What is BMP4 Protein?
The Bone Morphogenetic Protein 4, commonly referred to as BMP4, is an influential protein in the TGF-beta superfamily. This protein family is characterized by their integral role in cell proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis. BMP4 specifically, is a critical regulator of embryological development and tissue homeostasis.
The Genesis and Structure of BMP4 Protein
The groundbreaking discovery of BMPs occurred in the 1960s, with BMP4 being identified later, in the late 1980s. Over the ensuing years, intensive research efforts have delineated the gene locus, protein structure, and functional operations of BMP4. The gene that encodes this protein in humans is situated on the short arm of chromosome 14, specifically at location 14q22-q23.
In its mature form, BMP4 is a disulphide-linked homodimeric protein characterized by a highly conserved cysteine knot-like structure indicative of the transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) superfamily. It is produced as a precursor protein, which undergoes proteolytic cleavage to release the functional element, the BMP4 protein. This cleavage process is facilitated by a specific type of enzymes known as proprotein convertases.
BMP4 Function and Signaling Pathway
Functionally, BMP4 is seminal in the patterning and morphogenesis during embryonic development. It is involved in the formation of multiple tissues and organs including the heart, eyes, teeth, limbs, and neural tube. Additionally, BMP4 plays a vital role in bone and cartilage development, thus, quite literally, helping shape the form of an individual.
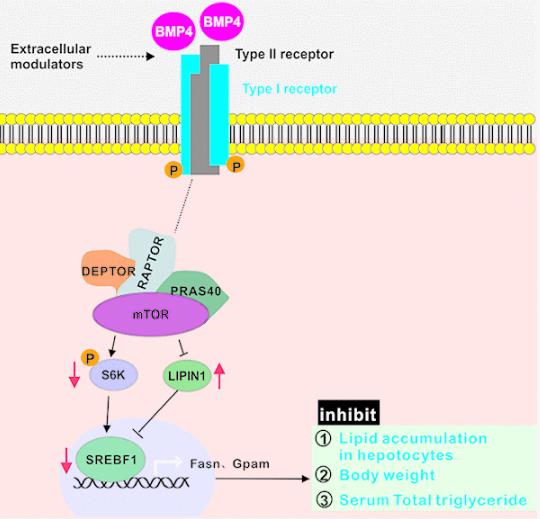
Fig1. BMP4 may suppress hepatic steatosis
The BMP4 signaling pathway cascades through the classic SMAD and non-SMAD pathways. Binding of the BMP4 ligand to its receptors BMPR1 and BMPR2 initiates the signaling transduction. This prompts the phosphorylation and activation of Receptor-SMAD (R-SMAD: SMAD1, SMAD5 & SMAD8), which then associates with SMAD4 to form a complex that translocates to the nucleus. Here, the complex regulates the transcription of BMP-responsive genes, in collaboration with other transcriptional co-activators or co-repressors. In the non-SMAD pathway, BMP4 interacts with pathways such as Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases (MAPK), PI3K/AKT, and small GTPases. These alternative pathways, although not yet fully understood, contribute to BMP4's multifaceted functionalities.
BMP4 in Disease Pathophysiology
Given its pivotal role in development, perturbations in BMP4 functions are implicated in several pathological conditions. Mutations in the BMP4 gene can lead to developmental disorders like eye anomalies, and severe craniofacial defects such as microphthalmia and anophthalmia. BMP4 is also implicated in osteoarthritis, where higher levels of the protein have been reported in synovial fluid of patients with the disease.
On the other hand, BMP4 has been found to contribute to cardiovascular diseases through endothelial damage and atherosclerosis. Recent studies have also linked BMP4 with cancer progression, EMT (epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition), and metastasis, making it a potential therapeutic target in the realm of oncology.
BMP4 in Biomedical Applications
Biomedically, BMP4 has a unique potential for therapeutic applications, particularly in regenerative medicine and tissue engineering. It is recognized for its osteoinductive capacities, hence it can be incorporated in bone graft substitutes to enhance bone healing and regeneration. Moreover, BMP4’s capability to induce pluripotent stem cells to differentiate into specific cell types makes it a vital tool in stem cell therapy.
In summary, the BMP4 protein, with its multifaceted roles, is a critical player in development and homeostasis. Its intricate signaling pathways and association with diverse diseases offer intriguing insights into the complex mechanisms driving health and disease. Furthermore, the promising potential of BMP4 in biomedical advancements accentuates its significance and calls for further research endeavors to fully comprehend this multifarious protein.
Our Featured Products
| Cat.No. | Product Name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BMP4-06H | Active Recombinant Human BMP4 | E.coli | N/A | |
| BMP4-01HG | Active GMP Recombinant Human BMP-4 Protein | CHO-K1 | ||
| BMP4-26171TH | Recombinant Human BMP4, His-tagged | E.coli | His | |
| BMP4-266H | Recombinant Human BMP4 Protein, GST-tagged | E.coli | GST | |
| BMP4-2600H | Recombinant Human BMP4 protein, His-SUMO-tagged | E.coli | His-SUMO | |
| BMP4-4364H | Recombinant Human BMP4 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | His (Fc)-Avi | |
| BMP4-402H | Recombinant Human BMP4 Protein | E.coli | Tag Free | |
| BMP4-279H | Active Recombinant Human BMP4 Protein (Lys303-Arg408), C-His tagged, Animal-free, Carrier-free | E.coli | C-His |
Reference
- Peng Q, Chen B, Wang H, Zhu Y, Wu J, Luo Y, Zuo G, Luo J, Zhou L, Shi Q, Weng Y, Huang A, He T, et al. Bone morphogenetic protein 4 (BMP4) alleviates hepatic steatosis by increasing hepatic lipid turnover and inhibiting the mTORC1 signaling axis in hepatocytes. Aging (Albany NY). 2019 Dec 12; 11:11520-11540 . https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.102552

