MYD88
-
Official Full Name
myeloid differentiation primary response 88 -
Overview
This gene encodes a cytosolic adapter protein that plays a central role in the innate and adaptive immune response. This protein functions as an essential signal transducer in the interleukin-1 and Toll-like receptor signaling pathways. These pathways regulate that activation of numerous proinflammatory genes. The encoded protein consists of an N-terminal death domain and a C-terminal Toll-interleukin1 receptor domain. Patients with defects in this gene have an increased susceptibility to pyogenic bacterial infections. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2010] -
Synonyms
MYD88;myeloid differentiation primary response 88;MYD88D;myeloid differentiation primary response protein MyD88;myeloid differentiation primary response gene (88)
Recombinant Proteins
- Mouse
- Zebrafish
- Human
- Rat
- Chicken
- Rhesus macaque
- Mammalian Cells
- E.coli
- Wheat Germ
- HEK293
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- His
- Non
- GST
- DDK
- Myc
- Avi
- Fc
- Flag
Background
What is MYD88 protein?
MYD88 gene (MYD88 innate immune signal transduction adaptor) is a protein coding gene which situated on the short arm of chromosome 3 at locus 3p22. This gene encodes a cytosolic adapter protein that plays a central role in the innate and adaptive immune response. This protein functions as an essential signal transducer in the interleukin-1 and Toll-like receptor signaling pathways. These pathways regulate that activation of numerous proinflammatory genes. The encoded protein consists of an N-terminal death domain and a C-terminal Toll-interleukin1 receptor domain. The MYD88 protein is consisted of 296 amino acids and MYD88 molecular weight is approximately 33.2 kDa.
What is the function of MYD88 protein?
The MYD88 protein is a vital adaptor molecule in the immune system, primarily involved in the signaling pathways of Toll-like receptors (TLRs) and interleukin-1 receptors (IL-1Rs). It plays a crucial role in mediating inflammatory responses to pathogens by relaying signals that activate transcription factors like nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) and various mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs), leading to the production of proinflammatory cytokines.
MYD88 related signaling pathway
The MYD88-related signaling pathway is a critical component of the innate immune response, playing a central role in mediating signaling downstream of Toll-like receptors (TLRs) and IL-1 receptor (IL-1R). Upon activation by microbial ligands or cytokines, MYD88 facilitates the recruitment and activation of downstream kinases such as IRAK, leading to the activation of NF-κB and MAPK pathways. This results in the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines, which are essential for host defense against infections. Dysregulation of this pathway is implicated in various inflammatory diseases and certain types of cancer.
MYD88 related diseases
MYD88-related diseases encompass a range of conditions primarily driven by dysregulation of the innate immune response. Central to these diseases is the overactivation of the MYD88 signaling pathway, which plays a crucial role in mediating inflammation through Toll-like receptors (TLRs) and IL-1 receptor (IL-1R). This leads to an excessive and prolonged inflammatory response that can result in autoimmune disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn's disease, and lupus. Additionally, mutations in MYD88 are associated with an increased risk of certain malignancies, including lymphomas and leukemias. Therapeutic strategies targeting MYD88 or its downstream pathways are being actively pursued to manage these conditions effectively.
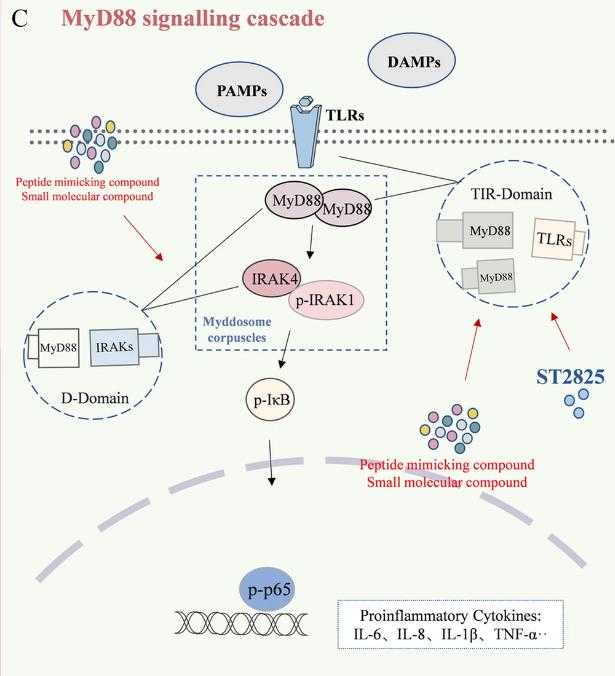
Fig1. The TLR/MyD88/NF-κB signalling pathway and target regions for designing MyD88 inhibitors. (Meiqi Liu, 2023)
Bioapplications of MYD88
The MYD88 protein is a central adapter molecule in the immune system's signaling pathways, primarily involved in the cascade of events initiated by Toll-like receptors (TLRs) and interleukin-1 receptors (IL-1Rs). It coordinates the innate immune response and helps establish the adaptive immune response. By activating various signaling pathways such as nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) and activator protein-1 (AP-1), MYD88 promotes the production of immune and inflammatory mediators. In the context of bioapplications, MYD88 is a promising therapeutic target for diseases like neuroinflammation, acute liver/kidney injury, autoimmune diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus, and B-cell lymphoma with the MyD88 L265P mutation. The development of specific inhibitors like ST2825 suggests potential therapeutic value in modulating host immune regulation for inflammatory diseases and therapies.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Yaxing Liu, 2024
The Myddosome, a complex involved in relaying inflammatory signals from Toll-like receptors (TLRs) and interleukin-1 receptors (IL-1Rs), is composed of MyD88 and IRAK kinases. Although the assembly and signaling regulation of Myddosome proteins are not well understood, this research has found that OTUD5 is crucial for MyD88 oligomerization and Myddosome formation. OTUD5 interacts with MyD88, cleaving specific polyubiquitin chains that enhance oligomerization following LPS stimulation, leading to Myddosome formation and the initiation of NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways, which produce inflammatory cytokines. Mice lacking OTUD5 show reduced sensitivity to sepsis from LPS and CLP. These findings highlight OTUD5's role in MyD88 oligomerization and suggest potential for treating inflammatory diseases.
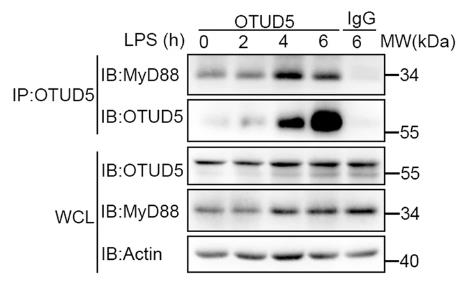
Fig1. WT PMs were stimulated with LPS (100 ng/mL) for various times to detect the endogenous interaction between OTUD5 and MyD88.
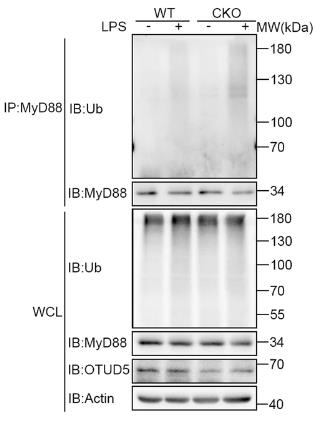
Fig2. Co-IP analysis of endogenous MyD88 ubiquitination.
Case Study 2: Qiu-yan Zhang, 2021
Recent studies suggest that TLR-mediated chronic inflammation plays a role in diabetic nephropathy. MyD88, a key adapter protein in TLR signaling, could be a potential therapeutic target for this condition. Using a novel MyD88 inhibitor, LM8, researchers investigated its protective effects on kidney inflammation in diabetes. Here MyD88 was activated in the kidneys of type 1 diabetic mice and in high glucose-treated tubular epithelial cells. LM8 or MyD88 siRNA treatment reduced high glucose-induced inflammation and fibrosis by inhibiting MyD88-TLR4 interaction and NF-κB activation. LM8 also decreased renal inflammation and fibrosis, and preserved kidney function in both type 1 and type 2 diabetic mice by limiting MyD88-TLR4 complex formation and inflammatory factor expression. These findings indicate that MyD88 inhibition with LM8 may be a therapeutic strategy for diabetic nephropathy.
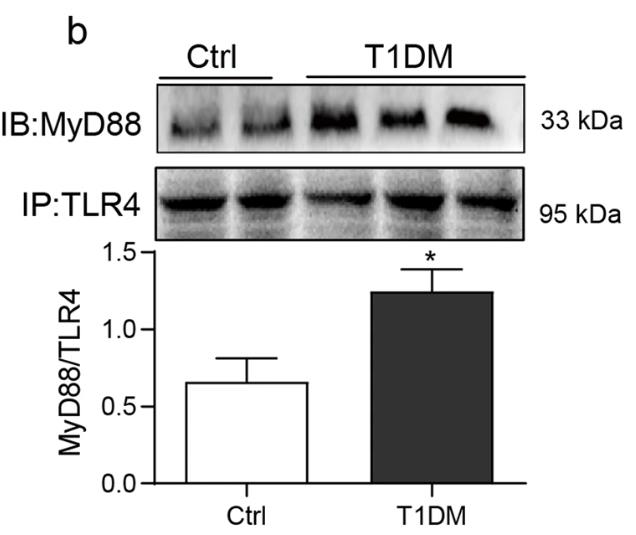
Fig3. Immunoblotting showing MyD88 and TLR4 complex formation in kidney samples from diabetic mice.
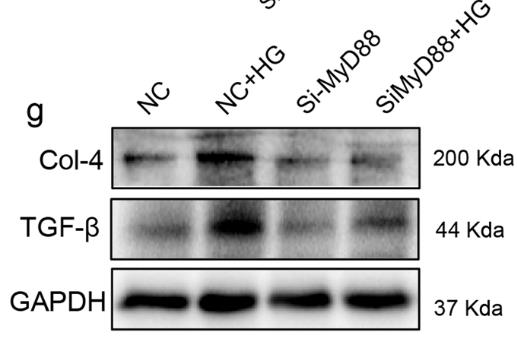
Fig4. NRK-52E cells with MyD88 siRNA were exposed to HG for 24 h.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (MYD88-5796H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (MYD88-687HFL)
Involved Pathway
MYD88 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways MYD88 participated on our site, such as NF-kappa B signaling pathway,Apoptosis,Toll-like receptor signaling pathway, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with MYD88 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Pertussis | IL1B,CASP1,C1QA,C1QC,MAPK1,IRF8,ITGB2,ITGB1,MAPK8,Il23a; Il12b |
| Measles | NFKB1,IKBKE,HSPA2,NFKBIB,NFKBIA,CBLB,TNFRSF10B,IFNA2,IFNA6,IL13 |
| Influenza A | IFNA10,PIK3CA,HSPA8,HLA-DRB1,OAS1A,TBK1,CXCL10,Ifna11,IRF3,PLG |
| Malaria | TNF,HBA1,Ccl12,THBS3,LRP1,THBS1,KLRB1,HBB,KLRK1,KLRC4-KLRK1 |
| Legionellosis | NFKB2,IL1B,SAR1A,CXCL1,TNF,HSPA6,IL12A,CXCL3,C3,CD14 |
| Toxoplasmosis | HLA-DRB4,IKBKB,NOS2,CYCS,BCL2L1,HSPA2,HLA-DQA2,MAP2K6,GNAI2,HLA-DOB |
| Leishmaniasis | FCGR2A,MAP3K7,TGFB3,TLR2,ITGB2,HLA-DPA1,Itgam&Itgb2,HLA-DMA,TNF,IL1A |
| African trypanosomiasis | IL1B,FAS,F2RL1,APOL1,FASLG,IL1B2,IL6,HBB-B1,HBB-B2,PRKCA |
| Toll-like receptor signaling pathway | TNF,NFKBIAB,MAP3K7,LY96,IFNAR1,IFNA13,RIPK1L,IFNA14,IL-8,IL6 |
Protein Function
MYD88 has several biochemical functions, for example, TIR domain binding,death receptor binding,identical protein binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by MYD88 itself. We selected most functions MYD88 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with MYD88. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| identical protein binding | ADIPOR1,PAICS,ITGB3,ATXN3,PVRL2,RUNX1T1,MICALL1,IFI203,ZNHIT6,CD247 |
| death receptor binding | RIPK1,TNFSF15,FEM1B,CASP8,BID,CFLAR,NOL3,PRDM4,Fasl,TMBIM1 |
| protein binding | ITGB1BP2,TAF7L,PYROXD1,HSP90AB1,IL15,GAS6,BNIP3L,SIL1,CD58,APAF1 |
Interacting Protein
MYD88 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with MYD88 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of MYD88.
TIRAP;SPOP;TNFRSF13B
Resources
Research Area
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Maeda, A; Bandow, K; et al. Induction of CXCL2 and CCL2 by pressure force requires IL-1 beta-MyD88 axis in osteoblasts. BONE 74:76-82(2015).
- Huang, HF; Zeng, Z; et al. Heme oxygenase-1 protects rat liver against warm ischemia/reperfusion injury via TLR2/TLR4-triggered signaling pathways. WORLD JOURNAL OF GASTROENTEROLOGY 21:2937-2948(2015).



