MMP14
-
Official Full Name
matrix metallopeptidase 14 (membrane-inserted) -
Overview
Proteins of the matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) family are involved in the breakdown of extracellular matrix in normal physiological processes, such as embryonic development, reproduction, and tissue remodeling, as well as in disease processes, such as arthritis and metastasis. Most MMPs are secreted as inactive proproteins which are activated when cleaved by extracellular proteinases. However, the protein encoded by this gene is a member of the membrane-type MMP (MT-MMP) subfamily; each member of this subfamily contains a potential transmembrane domain suggesting that these proteins are expressed at the cell surface rather than secreted. This protein activates MMP2 protein, and this activity may be involved in tumor invasion. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] -
Synonyms
MMP14;matrix metallopeptidase 14 (membrane-inserted);MMP-14;MMP-X1;MT-MMP;MT1MMP;MTMMP1;WNCHRS;MT1-MMP;MT-MMP 1;matrix metalloproteinase-14;membrane type 1 metalloprotease;membrane-type-1 matrix metalloproteinase;1
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Rhesus macaque
- Rat
- Mouse
- Human
- E.coli
- HEK293
- Mammalian Cells
- Non
- HeLa
- Wheat Germ
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- Non
- His
- Avi
- Fc
- Flag
- SUMO
- DDK
- Myc
- GST
Background
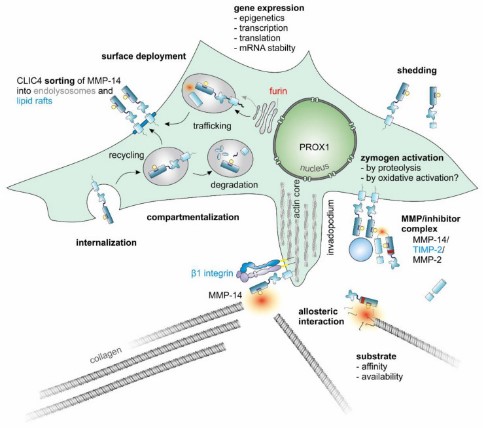
Fig1. The enzymatic activity of MMP-14 is subject to complex regulation.
What is MMP14 protein?
MMP14 (matrix metallopeptidase 14) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 14 at locus 14q11. Proteins of the matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) family are involved in the breakdown of extracellular matrix in normal physiological processes, such as embryonic development, reproduction, and tissue remodeling, as well as in disease processes, such as arthritis and metastasis. Most MMPs are secreted as inactive proproteins which are activated when cleaved by extracellular proteinases. However, the protein encoded by this gene is a member of the membrane-type MMP (MT-MMP) subfamily; each member of this subfamily contains a potential transmembrane domain suggesting that these proteins are expressed at the cell surface rather than secreted. The MMP14 protein is consisted of 582 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 65.9 kDa.
What is the function of MMP14 protein?
MMP14 is also known as membrane matrix metalloproteinase-1 (MT1-MMP). MMP14 is an endopeptidase that degrades various components of the extracellular matrix such as collagen. It is essential for pericellular collagenolysis and modeling of skeletal and extraskeletal connective tissues during development. It may be involved in actin cytoskeleton reorganization by cleaving PTK7 and acts as a positive regulator of cell growth and migration via activation of MMP15. And MMP14 is also involved in the formation of the fibrovascular tissues in association with pro-MMP2.
MMP14 Related Signaling Pathway
The biological process involved in MMP14 mainly include extracellular matrix degradation, tumor invasion and development, angiogenesis, and inflammatory response. In addition, MMP14 also plays an important role in the regulation of T cell function, and its expression level is closely related to T cell activation and function. Some signaling pathways are related with MMP14 including TGF-β signaling pathway, Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, FAK/PI3K/Akt signaling pathway, etc.
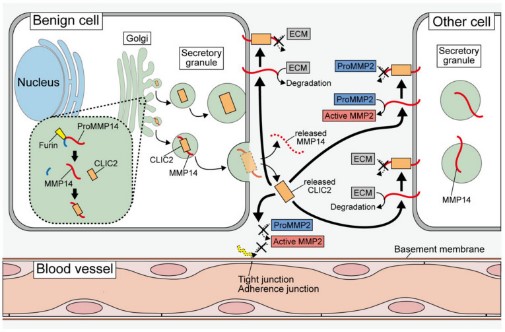
Fig2. Probable mechanisms underlying the chloride intracellular channel proteins (CLICs)-mediated suppression of tumor cell invasion and metastasis. In the secretory granules, CLIC2 binds to MMP14 and inhibits the localization of MMP14 in the plasma membrane.
MMP14 Related Diseases
MP14 plays an important role in the development and metastasis of tumors. The abnormal expression of MMP14 may lead to enhanced invasion and metastasis of tumor cells. It also plays a key role in the inflammatory response, participating in the degradation of joint tissues and the inflammatory response. Overactivation of MMP14 is involved in the destruction of artery walls and the formation of atherosclerosis.
Bioapplications of MMP14
MMP14 can be used as a drug target to develop inhibitors against MMP14, and its high expression can be used as a diagnostic marker and prognostic evaluation indicator for some tumors. Some of the inhibitors in development may also be used to treat related diseases.
Case Study
Case study 1: Chen Xu, 2023
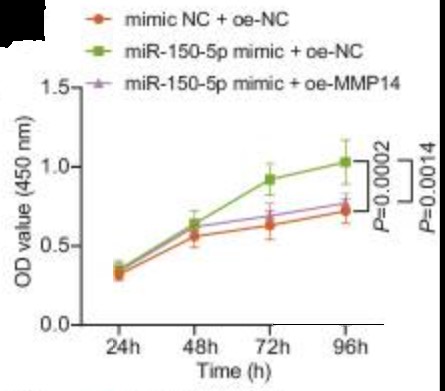
Extracellular vesicles derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSC-EVs) are emerged as carriers of therapeutic targets against bone disorders, yet its isolation and purification are limited with recent techniques. Magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) can load EVs with a unique targeted drug delivery system. Gold-coated magnetic nanoparticles (GMNPs) were constructed by decorating the surface of the Fe3O4@SiO2 core and a silica shell with poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG)-aldehyde (CHO) and the researchers examined the role of BMSC-EVs loaded on GMNPs in diabetic osteoporosis (DO). DO models were then established in Sprague-Dawley rats. GMNPE was prepared by combining GMNPs with anti-CD63, after which osteoblasts were co-cultured with the GMNPE-BMSC-EVs. BMSC-EVs delivered miR-150-5p to osteoblasts, where miR-150-5p targeted MMP14 and consequently activated Wnt/β-catenin pathway, resulting in promotion of osteogenesis.
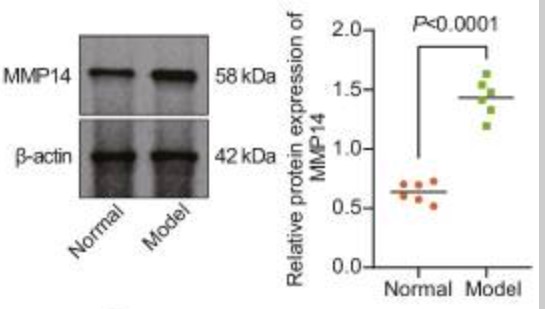
Fig1. Immunoblotting of MMP14 protein in the bone tissues of normal and DO rats.
Case study 2: Ensieh M Poursani, 2023
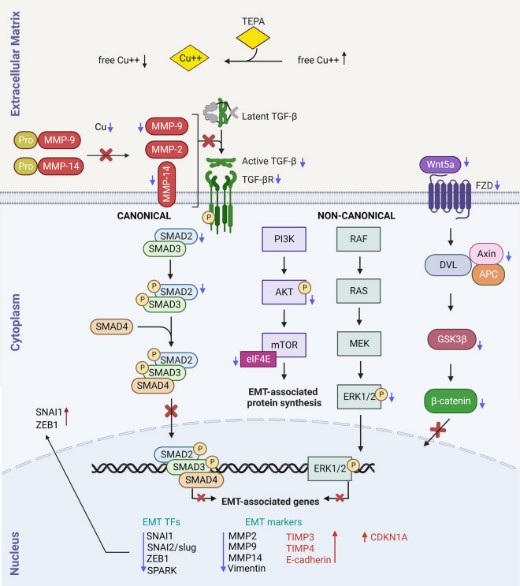
Metastatic cancer cells exploit Epithelial-mesenchymal-transition (EMT) to enhance their migration, invasion, and resistance to treatments. Clinical trials using copper chelators are associated with improved patient survival; however, the molecular mechanisms by which copper depletion inhibits tumor progression and metastasis are poorly understood. This article proposes that copper chelation inhibits metastasis by reducing TGF-β levels and EMT signaling and hypothesized that copper chelation therapy might be a less toxic alternative to target the TGF-β/EMT axis. To validate this hypothesis, the researchers performed single-cell imaging, protein assays, and in vivo studies. Mechanistically, TEPA significantly downregulated canonical (TGF-β/SMAD2&3) and non-canonical (TGF-β/PI3K/AKT, TGF-β/RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK, and TGF-β/WNT/β-catenin) TGF-β signaling pathways. Additionally, EMT markers of MMP-9, MMP-14, Vimentin, β-catenin, ZEB1, and p-SMAD2 were downregulated. This study suggests that copper chelation therapy represents a potentially effective therapeutic approach for targeting TGF-β and inhibiting EMT in a diverse range of cancers.
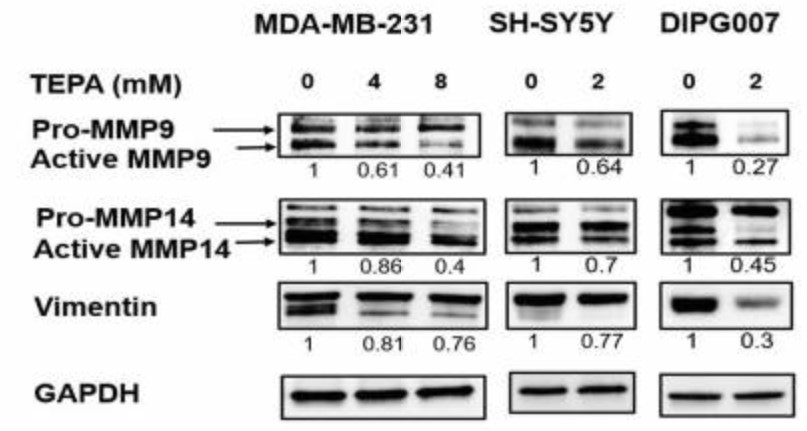
Fig3. Analysis of MMP-9, MMP-14, and vimentin at protein levels.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (MMP14-5423H) (PROTOCOL for western blot)
.
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (MMP14-181H) (PROTOCOL for western blot)
Involved Pathway
MMP14 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways MMP14 participated on our site, such as TNF signaling pathway,GnRH signaling pathway, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with MMP14 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| GnRH signaling pathway | HRASB,RAF1,CALML3,KRAS,MAP2K4A,CAMK2D1,CGNRH-R,MAPK8B,CDC42,CALM2 |
| TNF signaling pathway | NFKBIA,MAPK13,MAPK11,VCAM1,CCL5,Ccl12,MAP2K7,PIK3CD,IL18R1,CXCL3 |
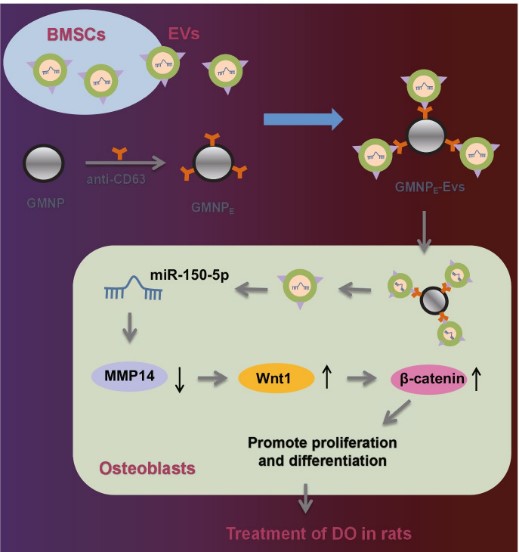
Fig2. Schematic diagram of the mechanism by which BMSC-EV-loaded GMNPs affect the progression of DO. (Chen Xu, 2023)
Protein Function
MMP14 has several biochemical functions, for example, calcium ion binding,integrin binding,metalloendopeptidase activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by MMP14 itself. We selected most functions MMP14 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with MMP14. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| zinc ion binding | BSPRY,P2RX2,LHX2B,BRD1,SPG7,TRIM40,CPB1,ADAM10,CCNB1IP1,PIAS4A |
| peptidase activator activity | MMP25,FN1,PSME4,APP,CAV1,PINK1,PSME4B,PCOLCE,CLPX,PCOLCE2 |
| protein binding | SWSAP1,SYCE3,FLOT2,FANCG,SEC23A,RNF165,IFIT2,VASNA,ZFP523,C19orf47 |
| calcium ion binding | FKBP9,SLC25A23,TMEM8C,PCDH2G4,MAN1B1,PCDH17,JAG1,AMY2A,PCDH15A,TTYH1 |
| metalloendopeptidase activity | PITRM1,NPSN,BMP1,ADAM1B,MMP19,MMP10,HE1A,MBTPS2,ADAM10,UQCRC2B |
| integrin binding | ICAM4,ESM1,NF2,WISP1,VWF,TSPAN8,ITGA3,THY1,ICAM3,VCAM1 |
Interacting Protein
MMP14 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with MMP14 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of MMP14.
ADI1;Gorasp2;LUM
Resources
Gene Families
Research Area
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Oh, G; Yoo, SW; et al. Intravital imaging of mouse colonic adenoma using MMP-based molecular probes with multi-channel fluorescence endoscopy. BIOMEDICAL OPTICS EXPRESS 5:1677-1689(2014).
- Ali, G; Borrelli, N; et al. Differential Expression of Extracellular Matrix Constituents and Cell Adhesion Molecules between Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma and Mesothelial Hyperplasia. JOURNAL OF THORACIC ONCOLOGY 8:1389-1395(2013).




