Recombinant Human PAX7
| Cat.No. : | PAX7-29057TH |
| Product Overview : | Recombinant fragment of Human PAX7 with N terminal proprietary tag, 38.21kDa inclusive of tag. |
- Specification
- Gene Information
- Related Products
- Citation
- Download
| Species : | Human |
| Source : | Wheat Germ |
| Tag : | Non |
| Protein Length : | 111 amino acids |
| Description : | This gene is a member of the paired box (PAX) family of transcription factors. Members of this gene family typically contain a paired box domain, an octapeptide, and a paired-type homeodomain. These genes play critical roles during fetal development and cancer growth. The specific function of the paired box 7 gene is unknown but speculated to involve tumor suppression since fusion of this gene with a forkhead domain family member has been associated with alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma. Three transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. |
| Molecular Weight : | 38.210kDa inclusive of tags |
| Form : | Liquid |
| Purity : | Proprietary Purification |
| Storage buffer : | pH: 8.00Constituents:0.3% Glutathione, 0.79% Tris HCl |
| Storage : | Shipped on dry ice. Upon delivery aliquot and store at -80oC. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. |
| Sequences of amino acids : | GGLDSATSISASCSQRADSIKPGDSLPTSQAYCPPTYSTT GYSVDPVAGYQYGQYGQSECLVPWASPVPIPSPTPRASCL FMESYKVVSGWGMSISQMEKLKSSQMEQFT |
| Sequence Similarities : | Belongs to the paired homeobox family.Contains 1 homeobox DNA-binding domain.Contains 1 paired domain. |
| Gene Name | PAX7 paired box 7 [ Homo sapiens ] |
| Official Symbol | PAX7 |
| Synonyms | PAX7; paired box 7; paired box gene 7; paired box protein Pax-7; Hup1; |
| Gene ID | 5081 |
| mRNA Refseq | NM_001135254 |
| Protein Refseq | NP_001128726 |
| MIM | 167410 |
| Uniprot ID | P23759 |
| Chromosome Location | 1p36.13 |
| Pathway | Transcriptional misregulation in cancers, organism-specific biosystem; Transcriptional misregulation in cancers, conserved biosystem; |
| Function | sequence-specific DNA binding; sequence-specific DNA binding transcription factor activity; |
| ◆ Recombinant Proteins | ||
| PAX7-132H | Recombinant Human PAX7 protein, T7/His-tagged | +Inquiry |
| PAX7-4801H | Recombinant Human PAX7 Protein (Arg355-Gln467), N-His tagged | +Inquiry |
| PAX7-6622C | Recombinant Chicken PAX7 | +Inquiry |
| PAX7-29057TH | Recombinant Human PAX7 | +Inquiry |
| PAX7-6754H | Recombinant Human PAX7 protein, GST-tagged | +Inquiry |
| ◆ Cell & Tissue Lysates | ||
| PAX7-3414HCL | Recombinant Human PAX7 293 Cell Lysate | +Inquiry |
| PAX7-3413HCL | Recombinant Human PAX7 293 Cell Lysate | +Inquiry |
DNA aptamers against the DUX4 protein reveal novel therapeutic implications for FSHD
Journal: The FASEB Journal PubMed ID: 32020675 Data: 2020/2/5
Authors: Christian Klingler, Jon Ashley, Jochen Kinter
Article Snippet:Aptamers were compared against 5′‐Atto647N labeled aptamers as probes with sequences described in in Supplemental Table T1.Aptamers were compared against 5′‐Atto647N labeled aptamers as probes with sequences described in in Supplemental Table T1.. The labeled aptamers were incubated with 1 nM of either StrepII‐SUMO‐DUX4‐His6, 1 nM of PAX7‐His6 (Creative BioMart, Shirley US‐NA), or 15 nM of PROP1‐cMyc‐DDK(FLAG) (OriGene Technologies, Inc, Rockville, US‐MD) recombinant proteins and various concentrations of test aptamers (Microsynth, Balgach, Switzerland) in an assay buffer containing 50 mM of Tris‐HCl pH 7.5, 150 mM of NaCl, 5 mM of MgCl 2 , 0.1% of BSA, 0.1% of Triton X‐100, 1 mM of DTT, and 0.35 nM of MAb anti‐6His Terbium cryptate Gold antibody (cisbio, Codolet, France) in white 384 well microplates (Greiner Bio‐one, Kremsmünster, Austria) for 24 hours at 4°C.. Donor fluorescence (340 nm/620 nm) and acceptor fluorescence (340 nm/665 nm) was quantified on a TECAN Spark microplate reader with a lag time of 100 μs and integration time of 300 μs at 37°C.Donor fluorescence (340 nm/620 nm) and acceptor fluorescence (340 nm/665 nm) was quantified on a TECAN Spark microplate reader with a lag..
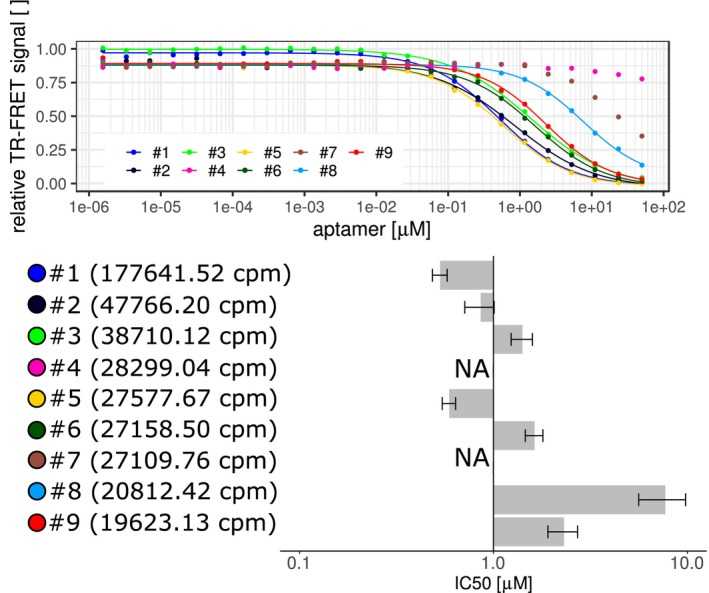
Testing the binding of SELEX‐originated aptamers. Comparing top nine list of SELEX generated aptamers in TR‐FRET assays. Aptamers were compared by competing against the 5′‐end Atto647N‐labeled template aptamer after incubation with
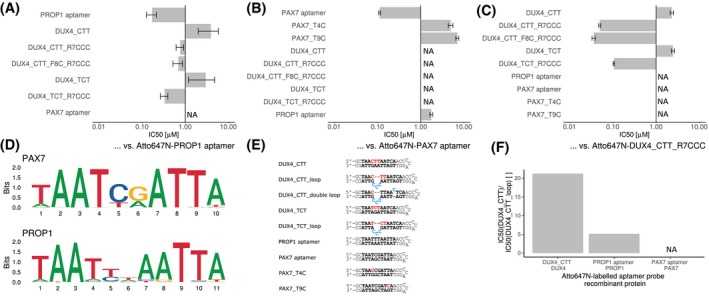
Specificity of DUX4 aptamers. A, Different aptamers were tested against the consensus PROP1 binding sequence inserted into the aptamer backbone by means of a TR‐FRET competition assays. Single experiment data is shown as IC50 values of various aptamers ± standard error of the data fitting to a four‐parameter logistic using R package “drc” (curves are provided in Supplemental Figures A‐C). B, TR‐FRET competition assay was performed to compare the binding of different aptamers to
Not For Human Consumption!
Inquiry
- Reviews (0)
- Q&As (0)
Ask a Question for All PAX7 Products
Required fields are marked with *
My Review for All PAX7 Products
Required fields are marked with *



