Active Recombinant Chicken IFNA
| Cat.No. : | IFNA-1127C |
| Product Overview : | Recombinant Chicken IFNA was expressed in E.coli . |
| Availability | January 14, 2026 |
| Unit | |
| Price | |
| Qty |
- Specification
- Gene Information
- Related Products
- Citation
- Download
| Species : | Chicken |
| Source : | E.coli |
| Tag : | Non |
| Description : | Chicken interferon alpha (IFN alpha) shares structural and biological properties with mammalian IFN1. Recombinant chicken IFN alpha (rChIFNa) has been shown to act as a highly potent anti-viral agent in vitro. rChIFNa also resulted in a noticeable delay in the progression of tumours in CC progressor chickens infected with Rous Sarcoma Virus, when admimistered intravenously. PAP004 is the immunogen used to produce the AbD Serotec chicken IFN alpha antibody. |
| Molecular Mass : | 19kD |
| Purity : | >85% by Ni chelate chromatography |
| Activity : | 1x107units/mg |
| BufferSolution : | 0.05M Sodium Acetate; 1M Sodium Chloride; 2M Urea; 10mM Beta-Mercaptoethanol |
| Storage : | Store at -20oC only. Storage in frost-free freezers is not recommended. Avoid repeated freezing and thawing as this may denature the protein. This product should be stored undiluted. Should this product contain a precipitate we recommend microcentrifugation before use. |
| Shelf Life : | 3 months from date of despatch. |
| OfficialSymbol : | IFNA3 |
| Publications : |
| Gene Name | IFNA3 interferon [ Gallus gallus ] |
| Synonyms | IFNA; IFNA1; IFNA2; IFNA6; IFN-alpha; IFN-gamma; interferon type A1/A2; IFN alpha; interferon alpha; interferon type A3 |
| Gene ID | 396398 |
| mRNA Refseq | NM_205427 |
| Protein Refseq | NP_990758 |
| UniProt ID | P42165 |
| Chromosome Location | Z |
| Pathway | Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction; Cytosolic DNA-sensing pathway; Herpes simplex infection |
| Function | cytokine activity; cytokine receptor binding |
| ◆ Recombinant Proteins | ||
| IFNa-1262S | Recombinant Sheep IFNa protein, His-tagged | +Inquiry |
| NCALD-727C | Recombinant Cynomolgus NCALD Protein, His-tagged | +Inquiry |
| IFNA-1127C | Active Recombinant Chicken IFNA | +Inquiry |
| NCALD-252H | Recombinant Human NCALD Protein, His-tagged | +Inquiry |
| NCALD-6238H | Recombinant Human NCALD Protein, Myc/DDK-tagged, C13 and N15-labeled | +Inquiry |
| ◆ Cell & Tissue Lysates | ||
| NCALD-3955HCL | Recombinant Human NCALD 293 Cell Lysate | +Inquiry |
Interferon Alpha Induces Multiple Cellular Proteins That Coordinately Suppress Hepadnaviral Covalently Closed Circular DNA Transcription
Journal: Journal of Virology PubMed ID: 32581092 Data: 2020/9/1
Authors: Junjun Cheng, Qiong Zhao, Ju-Tao Guo
Article Snippet:The human PML single guide RNA (sgRNA) CRISPR lentivector set (catalog no. K1673401) and STAT1 sgRNA CRISPR lentivector set (catalog no. K0002501) were purchased from Applied Biological Materials, Inc. Lenti-X packaging single shots (vesicular stomatitis virus G protein [VSV-G]) were from Clontech Laboratories, Inc. All primers and siRNAs were ordered from Integrated DNA Technologies, Inc.guide RNA (sgRNA) CRISPR lentivector set (catalog no. K1673401) and STAT1 sgRNA CRISPR lentivector set (catalog no. K0002501) were purchased from Applied Biological Materials, Inc. Lenti-X packaging single shots (vesicular stomatitis virus G protein [VSV-G]) were from Clontech Laboratories, Inc. All primers and siRNAs were ordered from Integrated DNA Technologies, Inc. ... Goat anti-mouse IgG (A-11001) and goat anti-rabbit IgG (A-11012) cross-adsorbed secondary antibodies were from Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc. Recombinant chicken IFN-α was purchased from Creative BioMart (catalog no. IFNA-1127C).. Human IFN-α-2b was purchased from BPS Bioscience Inc. Human IFN-α14 was purchased from PBL Assay Science Inc.Human IFN-α-2b was purchased from BPS Bioscience Inc. Human IFN-α14 was purchased from PBL Assay Science Inc.
![Recombinant chicken IFN-α inhibits DHBV cccDNA transcription in a dose-dependent manner. (A) A schematic presentation of experimental schedule. Briefly, dstet5 cells were cultured in the absence of tetracycline (tet) for 3 days and tet (1 μg/ml) was then added back into culture medium to stop pgRNA transcription from the transgene. The cells were cultured for more than 2 weeks to generate the cells in which viral DNA replication was solely supported by cccDNA; these cells were designated dstet5-CCC cells. To investigate the effects and mechanism of IFN-α on cccDNA transcription, dstet5-CCC cells were treated with 0, 0.3, 0.6, 1.25, 2.5, 5, and 10 ng/ml of recombinant chicken interferon-alpha (rChIFN-α) for 2 days and then harvested for analyses of DHBV cccDNA, mRNAs, and preC mRNA. (B) Hirt DNA was extracted and resolved by agarose gel electrophoresis. DHBV DNA was determined by Southern blot hybridization with an [α-32P]UTP-labeled full-length positive-sense RNA probe. mtDNA served as a loading control. The intensities of cccDNA and mtDNA bands in different treatment conditions were quantified by ImageJ. The amounts of cccDNA were normalized to mtDNA and are presented as relative amount in comparison with that in the mock-treated (NT) cells (lower portion). (C) Hirt DNA without prior treatment or restricted with EcoRI after denaturalization at 88°C for 8 min was resolved by agarose gel electrophoresis. DHBV DNA was determined by Southern blot hybridization with an [α-32P]UTP-labeled full-length positive-sense RNA probe. Dp-rc, deproteinized relaxed circular DNA; DP-dsl, deproteinized double-stranded linear DNA; cccDNA, covalently closed circular DNA; mtDNA, mitochondrial DNA. (D) DHBV RNAs were determined by Northern blot hybridization with an [α-32P]UTP-labeled full-length negative-sense RNA probe. rRNAs served as loading controls (upper portion). The intensities of DHBV RNA bands under different treatment conditions were quantified by ImageJ and normalized to rRNAs and are presented as relative amount in comparison with that in the mock-treated cells (lower portion). preC/pgRNA specifying both preC mRNA and pgRNA and 2.1- and 2.4-kb mRNA specifying small and large envelope protein are indicated. 28S and 18S rRNAs served as loading controls. (E) DHBV preC mRNA was determined by qRT-PCR assay. The level of preC mRNA was normalized to β-actin mRNA and is expressed as a fraction of that in the mock-treated cells. Means ± standard deviations are presented (n = 6 from three independent experiments).](productimages/extendimages/pmc07431811__JVI.00442-20-f0001.jpg)
Recombinant chicken
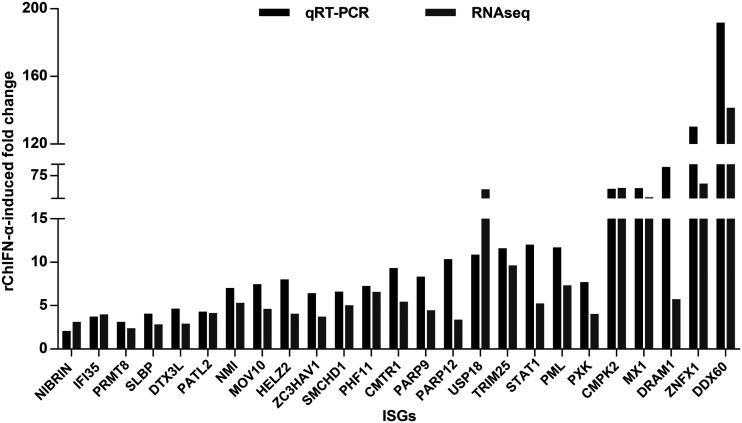
qRT-PCR and RNA-seq results consistently demonstrated the induction of selected ISGs by rChIFN-α. dstet5 cells were mock treated or treated with 10 ng/ml of rChIFN-α for 6 h. Total intracellular RNAs were then extracted for RNA-seq and qRT-PCR assays. The levels of ISG mRNA determined by qRT-PCR assay were normalized to β-actin mRNA and are expressed as the fold over that of the mock-treated control. The fold induction of ISGs by
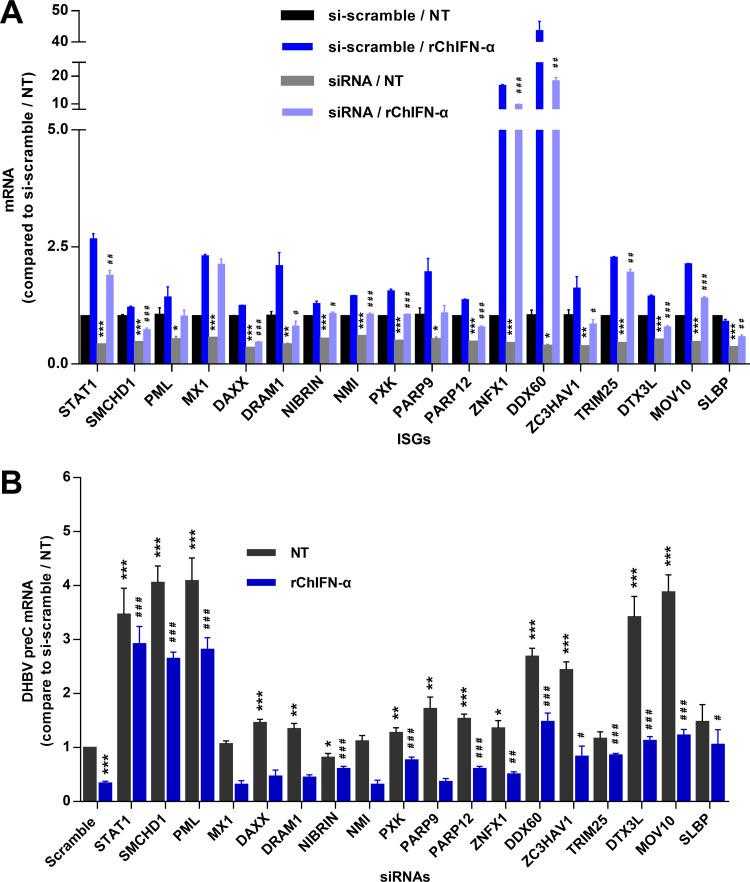
Identification of eight ISGs that may mediate
Not For Human Consumption!
Inquiry
- Reviews (0)
- Q&As (0)
Ask a Question for All IFNA Products
Required fields are marked with *
My Review for All IFNA Products
Required fields are marked with *



