CCL20
-
Official Full Name
chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 20 -
Overview
Chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 20 (CCL20) or liver activation regulated chemokine (LARC) or Macrophage Inflammatory Protein-3 (MIP3A) is a small cytokine belonging to the CC chemokine family. It is strongly chemotactic for lymphocytes and weakly attracts neutrophils. CCL20 is implicated in the formation and function of mucosal lymphoid tissues via chemoattraction of lymphocytes and dendritic cells towards the epithelial cells surrounding these tissues. CCL20 elicits its effects on its target cells by binding and activating the chemokine receptor CCR6. -
Synonyms
CCL20;chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 20;CKb4;LARC;ST38;MIP3A;MIP-3a;SCYA20;C-C motif chemokine 20;exodus-1;MIP-3-alpha;CC chemokine LARC;OTTHUMP00000164245;OTTHUMP00000204113;beta chemokine exodus-1;beta-chemokine exodus-1;small-inducible cytokine A20;macrophage inflammatory protein 3 alpha;liver and activation-regulated chemokine;small inducible cytokine subfamily A (Cys-Cys), member 20;MIP-3[a];OTTMUSP00000017965;OTTMUSP00000017966
Recombinant Proteins
- Rabbit
- Human
- Rat
- Chicken
- Macaca mulatta
- Mouse
- Rhesus macaque
- Bovine
- Yeast
- E.coli
- Wheat Germ
- Mammalian Cells
- CHO
- Insect Cells
- Human Cells
- HEK293
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- Non
- GST
- His
- Fc
- mIgG2a
- SUMO
- rFc
- Avi
Background
What is CCL20 protein?
CCL20 (C-C motif chemokine ligand 20) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 2 at locus 2q36. This antimicrobial gene belongs to the subfamily of small cytokine CC genes. Cytokines are a family of secreted proteins involved in immunoregulatory and inflammatory processes. The CC cytokines are proteins characterized by two adjacent cysteines. The protein encoded by this gene displays chemotactic activity for lymphocytes and can repress proliferation of myeloid progenitors. The CCL20 protein is consisted of 96 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 10.8 kDa.
What is the function of CCL20 protein?
CCL20 protein is a chemokine that is mainly involved in recruitment and migration of immune cells. CCL20 can attract a variety of immune cells, such as dendritic cells, T cells and B cells, and thus participate in the immune response process. CCL20 can affect the function of immune cells, such as promoting the maturation and activation of dendritic cells, and enhancing the proliferation and differentiation of T cells. CCL20 is highly expressed at the site of inflammation and participates in the occurrence and development of inflammatory response by recruiting immune cells and regulating their function.
CCL20 Related Signaling Pathway
The interaction between CCL20 and CCR6 plays a key role in promoting tumor progression, inflammatory response, tissue damage and other pathophysiological activities. By inducing the differentiation of myeloid progenitor cells (GMPs), granulocyte line MDSCs (PMN-MDSCs) with immunosuppressive function were promoted, and then CXCR2/NOTCH1/HEY1 signaling pathway of tumor cells was activated through the secretion of CXCL2, resulting in the enrichment of breast tumor stem cells. CCL20 is also involved in regulating the function of tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs), enhancing the tumor's immunosuppressive microenvironment by promoting the recruitment and activation of TAMs, thereby promoting tumor growth and metastasis.
CCL20 Related Diseases
CCL20 protein is associated with a variety of diseases, including inflammatory diseases, infectious diseases, tumors and autoimmune diseases. In inflammatory diseases, CCL20 is involved in the occurrence and development of inflammatory responses, such as enteritis, pneumonia and nephritis, by recruiting immune cells, such as dendritic cells and T cells. In addition, CCL20 is also closely related to infectious diseases, such as HIV infection, hepatitis virus (HBV and HCV) infection, and changes in its expression level may affect the replication and transmission of the virus. In terms of cancer, CCL20 is involved in the growth, invasion and metastasis of tumors, such as breast cancer, colon cancer and prostate cancer, by regulating the infiltration of immune cells in the tumor microenvironment. At the same time, CCL20 is also associated with autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, and its abnormal expression may lead to immune system disorders and tissue damage.
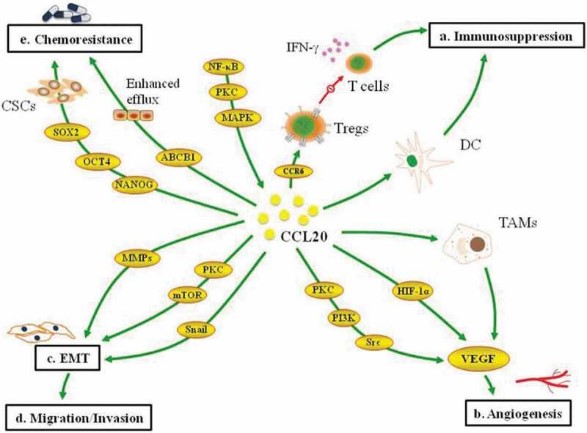
Fig1. Multifaceted roles of CCL20 in breast cancer progression. (Louis Boafo Kwantwi, 2021)
Bioapplications of CCL20
CCL20's role in inflammation and immune responses also makes it a potential target for anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory therapies. In clinical diagnosis, the expression level of CCL20 is associated with the invasion degree of certain tumors, the infiltration of immune cells in tumor tissues, and the survival rate of patients. Therefore, CCL20 is also studied as a potential biomarker for tumor diagnosis, prognosis assessment, and monitoring of treatment effects.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Chenglong Zhao, 2018
Giant cell tumor of bone (GCTB), one of the most common primary bone tumors, leads to extensive bone destruction. However, the mechanisms underlying GCTB progression remain elusive and prognostic factors and treatment targets are required. This study explored the function of the chemokine family member CCL20 in GCTB progression. Clinical analyses of the role of CCL20 in tumor progression were performed based on the patient cohort of our institution. The role of CCL20 in tumor proliferation was evaluated by MTS assay, migration ability was measured by a Transwell assay, and osteoclastogenesis was induced by CCL20 or GCTSC-conditioned medium. CCL20 induced GCTSC proliferation and migration in an autocrine manner. In addition, CCL20 recruited mononuclear cells and induced osteoclastogenesis by overactivating the AKT and NF-κB signaling pathways. Antibody blockade of CCL20 abolished the exacerbated osteoclastogenesis.
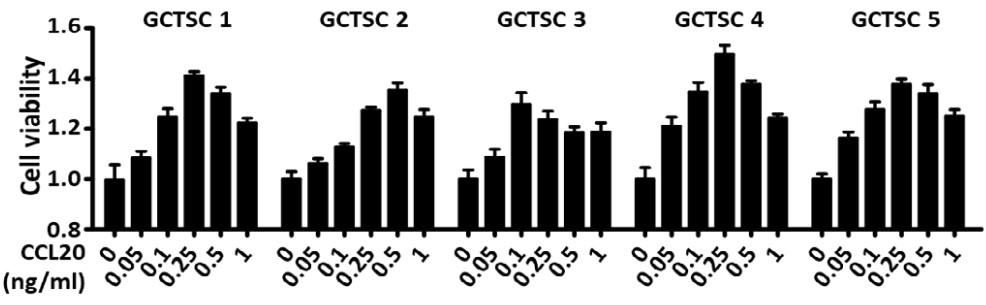
Fig1. Cell viability assay of GCTSCs from five patients after rhCCL20 treatment at the indicated concentrations.
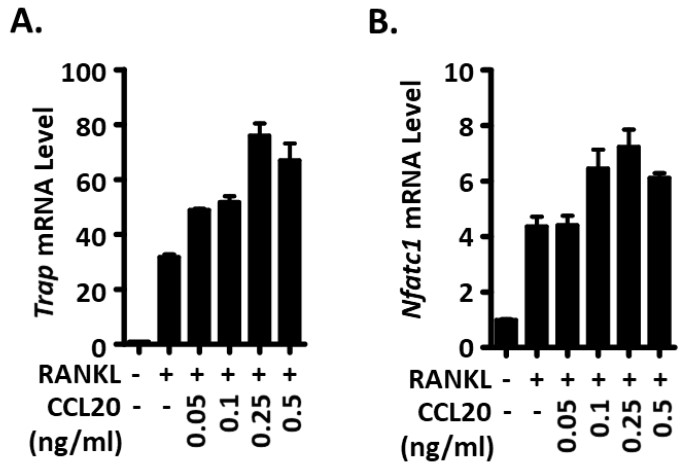
Fig2. Osteoclast marker genes are significantly upregulated after CCL20 treatment.
Case Study 2: Weilong Chen, 2018
Chemotherapeutic resistance in triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) has brought great challenges to the improvement of patient survival. The mechanisms of taxane chemoresistance in TNBC have not been well investigated. The results illustrated C-C motif chemokine ligand 20 (CCL20) was significantly elevated during taxane-containing chemotherapy in breast cancer patients with nonpathologic complete response. Furthermore, CCL20 promoted the self-renewal and maintenance of breast cancer stem cells (BCSCs) or breast cancer stem-like cells through protein kinase Cζ (PKCζ) or p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK)-mediated activation of p65 nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) pathway, significantly increasing the frequency and taxane resistance of BCSCs. Moreover, CCL20-promoted NF-κB activation increased ATP-binding cassette subfamily B member 1 (ABCB1)/multidrug resistance 1 (MDR1) expression, leading to the extracellular efflux of taxane. In addition, NF-κB activation increased CCL20 expression, forming a positive feedback loop between NF-κB and CCL20 pathways, which provides sustained impetus for chemoresistance in breast cancer cells.
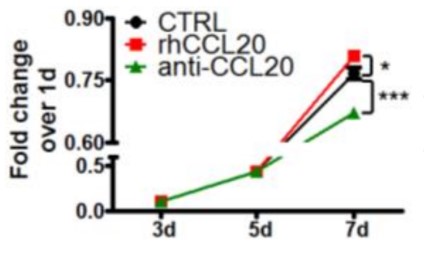
Fig3. MTT assay conducted with MDA-MB-231 cells in the presence or absence of rhCCL20 (10 ng/ml) or anti-CCL20 (200 ng/ml).
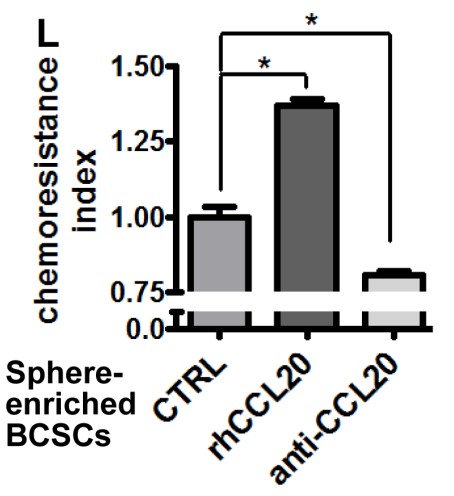
Fig4. Single cells digested from cultured tumorspheres of MDA-MB-231 cells were treated with DOC (14.10 nM) in the absence (CTRL) or presence of rhCCL20 (10 ng/ml) or anti-CCL20 (200 ng/ml) for 24 hours, and the chemoresistance was analyzed subsequently.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (CCL20-11H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (CCL20-0624H)
Involved Pathway
CCL20 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways CCL20 participated on our site, such as Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction,Chemokine signaling pathway,TNF signaling pathway, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with CCL20 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Chemokine signaling pathway | GM13304,AMCF-II,CCL11,RASGRP2,CXCL11,NFKBIA,PIK3R1,PIK3CB,CRKL,PIK3CD |
| Rheumatoid arthritis | HLA-DMB,ATP6V1D,HLA-DRB3,ATP6V1E2,CD86,ATP6V0E,MMP1,ATP6V0A1,ACP5,ATP6V1G2 |
| TNF signaling pathway | CASP10,MAP2K6,TNFRSF1B,IKBKB,IL18R1,IKBKG,TRAF2,RIPK1,TNF,FAS |
| Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction | Il2,IL8L2,CCL26,INHBB,BMPR1AA,CRLF2,IL18RAP,CCL22,ACVR2B,TNFRSF10B |
Protein Function
CCL20 has several biochemical functions, for example, CCR chemokine receptor binding,chemokine activity,protein binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by CCL20 itself. We selected most functions CCL20 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with CCL20. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| chemokine activity | CCL21B,CXCL12B,CXCL18B,CXCL13,CCL2,CCL34B.1,CXCL20,CX3CL1,CCL27B,CCL24 |
| protein binding | CALCR,CCNL1,CCNL2,IL17RA,USP37,BAG1,TCEB1,PITX1,SLA,RNF220 |
| CCR chemokine receptor binding | CCL38A.5,CCL16,CCL19B,CCL34A.4,CCL25B,CCL8,CCL13,CCL24,CCL35.1,CCL34B.4 |
Interacting Protein
CCL20 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with CCL20 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of CCL20.
RALBP1;TRAF6;TGFB3
Resources
Gene Families
Research Area
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Qin, T; Yin, YY; et al. Whole inactivated avian Influenza H9N2 viruses induce nasal submucosal dendritic cells to sample luminal viruses via transepithelial dendrites and trigger subsequent DC maturation. VACCINE 33:1382-1392(2015).
- Wu, HH; Hwang-Verslues, WW; et al. Targeting IL-17B-IL-17RB signaling with an anti-IL-17RB antibody blocks pancreatic cancer metastasis by silencing multiple chemokines. JOURNAL OF EXPERIMENTAL MEDICINE 212:333-349(2015).



