BID
-
Official Full Name
BH3 interacting domain death agonist -
Overview
This gene encodes a death agonist that heterodimerizes with either agonist BAX or antagonist BCL2. The encoded protein is a member of the BCL-2 family of cell death regulators. It is a mediator of mitochondrial damage induced by caspase-8 (CASP8); CASP8 cleaves this encoded protein, and the COOH-terminal part translocates to mitochondria where it triggers cytochrome c release. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found, but the full-length nature of some variants has not been defined. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] -
Synonyms
BID;BH3 interacting domain death agonist;FP497;BH3-interacting domain death agonist;p22 BID;BID isoform Si6;BID isoform L(2);BID isoform ES(1b);desmocollin type 4;apoptic death agonist;Human BID coding sequence
Recombinant Proteins
- Mouse
- Human
- Chicken
- Rat
- E.coli
- Sf9 Cells
- Wheat Germ
- Mammalian Cells
- HEK293
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- GST
- His
- Non
- T7
- Avi
- Fc
- DDK
- Myc
- SUMO
Background
What is BID protein?
BID (BH3 interacting domain death agonist) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 22 at locus 22q11. This gene encodes a death agonist that heterodimerizes with either agonist BAX or antagonist BCL2, and thus regulate apoptosis. The encoded protein is a member of the BCL-2 family of cell death regulators. It is a mediator of mitochondrial damage induced by caspase-8 (CASP8); CASP8 cleaves this encoded protein, and the COOH-terminal part translocates to mitochondria where it triggers cytochrome c release. The BID protein is consisted of 195 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 22.0 kDa.
What is the function of BID protein?
In the cell, BID protein is mainly located in the outer membrane of mitochondria, and through its special domain interaction with other proteins, it mediates the apoptosis of the mitochondrial pathway. Specifically, BID protein can promote the opening of permeability transition pores between the inner and outer membranes of mitochondria, leading to events such as mitochondrial membrane potential decline, cytochrome C release, and cysteine protease activation, ultimately leading to apoptosis. In addition, the BID protein also regulates biological functions such as cell cycle progression and DNA repair.
BID Related Signaling Pathway
BID protein is a key factor of apoptosis (programmed cell death), mainly involved in the regulation of apoptosis in the mitochondrial pathway. In response to external stimuli, such as growth factor removal or DNA damage, BID can be activated by the cleavage of proteases such as caspase-8. Activated tBID (truncated BID) will transfer to the mitochondrial outer membrane, promote the oligomerization and insertion of pro-apoptotic Bcl-2 family members such as Bax and Bak into the mitochondrial outer membrane, thereby increasing the permeability of mitochondrial membrane and releasing apoptosis efflux molecules such as cytochrome c into the cytoplasm. Further activation of the downstream executor of the caspase family leads to apoptosis. In addition, BID can also affect other signaling pathways through non-classical mechanisms, including endoplasmic reticulum stress response, autophagy, and inflammatory response, but its main role is still mitochondria-related apoptotic pathways.
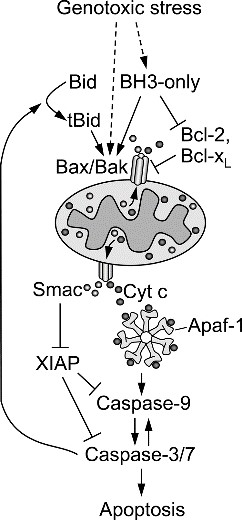
Fig1. Hypothetical scheme of etoposide-induced apoptosis. (Shary N Shelton, 2009)
BID Related Diseases
BID protein is mainly involved in apoptosis, cell cycle regulation, inflammatory response and tumorigenesis. BID protein-related diseases include but are not limited to: neurodegenerative diseases (such as Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease), cardiovascular diseases (such as myocardial infarction, heart failure), inflammatory diseases (such as rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease), tumors (such as breast cancer, lung cancer), etc.
Bioapplications of BID
Because of its role in the apoptosis pathway, the BID protein is considered a potential cancer therapeutic target. Researchers are exploring how to regulate the activity or expression of BID to promote apoptosis of cancer cells, thereby providing new strategies for cancer treatment.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Jordi Bertran-Alamillo, 2023
Drugs targeting the spindle assembly checkpoint (SAC), such as inhibitors of Aurora kinase B (AURKB) and dual specific protein kinase TTK, are in different stages of clinical development. However, cell response to SAC abrogation is poorly understood and there are no markers for patient selection.
The effects of drugs were analyzed by MTT and flow cytometry. Copy number status was determined by FISH and Q-PCR; mRNA expression by nCounter and RT-Q-PCR and protein expression by Western blotting. CRISPR-Cas9 technology was used for gene knock-out (KO) and a doxycycline-inducible pTRIPZ vector for ectopic expression. Tumor cells and patient-derived xenografts (PDXs) sensitive to AURKB and TTK inhibitors consistently showed high expression levels of BH3-interacting domain death agonist (BID), while cell lines and PDXs with low BID were uniformly resistant. Gene silencing rendered BID-overexpressing cells insensitive to SAC abrogation while ectopic BID expression in BID-low cells significantly increased sensitivity. A prevalence study revealed high BID mRNA in 6% of human solid tumors.
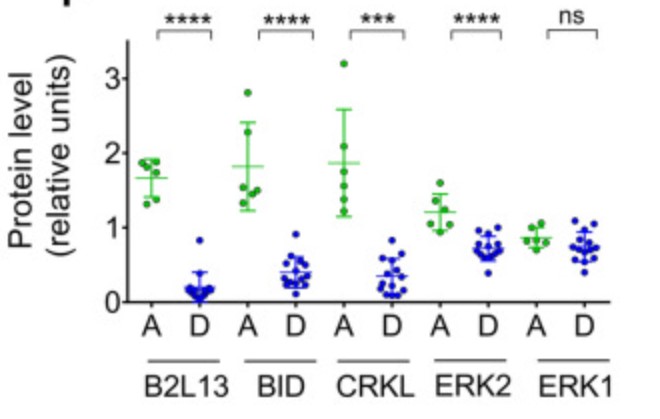
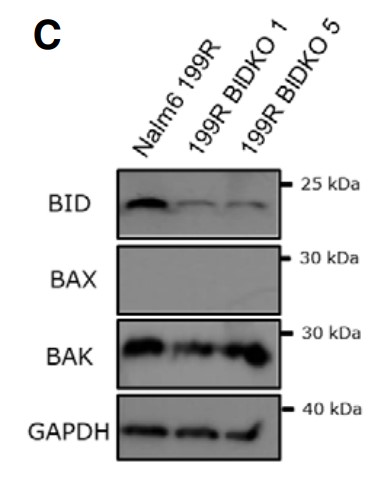
Fig1. Levels of four Chr22q11-codified proteins (B2L13, BID, CRKL and Erk1) in PC9 and 11-18 derived clones.
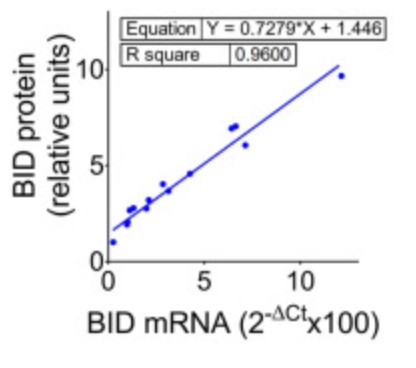
Case Study 2: Luciana R Muniz-Bongers, 2021
During apoptosis, the BCL-2-family protein tBID promotes mitochondrial permeabilization by activating BAX and BAK and by blocking anti-apoptotic BCL-2 members. Here, the researchers report that tBID can also mediate mitochondrial permeabilization by itself, resulting in release of cytochrome c and mitochondrial DNA, caspase activation and apoptosis even in absence of BAX and BAK. This previously unrecognized activity of tBID depends on helix 6, homologous to the pore-forming regions of BAX and BAK, and can be blocked by pro-survival BCL-2 proteins. Importantly, tBID-mediated mitochondrial permeabilization independent of BAX and BAK is physiologically relevant for SMAC release in the immune response against Shigella infection. Furthermore, it can be exploited to kill leukaemia cells with acquired venetoclax resistance due to lack of active BAX and BAK. These findings define tBID as an effector of mitochondrial permeabilization in apoptosis and provide a new paradigm for BCL-2 proteins, with implications for anti-bacterial immunity and cancer therapy.
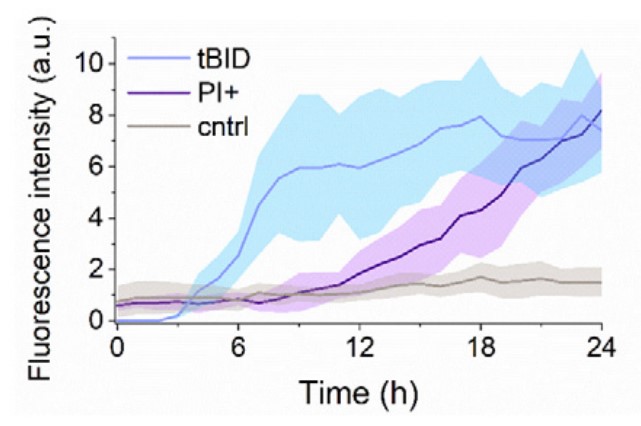
Fig3. Kinetics of the expression of tBID-GFP (blue) and PI intake upon tBID expression (purple) and untransfected HCT116 AKO cells (in grey).
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
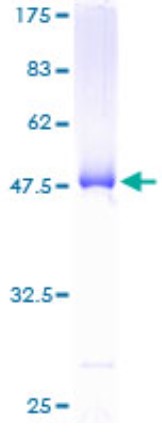
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (BID-218H) (PROTOCOL for western blot)
.
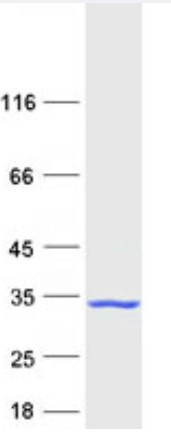
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (BID-1625H) (PROTOCOL for western blot)
Involved Pathway
BID involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways BID participated on our site, such as Sphingolipid signaling pathway,p signaling pathway,Apoptosis, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with BID were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) | MAP3K5,NEFH,CASP1,PPP3R1,BAD,CAT,TOMM40,DERL1,NEFM,CYCS |
| p signaling pathway | GADD45BB,Casp3,EI24,RRM2B,CD82A,BAI1,CCNB2,CASP9,SESN1,GADD45AA |
| Pathways in cancer | FZD9,PGF,PIK3CB,VEGFA,ROCK1,STAT5A,TRP53,GRB2,CDH1,MMP2 |
| Tuberculosis | FCGR1A,ITGB2,EEA1,TRAF6,Ifna15,FCGR2B,RAB7A,RIPK2,IFNA14,HLA-DPB1 |
| Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) | TRAF2,COX7A2,NDUFS5,COX7A2L,IL1B,IL-8,SDHA,SDHC,NDUFB1,CDC42 |
| Alzheimers disease | APP,CALM2,PPP3CC,NDUFB1,LPL,COX7A2,NDUFS1,ATP2A1,NDUFB6,CDK5R1 |
| Sphingolipid signaling pathway | PIK3CB,CERS5,TP53,PPP2R3A,NRAS,SGPP1,AKT2,PPP2R2B,PIK3CG,GNAI1 |
| Viral myocarditis | CYCS,PRF1,SGCD,HLA-DRB5,HLA-DOA,EIF4G3,ITGB2L,Casp3,EIF4G2,HLA-A |
| Natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity | FYN,PPP3R1,ITGB2L,PIK3R3,SHC4,IFNAR2,KIR2DS2,RAC2,Casp3,RAF1 |
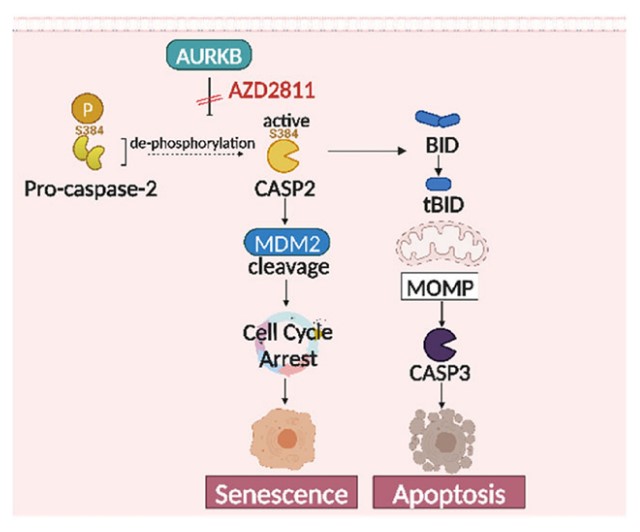
Fig1. Schematic depicting the hypothetical transduction pathways triggered by TTK and AURKB inhibitors in cancer cells. (Jordi Bertran-Alamillo, 2023)
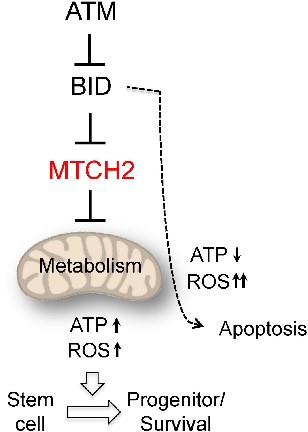
Fig2. Mitochondria metabolism regulates the fate of haematopoietic stem cells. (Atan Gross, 2016)
Protein Function
BID has several biochemical functions, for example, death receptor binding,protein binding,ubiquitin protein ligase binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by BID itself. We selected most functions BID had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with BID. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| protein binding | ZFAND2B,PLK2,COA5,NCBP2,BIN2,GSDMD,NEURL1B,PBLD,C12orf43,ZYX |
| ubiquitin protein ligase binding | WASH1,UBE2O,FHIT,TRIB1,PIAS4,TRAF2,UBE2V2,CLU,LC3,SMC6 |
| death receptor binding | FADD,RIPK1,TNFSF15,CASP8,CFLAR,Fasl,TMBIM1,FEM1B,PRDM4,Casp3 |
Interacting Protein
BID has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with BID here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of BID.
BCL2;BCL2L1;BAX
Resources
Gene Families
Research Area
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Chandran, SR; Tesch, GH; et al. Spleen tyrosine kinase contributes to acute renal allograft rejection in the rat. INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF EXPERIMENTAL PATHOLOGY 96:54-62(2015).
- Singh, SV; Singh, PK; et al. Evaluation of goat based 'Indigenous vaccine' against Bovine Johne's Disease in endemically infected native cattle herds. INDIAN JOURNAL OF EXPERIMENTAL BIOLOGY 53:16-24(2015).



