Ctsd
-
Official Full Name
cathepsin D -
Overview
This gene encodes a lysosomal aspartyl protease composed of a dimer of disulfide-linked heavy and light chains, both produced from a single protein precursor. This proteinase, which is a member of the peptidase C1 family, has a specificity similar to but narrower than that of pepsin A. Transcription of this gene is initiated from several sites, including one which is a start site for an estrogen-regulated transcript. Mutations in this gene are involved in the pathogenesis of several diseases, including breast cancer and possibly Alzheimer disease. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] -
Synonyms
CTSD;cathepsin D;CPSD;CLN10;HEL-S-130P;lysosomal aspartyl protease;lysosomal aspartyl peptidase;ceroid-lipofuscinosis, neuronal 10;epididymis secretory sperm binding protein Li 130P
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Rhesus macaque
- Mouse
- Cynomolgus
- Chicken
- Rat
- Zebrafish
- Cricetulus Griseus
- HEK293
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cells
- Human Plasma
- Human Liver
- Wheat Germ
- Human Cells
- Rabbit
- HeLa
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- Yeast
- His
- GST
- Non
- Avi
- Fc
- Myc
- SUMO
Background
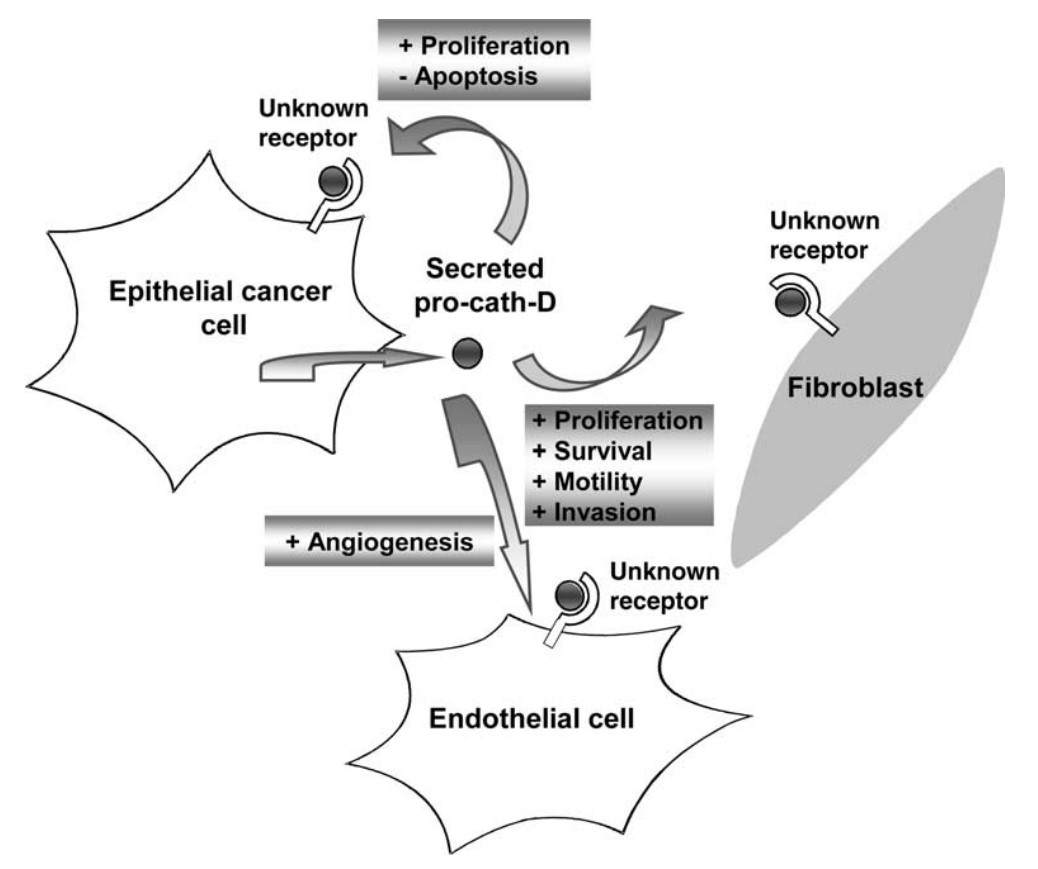
Fig1. Role of cath-D in cancer progression. (Emmanuelle Liaudet-Coopman, 2006)
What is CTSD protein?
CTSD (cathepsin D) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the short arm of chromosome 11 at locus 11p15. This gene encodes a lysosomal aspartyl protease composed of a dimer of disulfide-linked heavy and light chains, both produced from a single protein precursor. This proteinase, which is a member of the peptidase C1 family, has a specificity similar to but narrower than that of pepsin A. The CTSD protein is consisted of 412 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 44.6 kDa.
What is the function of CTSD protein?
CTSD is an aspartate protease, which mainly exists in lysosomes. CTSD is one of the main protein-degrading enzymes in lysosomes, and is involved in the degradation and renewal of proteins in cells. It is also involved in the regulation of autophagy and apoptosis. In addition, CTSD can degrade MHC-II molecules, thereby affecting immune processes such as antigen presentation and T cell activation.
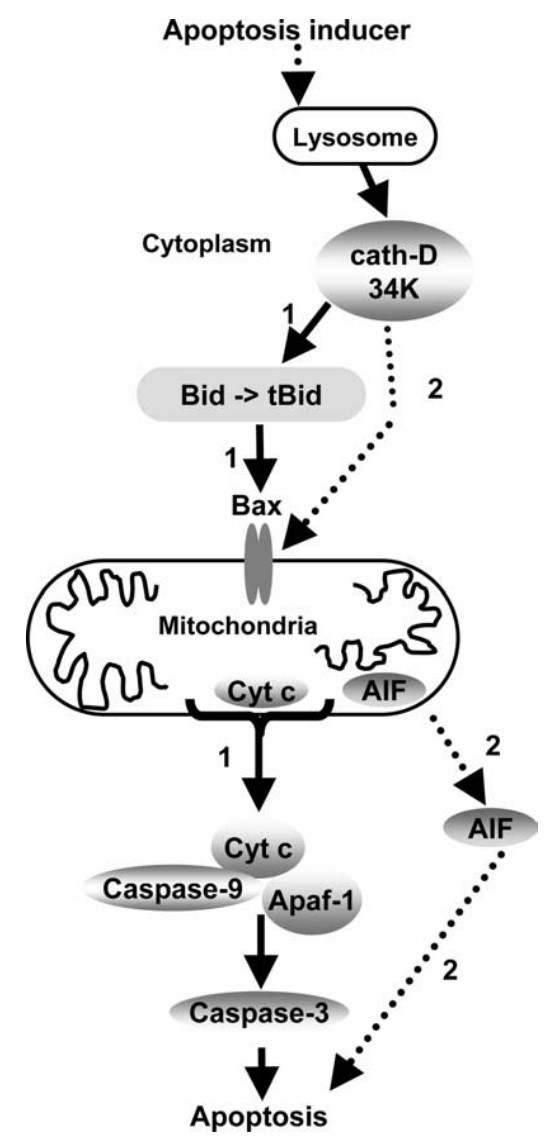
Fig2. Role of cath-D in apoptosis induction. (Emmanuelle Liaudet-Coopman, 2006)
CTSD Related Signaling Pathway
CTSD plays an important role in apoptosis, influencing cell fate and survival by regulating apoptosis-related signaling pathways, such as Bcl-2 family proteins. By mediating lysosomal function, it affects the development of cells and diseases, including tumors and neurological diseases.
CTSD Related Diseases
Mutations in this gene play a causal role in neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis-10 and may be involved in the pathogenesis of several other diseases, including breast cancer and possibly Alzheimer's disease.
Bioapplications of CTSD
As a potential therapeutic target, CTSD protein is also currently being used in research for disease diagnosis and treatment. Diseases include tumors, autoimmune diseases and neurological diseases.
Case Study
Case study 1: Eleonora Secomandi, 2022
Neuroblastoma is a malignant extracranial solid tumor arising from the sympathoadrenal lineage of the neural crest and is often associated with N-MYC amplification. Cathepsin D has been associated with chemoresistance in N-MYC-overexpressing neuroblastomas. Increased EGFR expression also has been associated with the aggressive behavior of neuroblastomas. This work aimed to understand the mechanisms linking EGFR stimulation and cathepsin D expression with neuroblastoma progression and prognosis.
Low CTSD expression was associated with poor clinical outcome. CTSD expression was negatively correlated with CCNB2, CCNA2, CDK1 and CDK6 genes involved in cell cycle division. Cathepsin D overexpression decreased the proliferative potential of neuroblastoma cells through downregulation of the pro-oncogenic MAPK signaling pathway. EGFR stimulation downregulated cathepsin D expression, thus favoring cell cycle division.
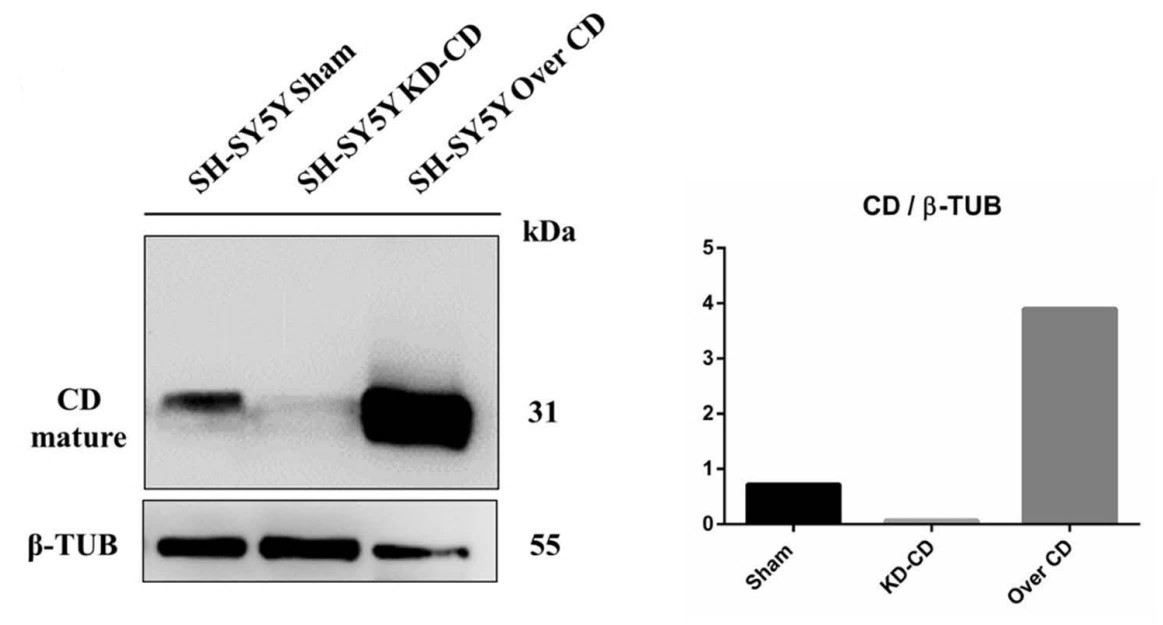
Fig1. Western blot of cathepsin D in SH-SH5Y Sham, 486 (KD-CD) and Over CD clones.
Case study 2: Yuan Li, 2017
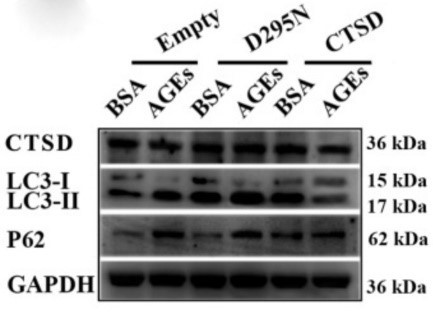
This study aimed to investigate the effect of advanced glycation end products (AGEs) on the proliferation and migration ability of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs). Cell proliferation was detected by methyl thiazolyl tetrazolium (MTT) assay, real-time cell analyzer and 5-Ethynyl-2'-deoxyuridine (EdU) staining. Cell migration was detected by wound-healing and transwell assay. AGEs significantly inhibited the proliferation and migration of HUVECs in a time-and dose-dependent way.
AGEs reduced cathepsin D (CTSD) expression in a time-dependent way. Overexpression of wild-type CTSD significantly decreased the ratio of LC 3 II/I as well as p62 accumulation induced by AGEs, but overexpression of catalytically inactive mutant CTSD had no such effects. Only overexpression of wild-type CTSD could restore the proliferation of HUVECs inhibited by AGEs.
This study found that AGEs inhibited the proliferation and migration in HUVECs and promoted autophagic flux, which in turn played a protective role against AGEs-induced cell injury. CTSD, in need of its catalytic activity, may promote proliferation in AGEs-treated HUVECs independent of the autophagy-lysosome pathway.
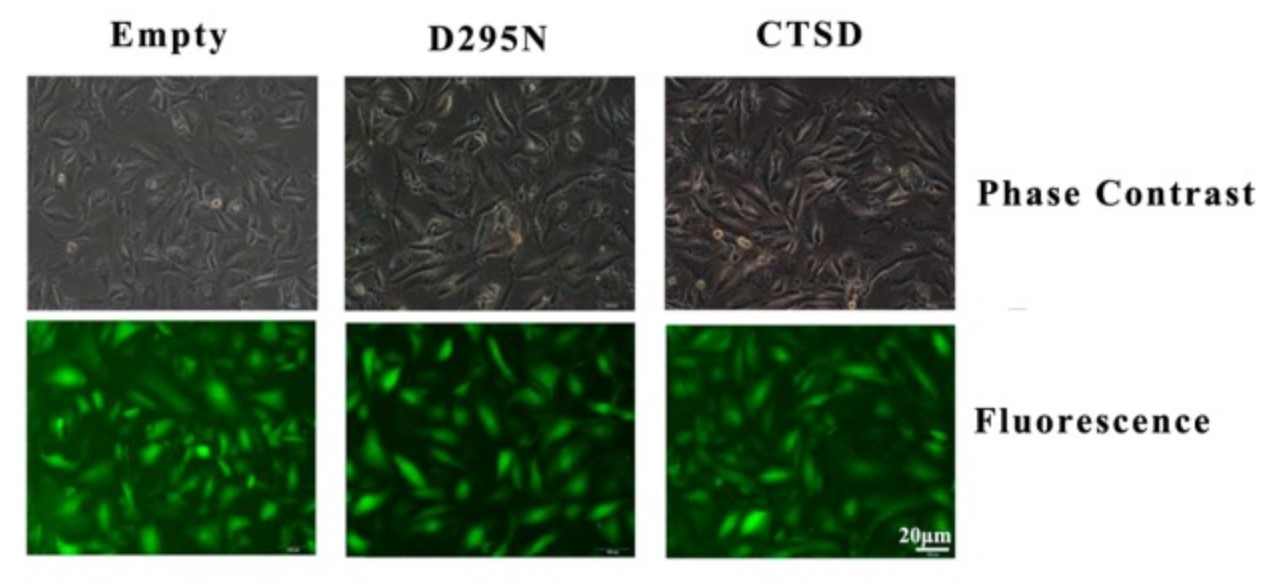
Fig3. CTSD was successfully transfected into cells. Green cells were labelled with green fluorescent protein, which indicated the transfection was successful.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
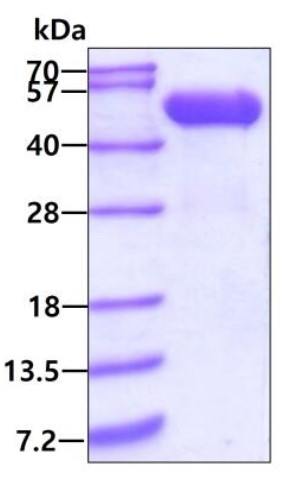
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (CTSD-04H) (PROTOCOL for western blot)
.
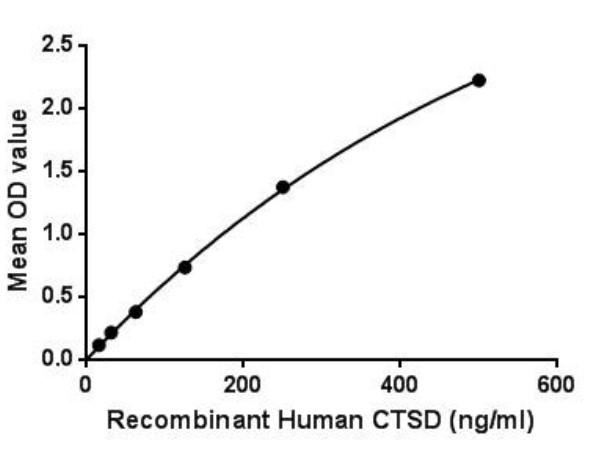
Fig2. Activity Data. (CTSD-877H)
Involved Pathway
Ctsd involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways Ctsd participated on our site, such as Adaptive Immune System,Ceramide signaling pathway,Collagen degradation, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with Ctsd were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Degradation of the extracellular matrix | KLK7,ADAMTS1,COL15A1B,MMP15,FURINA,BMP1B,CTS7,CTSLL,COL19A1,TLDC2 |
| Extracellular matrix organization | FMOD,CTS7,LTBP3,EFEMP1,ITGB3A,COL28A1A,COL2A1,PTPRS,ADAM8A,ABHD1 |
| Ceramide signaling pathway | PAWR,DERL3,CRADD,EGF |
| Adaptive Immune System | MGC174857,DYNC1I1,KIF2A,FRS2A,ITK,LTN1,KIF5A,CD96,PPIAL4A,RNF34 |
| Direct p53 effectors | FDXR,TADA2B,SCN3B,PRDM1,ARID3A,EDN2,PPM1J,RNF144B,DGCR8,CEBPZ |
| Collagen degradation | CTSB,TLDC2,MMP13,COL17A1,MMP8,ADAM9,COL19A1,MMP10,MMP19,ADAM10 |
| LKB1 signaling events | SIK3,STK11IP,CDC37,MAP2,MARK2,MARK4 |
| Immune System | NCKAP1,TXN,UBE2F,NLRP3,LILRB2,SIGLEC14,KIF4,SIGLEC5,KLRB1B,ABI1A |
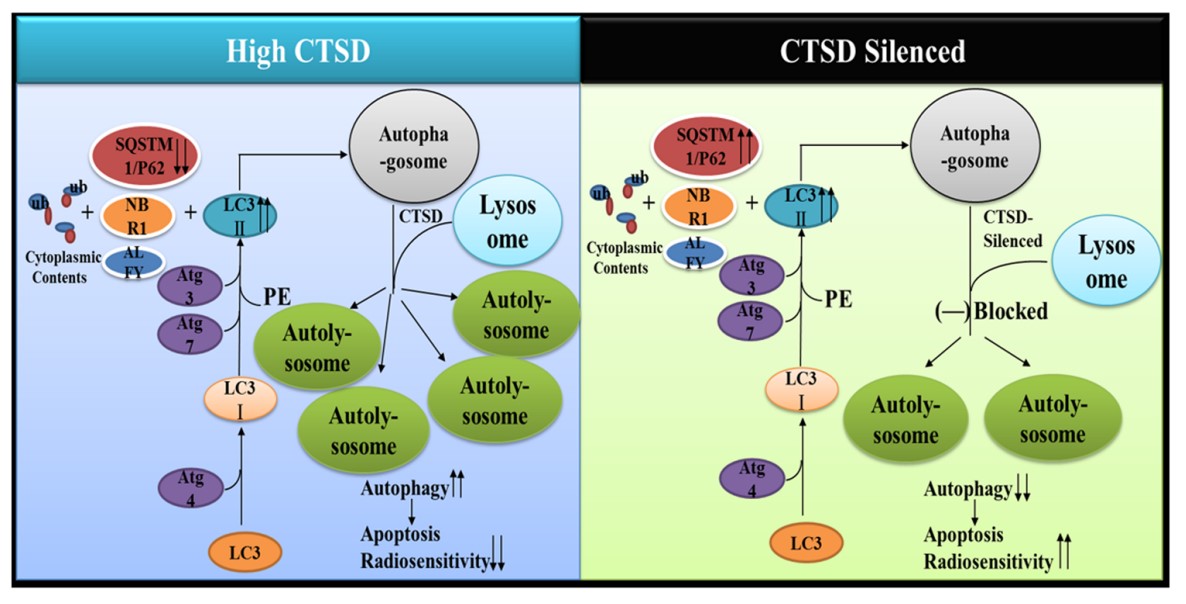
Fig1. In GBM cells, inhibition of CTSD blocked the fusion of autophagosome and lysosome which decreased the formation of autolysosome. (Wang Zheng, 2020)
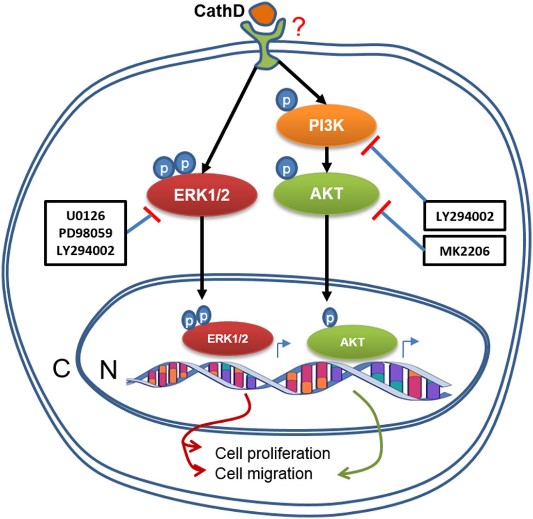
Fig2. A summary of CathD -induced activation of the ERK1/2 and AKT pathways, and cellular functions in HOMECs. (Md Zahidul I Pranjol, 2018)
Protein Function
Ctsd has several biochemical functions, for example, aspartic-type endopeptidase activity,protein binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by Ctsd itself. We selected most functions Ctsd had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with Ctsd. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| aspartic-type endopeptidase activity | PGA5,ATP6AP2,CTSE,Casp3,CNTNAP5A,NRIP3,NOTS,ASPRV1,REN,SPPL3 |
| protein binding | TSKS,SMAD6,KLHL6,F5,DPYSL3,VEGFB,APEH,MED4,IGF2BP1,TXLNB |
Interacting Protein
Ctsd has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with Ctsd here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of Ctsd.
env;APP;hly;HBA1;MAPK1;purT;q7cjw2_yerpe;leuD;RASSF10;ere_dna;RASSF9;cona_canen;H2AFX;VCAM1;ATP6V1A;RASSF7
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References



