Principle and Protocol of Prokaryotic Expression and Detection
The prokaryotic expression system of protein is the most popular protein expression system at present. By constructing the obtained target gene into the prokaryotic expression vector, and then transforming it into highly expressed Escherichia coli, the target protein can be expressed in large quantities in the presence of the inducer isopropyl β-D-1-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG). The expression of the target protein can be detected by Coomassie brilliant blue staining or immunoblotting, so as to prepare for a large number of expanded cultures of bacteria and protein purification.
Master the basic principles and main steps of prokaryotic expression of the target protein, and master the basic steps and precautions of Coomassie brilliant blue staining and immunoblotting experiment.
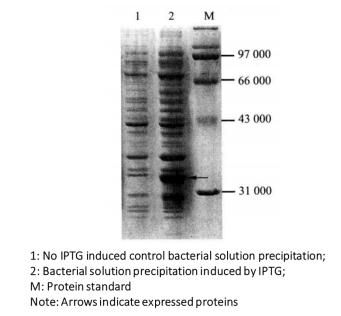 Figure 3-1-1 pGEX-KG Expression Vector
Figure 3-1-1 pGEX-KG Expression Vector
In this experiment, the plasmid constructed by pGEX-KG expression vector (Figure 3-1-1) is taken as an example for prokaryotic expression and detection of the target protein.
pGEX-KG contains an ampicillin resistance (Ampr) gene, a pBR322 replication starting point, a GST expression gene, and multiple restriction endonuclease polyclonal sites (MCS) for foreign gene insertion. Ptac is the promoter of GST fusion protein expression and is regulated by lac repressor protein, which is the expression product of lac I gene. Lac repressor proteins, such as BL21, are expressed at a high level and tightly bind to the control genes downstream of the promoter to prevent the initiation of transcription. In the presence of lactose analogues such as IPTG, they will change their conformation after binding with repressor proteins, resulting in reduced binding ability with the manipulation genes and dissociation, and the transcription factors of lac operators will be activated, so that GST fusion proteins can be expressed.
Objective Protein expression can be detected by Coomassie brilliant blue staining or Western blot. Coomassie Brilliant Blue R-250 is an amino triphenylmethane dye, which can be combined with proteins non-specifically. Western blotting is used to detect the expression of target protein through specific antibody antigen reaction.
1. Main Instruments and Equipment
Pipette, micro centrifuge, 1.5mL centrifuge tube, 50mL centrifuge tube, thermostatic water bath, ice maker, thermostatic shaker, ultra clean workbench, thermostatic incubator, shaker, oscillator, centrifuge, metal bath, petri dish, semi dry electric rotator, Kodak IS2000R image workstation.
2. Experimental Materials
Vector: pGEX-KG; E. coli strain: BL21; antibody: anti GST monoclonal or polyclonal antibody; Whatman 3 mm filter paper; PVDF membrane; 0.1 mol/L isopropyl β-D-1-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG); SDS; acrylamide; methylene acrylamide, etc.
3. Main Reagents
(1) LB liquid medium: containing 50 μg/mL ampicillin
(2) 12% SDS-PAGE gel
(3) Cathode buffer solution: 25 mmol/L Tris HCl, 40 mmol/L glycine, 10% (volume fraction) methanol (pH 9.4)
(4) Anode buffer I: 0 3mmol/L Tris HCl, 10% (volume fraction) methanol (pH10.4)
(5) Anode buffer II: 25 mmol/L Tris HCl, 10% (volume fraction) methanol (pH 10.4)
(6) TBST (Tris buffered saline Tween-20) buffer solution: add 0 1% (volume fraction) Tween - 20
(7) Closed buffer: 5% skimmed milk powder is added to TBST
(8) First antibody dilution buffer: TBST with 5% BSA
(9) Second antibody dilution buffer: TBST containing 5% skimmed milk powder
(10) LumiGLO mixture: 0 5mL 20 × LumiGLO, 0.5mL 20 × H2O2
(11) 6 × SDS loading buffer
| 300 mmol/L | Tris-HCl (pH 6.8) |
| 600 mmol/L | DTT |
| 12% | SDS |
| 60% (volume fraction) | Glycerol |
| 0.6% | Bromophenol Blue |
(12) Commassie Blue Staining Solution
| 0.25% | Coomassie brilliant blue R-250 |
| 45% (volume fraction) | Methanol |
| 45% (volume fraction) | Water |
| 100% (volume fraction) | Glacial acetic acid |
(13) Coomassie Brilliant Blue Decolorizing Solution
| 45% (volume fraction) | Methanol |
| 45% (volume fraction) | Water |
| 100% (volume fraction) | Glacial acetic acid |
(14) Tris-buffered saline, TBS
| 100 mmol/L | Tris-HCl (pH7.5) |
| 0.9% | NaCl |
1. Induced Expression of Target Protein
(1) The constructed prokaryotic expression plasmid was transformed into BL21 expression strain.
(2) Take a single colony, put it into 5mL LB culture solution containing ampicillin, and culture it overnight at 37°C.
(3) 50 μL overnight culture was inoculated into 5mL LB culture medium containing ampicillin, and cultured at 37°C for more than 2h by shaking until the metaphase of logarithm of bacterial growth (A600=0.5-0.6).
(4) Suck out 500 μL uninduced culture is placed in a microcentrifuge tube, treated according to the following steps (6) and (7), and 1mL of bacterial liquid is reserved for expanded culture*1.
(5) Add IPTG*2 to the remaining culture until the final concentration is 1mmol/L, and continue to ventilate at 20~37°C*3.
(6) At different times of induction, 500 μL of the sample was placed in a microcentrifuge tube and centrifuged at high speed for 1 min at room temperature.
(7) Sediment suspended at 100 μL 1 × SDS gel was added with sample buffer solution, heated at 100°C for 5min, centrifuged at room temperature for 1min at high speed, placed on ice, and all samples were processed before loading.
(8) SDS-PAGE*4 electrophoresis.
(9) Coomassie brilliant blue staining or immunoblotting were used to observe the product bands.
2. Detection of Protein Expression by Coomassie Brilliant Blue Staining
(1) Soak the gel in Coomassie brilliant blue staining solution, place it on a gently shaking table, and dye it at room temperature for more than 4h.
(2) Remove the dye solution, soak the gel in the decolorizing solution, decolorize it on the shaker for 4h, and replace the decolorizing solution several times during this period.
() After decolorization, the gel is stored in water and the image is scanned on the scanner.
(3) The expression of the target protein is judged according to the changes of the bands on the gel and the relative molecular weight of the expressed protein (Figure 3-1-2).
 Figure 3-1-2 Detection of Induced Expression of GST Fusion Protein by Coomassie Brilliant Blue Staining
Figure 3-1-2 Detection of Induced Expression of GST Fusion Protein by Coomassie Brilliant Blue Staining
3. Detection of Protein Expression by Western Blot
(1) After SDS-PAGE electrophoresis is completed, remove the concentrated gel, repair the separating gel with a rubber ruler, and make position indication marks.
(2) Put the gel in the cathode buffer solution to balance for 15min.
(3) Cut six Whatman 3mm filter papers and one PVDF film with the same size as the gel, and mark one corner of the film with a soft pencil*5.
(4) Add two Whatman 3mm filter papers to the anode buffer I. Add a Whatman 3mm filter paper to the anode buffer II. Add 3 Whatman 3mm filter papers to the cathode buffer solution.
(5) The PVDF membrane is soaked in methanol until translucent, and then transferred to aqueous solution for 2min. Put it into anode buffer solution II for at least 5min.
(6) Clean the cathode and anode plate with distilled water and keep them wet.
(7) On the bottom graphite electrode (anode) of the electro rotator, cover two Whatman 3mm filter papers soaked in anode buffer I, one Whatman 3mm filter paper soaked in anode buffer II, PVDF film, gel and three Whatman 3mm filter papers*6 soaked in cathode buffer (Figure 3-1-3).
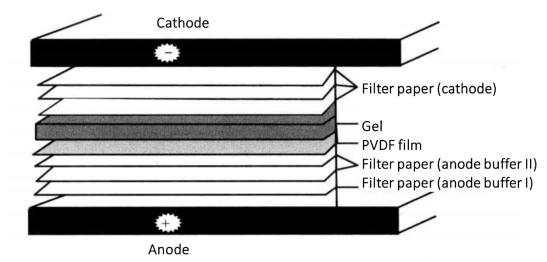 Figure 3-1-3 Schematic Diagram of Protein Transfer
Figure 3-1-3 Schematic Diagram of Protein Transfer
(8) Install the upper electrode of the electric rotator, namely the cathode, switch on the power supply and rotate the film. The film turning current (mA) is 2-3 times of the film area (cm2), and the film turning time is 45min-1h.
(9) After the transfer, remove the filter paper with tweezers. The transferred gel was dyed in Coomassie brilliant blue to determine whether the transfer was complete.
(10) Clamp a corner of PVDF film with tweezers, put it into 25mL sealing buffer solution*7, and wash it with shaking table at room temperature for 1h.
(11) Wash with 15mL TBST for three times, shake the shaking table for washing, 5min /time.
(12) Dilute the first antibody to a suitable concentration with the first antibody dilution buffer, incubate it with the membrane at 4°C and shake it gently overnight.
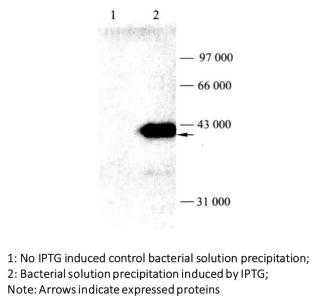 Figure 3-1-4 Detection of Induced Expression of GST Fusion Protein by Western Blot
Figure 3-1-4 Detection of Induced Expression of GST Fusion Protein by Western Blot
(13) Wash with 15m LTBST for 3 times, 5min / time.
(14) Dilute the secondary antibody (anti rat or anti rabbit IgG coupled with horseradish peroxidase) to an appropriate concentration with the dilution buffer of the secondary antibody, and incubate it with the membrane at room temperature for 1h*8.
(15) Wash with 15m LTBST for 3 times, 5min / time.
(16) Press the PVDF membrane dry with filter paper to prepare LumiGLO mixture, and drop the mixture evenly on the PVDF membrane.
(17) Chemiluminescence detection is performed on Kodak IS2000R image workstation.
(18) Analyze the obtained band results and determine the expression of the target protein (Figure 3-1-4)
1. Factors to be considered for inducing protein expression in prokaryotic cells
The growth rate of cells affects the expression of foreign proteins, so it is necessary to optimize the state of bacterial growth before induction, the concentration of IPTG induction, the induction temperature and the induction time. Too fast growth of Escherichia coli and excessive expression of foreign proteins tend to lead to the formation of inclusion bodies, which is not conducive to the purification of proteins.
2. Detection of induced expression of target protein
In general, the protein expression can be determined by coomassie brilliant blue staining; If you want to further determine the expression of the target protein, use Western blot to detect it.
3. Precautions for immunoblotting
(1) Do not touch the film directly with your hands, and do not use tooth tweezers to clamp the film. The container containing the film shall be cleaned with detergent, and then washed with ethanol and double distilled water once respectively before use.
(2) The volume of various solutions incubated with the membrane must be enough to cover the membrane, and placed on a shaker for mild seeding; The volume of each washing solution must be sufficient.
(3) The signal of result is too strong, scattered or uneven, with stains.
The possible reason is that the antibody concentration is too high, which will lead to too strong signal. It is recommended to reduce the amount of antibody; If there are problems with gel, such as improper gel concentration and transfer conditions, the protein bands and signals can be dispersed; Bubbles left between the membrane, gel and filter paper can cause uneven transfer, strip dispersion and reduced transfer efficiency; Membrane quality problems such as membrane hydrophilicity and uneven density will lead to uneven imprinting.
(4) The background is too high.
The possible reason is that the non-specific binding site is not completely blocked. It is recommended to replace the sealing solution or extend the sealing time.
If the concentration of the first and second antibodies is too high, the background will be too high. It is recommended to reduce the concentration of the first and second antibodies.
It should be noted that the sensitivity of the chemiluminescence method is higher than that of the chemical color method, so the required antibody concentration is lower than that of the chemical color method.
Inadequate washing each time will also lead to high background. Increase the washing times or Tween-20 concentration to extend the washing time.
Equipment such as containers and plastic wrap are polluted, and it is recommended to clean or replace them.
Improper membrane selection and use. Select high-quality membrane to keep the membrane clean. When washing, the solution should saturate the entire membrane. Do not use the membrane with nodes or damage. Do not hold the membrane with hands or toothed tweezers. It is recommended to shorten the exposure time because of overexposure.
(5) No signal or weak signal
The possible reason is that the protein has not been transferred to the membrane or has been transferred excessively. It is recommended to check the amount of protein on the gel before and after the transfer, and then determine the experimental conditions for transferring protein, such as changing the gel concentration, changing the transfer time, changing the pH of the transfer buffer and the concentration of the components. If the second antibody is contaminated by bacteria and HRP fails, replace the second antibody. The first antibody problem is that the first antibody cannot recognize the denatured or reduced protein, which can be identified by the dot blot parallel detection of denatured or reduced protein and natural protein method. If the first antibody cannot recognize the denatured or reduced protein, try the non-denatured gel system. The affinity of the first antibody is low and the incubation time is prolonged. Reduce the concentration of Tween-20, shorten the washing time and extend the exposure time.
*1 The purpose of expanded culture is to collect a large number of bacteria for protein purification.
*2 In the experiment, the concentration of IPTG should be changed within the range of 0.01-5mmol/L. In general, 1mmol/L concentration is used for the first induction.
*3 A major factor affecting the expression of E. coli is temperature. The growth rate of Escherichia coli at room temperature is four times slower than that at 37°C, but the metabolism of bacteria is slow at low temperature, and it is not easy to form inclusion bodies.
*4 The concentration of gel is determined according to the size of the target protein.
*5 When touching the glue, membrane or filter paper with your hands, you should wear gloves because the oil and secretion on the skin will affect the transfer of protein from the glue to the membrane.
*6 The mark on the membrane corresponds to the mark on the gel to eliminate all bubbles.
*7 Antibodies can bind to the membrane just like proteins in electrotransfer. Therefore, the sensitivity of Western Blotting depends on the blocking of potential binding sites of some unrelated proteins. Generally, it is better to use skimmed milk powder or serum albumin. If the non-specific background is still very high, Tween-20 can be added to the blocking solution to make its final concentration 0.02%. Generally, the existence of Tween-20 does not affect the binding of antibody and target antigen.
*8 While washing the membrane, dilute HRP second antibody, biotin labeled second antibody or HRP chain avidin into the sealing solution according to the proportion recommended by the manufacturer. Transfer the membrane to a solution containing the second antibody. Incubate at room temperature under shaking table for 1h or overnight at 4°C.

