saline.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (Cat. No.: MMP13-733P)
Involved Pathway
MMP13 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways MMP13 participated on our site, such as AGE/RAGE pathway,Activation of Matrix Metalloproteinases,Assembly of collagen fibrils and other multimeric structures, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with MMP13 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Extracellular matrix organization | BGNA,MGC174155,VCANB,COL15A1B,MMP20,KLK7,COL4A5,MMP12,MGC174152,LTBP2 |
| AGE/RAGE pathway | ATF2,CHUK,MAPK14,EGFR,TIRAP,AGER,LGALS3,DDOST,JAK2,DIAPH1 |
| Activation of Matrix Metalloproteinases | MMP15,MGC174857,TIMP2B,MGC174155,TIMP2A,LOC100686744,MGC174152,MMP17,FURINA,FURINB |
| Degradation of the extracellular matrix | COL13A1,CMA1,ADAMTS5,MMP24,EMID2,BMP1B,MGC174152,CTSL2,FURINA,COL19A1 |
| Collagen formation | DST,BMP1A,COL5A3A,PCOLCE2,COL10A1,ABHD1,COL5A2,COL9A1,COL4A3,COL19A1 |
| Assembly of collagen fibrils and other multimeric structures | COL2A1,LOX,CD151,ABHD1,COL4A5,CTSL1,COL3A1,BMP1B,COL6A2,COL6A1 |
| Collagen degradation | MGC174155,MMP20,COL19A1,COL23A1,ADAM10,ELANE,EMID2,LOC100686744,CTSLL,CTS7 |
| Endochondral Ossification | IFT88,RUNX2A,COL2A1,KIF3A,CST5,ADAMTS1,SOX5,COL10A1A,SOX9A,FRZB |
Protein Function
MMP13 has several biochemical functions, for example, calcium ion binding,calcium-dependent protein binding,collagen binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by MMP13 itself. We selected most functions MMP13 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with MMP13. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| metalloendopeptidase activity | ADAMTSL4,PAPPAB,UQCRC2B,PITRM1,MBTPS2,MIPEP,MMP11,ECE2,ADAM9,ADAMDEC1 |
| fibronectin binding | ITGA4,FSTL3,CTSK,ITGA3,IGFBP5,ITGAV,PLEKHA2,MYOC,SFRP2,ITGB3 |
| collagen binding | CCBE1,NID2,ITGA1,LUM,PCOLCE2,Pdgfa&Pdgfb,COMP,CTSS,ASPN,CTSK |
| calcium ion binding | FBN1,CETN2,MYO5A,PSPH,EFHC2,FBN2B,RPH3A,PCDH2AB2,PCDH2G10,SRI |
| low-density lipoprotein particle receptor binding | APOE,LRPAP1,LANCL1,CCDC167,APOA5,LDLRAP1,AP2M1,DNAJA1,LRP2,APOEA |
| zinc ion binding | ADAMTS3,CA15A,RNPEP,TCEA3,UBR1,TRIM35-19,ZRANB1,UBR7,RNF144A,TK1 |
| calcium-dependent protein binding | TSG101,MYO5A,C9orf9,S100P,STX2,TNNT3,KOP,SLC9A1,CASQ2,STX1A |
Interacting Protein
MMP13 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with MMP13 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of MMP13.
Resources
Gene Families
Research Area
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Ma, J; Zhou, D; et al. Keratocytes Create Stromal Spaces to Promote Corneal Neovascularization Via MMP13 Expression. INVESTIGATIVE OPHTHALMOLOGY & VISUAL SCIENCE 55:-(2014).
- Jackson, MT; Moradi, B; et al. Activation of Matrix Metalloproteinases 2, 9, and 13 by Activated Protein C in Human Osteoarthritic Cartilage Chondrocytes. ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATOLOGY 66:1525-1536(2014).



