Th17 Cells
Related Symbol Search List
- CCRL2
- BATF
- CD4
- CD3e
- IL22
- IL23R
- Il6
- KLRB1
- RORC
- CD3G
- IL17RA
- IL21
- IL21R
- IL4R
- Il6ra
- IL6ST
- JAK1
- STAT3
- IL18
- CCL20
- CNOT6
- IL17B
- IL17D
- IL17RE
- IL1B
- IL1R1
- IL1RAP
- IL23A
- IL26
- RORA
- Tgfb1
- TGFBR1
- TGFBR2
Immunology Background
Available Resources Related to Th17 Cells
Creative BioMart is dedicated to providing a broad range of products, custom services, and resources to support researchers studying Th17 Cells. We aim to provide researchers with the tools and knowledge they need to unravel the complexity of Th17 cells and their role in health and disease. Our team constantly stays abreast of the latest literature, attends conferences, and collaborates with leading researchers in the field. This enables us to anticipate emerging trends and develop innovative products and services to meet the changing needs of the scientific community.
| We offer a wide range of high-quality research products designed specifically for the study of Th17 cells, including recombinant proteins, cell and tissue lysates, chromatography reagents, antibodies, and small molecules targeting key Th17 cell markers, cytokines, and signaling pathways. | |
| Our team of experienced scientists provides customized services to meet specific research needs. We offer custom protein expression and purification, antibody production, and more. These services ensure reliable and reproducible results for your Th17 cell research. | |
| To support researchers conducting Th17 cell research, we have collected a range of resources related to Th17 cell research to promote a deeper understanding of Th17 cell biology, including protein functions, protein interactions, involved pathway, and other valuable information. |
About Th17 Cells
Th17 cells are a subset of CD4+ T cells in the immune system that play a crucial role in regulating immune responses, particularly in the context of inflammation and autoimmune diseases. They are characterized by their secretion of the cytokine interleukin-17 (IL-17) and are distinct from other CD4+ T cell subsets, such as Th1 and Th2 cells.
Differentiation and Transcription Factors
Th17 cells are differentiated from naïve CD4+ T cells in the presence of specific cytokines, primarily interleukin-6 (IL-6) and transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β). The differentiation process involves the activation of various transcription factors, including retinoic acid receptor-related orphan receptor gamma t (RORγt) and signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3). These transcription factors are crucial for driving the expression of genes associated with Th17 cell differentiation and function.
Cytokine Production and Function
Th17 cells are known for their production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, with IL-17 being the signature cytokine. IL-17 plays a key role in promoting inflammation and recruiting immune cells to sites of infection or tissue damage. It stimulates the production of other cytokines, chemokines, and antimicrobial peptides, further amplifying the inflammatory response.
Th17 cells also produce other cytokines, including IL-21 and IL-22, which contribute to their effector functions. IL-21 promotes B cell activation and antibody production, while IL-22 has antimicrobial properties and plays a role in tissue repair and barrier function.
Role in Immune-Mediated Diseases
Th17 cells have been implicated in the pathogenesis of various immune-mediated diseases, including autoimmune disorders and chronic inflammatory conditions. Excessive or dysregulated Th17 cell responses can lead to tissue damage and contribute to disease progression.
Autoimmune diseases such as multiple sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, and inflammatory bowel disease have been associated with increased Th17 cell activity. The pro-inflammatory cytokines produced by Th17 cells, along with their ability to recruit immune cells, can contribute to tissue inflammation and immune dysregulation in these diseases.
Regulation and Cross-Talk
The differentiation and function of Th17 cells are tightly regulated by various factors and interactions with other immune cells. Regulatory T cells (Tregs) and anti-inflammatory cytokines like IL-10 and TGF-β can inhibit Th17 cell differentiation and suppress their activity, helping to maintain immune homeostasis.
There is also considerable cross-talk between Th17 cells and other CD4+ T cell subsets. Th1 and Th2 cells, for example, can influence the differentiation and function of Th17 cells through the secretion of their respective cytokines. This interplay between different CD4+ T cell subsets adds complexity to the immune response and can impact disease outcomes.
Therapeutic Targeting
Given their involvement in immune-mediated diseases, Th17 cells and their associated cytokines have become attractive targets for therapeutic interventions. Strategies aimed at modulating Th17 cell differentiation or inhibiting the production or activity of IL-17 have been explored for the treatment of autoimmune disorders and inflammatory conditions.
Inhibitors targeting cytokine receptors or downstream signaling pathways involved in Th17 cell function, as well as antibodies against specific Th17 cell-associated cytokines, are being investigated in preclinical and clinical studies.
Th17 cells represent a distinct subset of CD4+ T cells with critical functions in immune regulation and inflammation. Understanding their differentiation, cytokine production, and interactions with other immune cells is essential for unraveling their roles in health and disease and developing targeted therapeutic approaches.
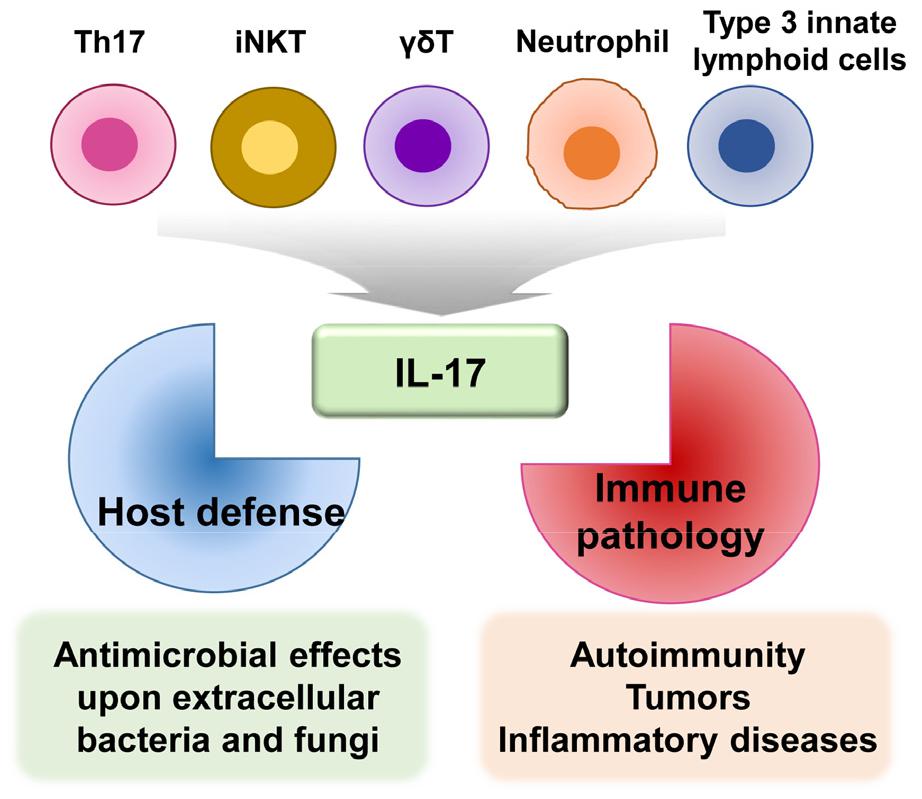 Fig.1 IL-17 production and function. (Martonik D, et al., 2021)
Fig.1 IL-17 production and function. (Martonik D, et al., 2021)
Key Molecules Involved in the Function of Th17 Cells
Here is a list of key molecules involved in the function of Th17 cells and their roles in Th17 cell differentiation and function (These are just a few examples of the molecules associated with Th17 cells. ):
| Key molecules type | Functions |
|---|---|
| Cytokines that Promote Th17 Cell Differentiation |
|
| Transcription Factors Involved in Th17 Cell Differentiation |
|
| Cytokines Produced by Th17 Cells |
|
| Molecules Involved in Th17 Cell Trafficking and Homing |
|
| Molecules that Inhibit or Regulate Th17 Cells |
|
| Molecules Targeted in Th17 Cell-Associated Therapies |
|
These are just a few examples of the molecules associated with Th17 cells. The interplay between these molecules and their regulation is complex and can have significant implications for immune responses and disease pathogenesis. Further research is needed to fully understand the roles of these molecules and their potential as therapeutic targets in Th17 cell-related disorders.
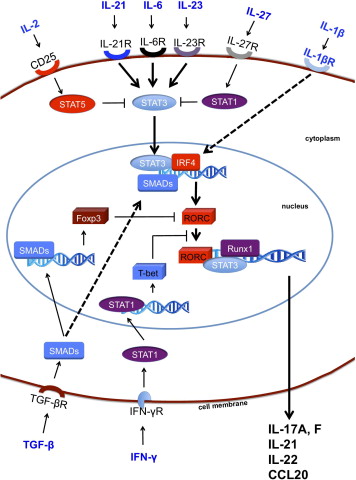 Fig.2 Mechanisms of Th17 cell induction. TGF-β is essential for the generation of both induced regulatory T cells and Th17 cells via the induction of FoxP3 and RORC. However, in the absence of inflammation, FoxP3 represses RORC and promotes iTregs. Signaling via inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-6, IL-21, and IL-23, results in STAT3 phosphorylation, relieves RORC from the suppression of FoxP3, and initiates Th17 programming. STAT3 in combination with IFN regulatory factor 4 (IRF4) further induces RORC expression. The transcription factors STAT3, RORC, and Runx1 bind to the promoter regions of the IL17, IL21, IL22, and CCL20 genes and induce IL-17, IL-21, IL-22, and CCL20. Th17 programming can be antagonized by cytokines, such as IFN-γ, IL-2, and IL-27. IL-2-mediated and IL-27-mediated activation of STAT5 and STAT1 inhibit STAT3, whereas T-bet induced by IFN-γ can block RORC. (Maddur MS, 2012)
Fig.2 Mechanisms of Th17 cell induction. TGF-β is essential for the generation of both induced regulatory T cells and Th17 cells via the induction of FoxP3 and RORC. However, in the absence of inflammation, FoxP3 represses RORC and promotes iTregs. Signaling via inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-6, IL-21, and IL-23, results in STAT3 phosphorylation, relieves RORC from the suppression of FoxP3, and initiates Th17 programming. STAT3 in combination with IFN regulatory factor 4 (IRF4) further induces RORC expression. The transcription factors STAT3, RORC, and Runx1 bind to the promoter regions of the IL17, IL21, IL22, and CCL20 genes and induce IL-17, IL-21, IL-22, and CCL20. Th17 programming can be antagonized by cytokines, such as IFN-γ, IL-2, and IL-27. IL-2-mediated and IL-27-mediated activation of STAT5 and STAT1 inhibit STAT3, whereas T-bet induced by IFN-γ can block RORC. (Maddur MS, 2012)
The Role of Th17 Cells and Related Molecules in Various Diseases
Th17 cells and related molecules play intricate roles in various diseases, contributing to both protective and pathological immune responses. Here is a detailed introduction to their roles in different disease contexts:
Autoimmune Diseases
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS): Th17 cells infiltrate the central nervous system (CNS) in MS patients and contribute to neuroinflammation and demyelination. Th17 cell-derived interleukin-17 (IL-17) and other pro-inflammatory cytokines promote the recruitment of immune cells and disrupt the blood-brain barrier, leading to CNS damage.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): Th17 cells are implicated in the pathogenesis of RA. They promote synovial inflammation by producing IL-17 and IL-22, leading to the recruitment of neutrophils and macrophages. This results in chronic inflammation, joint destruction, and cartilage damage.
- Psoriasis: Th17 cells play a central role in psoriasis, a chronic inflammatory skin disorder. They produce high levels of IL-17, which triggers keratinocyte proliferation and the release of pro-inflammatory mediators. This leads to epidermal hyperplasia, thickening of the skin, and the formation of psoriatic plaques.
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)
- Crohn's Disease (CD) and Ulcerative Colitis (UC): Th17 cells are implicated in the pathogenesis of both CD and UC. Increased Th17 cell activity and elevated levels of IL-17 and IL-23 have been observed in the inflamed gut mucosa of IBD patients. Th17 cells contribute to the recruitment of immune cells, intestinal barrier dysfunction, and persistent inflammation, leading to tissue damage in the gut.
Asthma
- Th17 cells and their cytokines have been implicated in the development and severity of asthma. IL-17 and IL-22 contribute to airway inflammation, mucus hypersecretion, and airway remodeling. Th17 cells interact with other immune cells, such as eosinophils and mast cells, amplifying the inflammatory response in the airways.
Allergic Diseases
- Allergic Rhinitis: Th17 cells and IL-17 play a role in the pathogenesis of allergic rhinitis. Th17 cells are involved in the recruitment and activation of eosinophils and mast cells, contributing to nasal inflammation, mucus production, and allergic symptoms.
- Atopic Dermatitis (AD): Th17 cells and IL-17 are implicated in AD, a chronic inflammatory skin condition. Th17 cell-derived cytokines contribute to skin inflammation, barrier dysfunction, and the recruitment of immune cells, exacerbating AD symptoms.
Cancer
- Th17 cells exhibit both anti-tumor and pro-tumor effects, depending on the context. In some cancers, Th17 cells are associated with enhanced anti-tumor immune responses and improved patient outcomes. On the other hand, Th17 cells can also promote tumor growth and metastasis in certain tumor microenvironments by stimulating angiogenesis and immune suppression.
Understanding the roles of Th17 cells and related molecules in various diseases provides insights into disease mechanisms, facilitates the development of targeted therapies, and opens avenues for immunomodulatory interventions to restore immune balance and control disease progression.
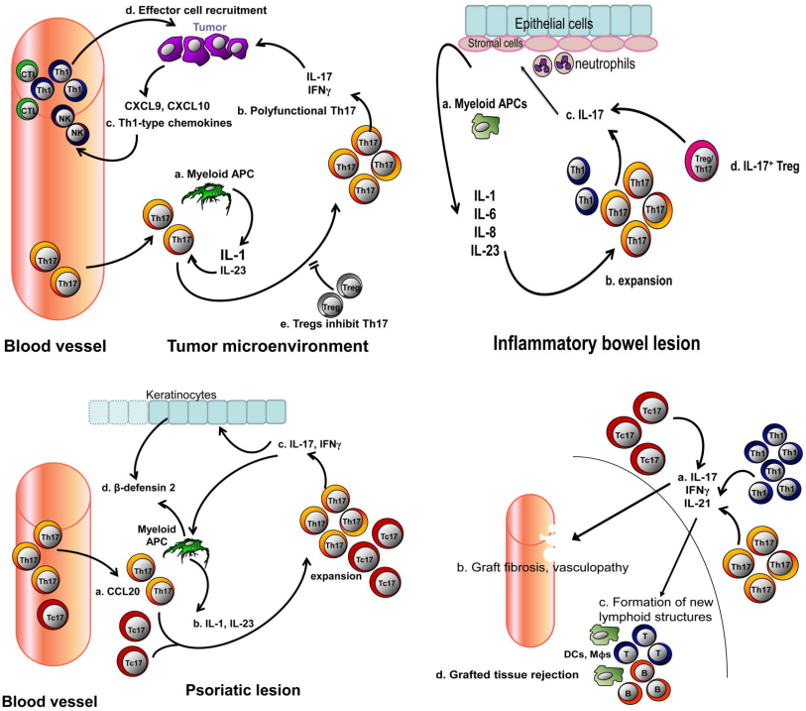 Fig.3 IL-17+ cells and cancer, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), psoriasis, transplant. (Wilke CM, et al., 2011)
Fig.3 IL-17+ cells and cancer, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), psoriasis, transplant. (Wilke CM, et al., 2011)
Creative BioMart is a trusted partner for researchers studying Th17 cells. Through our comprehensive product offerings, custom services, resources, and expert support, we aim to enable breakthrough discoveries in Th17 cell biology, advancing our understanding of immune responses, autoimmune diseases, inflammation, and other related fields. We are dedicated to supporting researchers in their quest to unravel the complexities of Th17 cells and translate their findings into meaningful scientific applications. For more information, please contact our team of experts for personalized assistance.
Related References
- Martonik D, Parfieniuk-Kowerda A, Rogalska M, Flisiak R. The Role of Th17 Response in COVID-19. Cells. 2021;10(6):1550.
- Maddur MS, Miossec P, Kaveri SV, Bayry J. Th17 cells: biology, pathogenesis of autoimmune and inflammatory diseases, and therapeutic strategies. Am J Pathol. 2012;181(1):8-18.
- Tesmer LA, Lundy SK, Sarkar S, Fox DA. Th17 cells in human disease. Immunol Rev. 2008;223:87-113.
- Wilke CM, Bishop K, Fox D, Zou W. Deciphering the role of Th17 cells in human disease. Trends Immunol. 2011;32(12):603-611.

