FASLG
-
Official Full Name
Fas ligand (TNF superfamily, member 6) -
Overview
The Fas receptor (FasR) is a death receptor on the surface of cells that leads to programmed cell death (apoptosis). It is one of two apoptosis pathways, the other being the mitochondrial pathway. FasR is also known as CD95, Apo-1, and tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily, member 6 (TNFRSf6). FasR is located on chromosome 10 in humans and 19 in mice. Similar sequences related by evolution are found in most mammals. Cytokine that binds to TNFRSF6/FAS, a receptor that transduces the apoptotic signal into cells. May be involved in cytotoxic T-cell mediated apoptosis and in T-cell development. TNFRSF6/FAS-mediated apoptosis may have a role in the induction of peripheral tolerance, in the antigen-stimulated suicide of mature T-cells, or both. Binding to the decoy receptor TNFRSF6B/DcR3 modulates its effects. The protein encoded by this gene is the ligand for FAS. Both are transmembrane proteins. Interaction of FAS with this ligand is critical in triggering apoptosis of some types of cells such as lymphocytes. Defects in this gene may be related to some cases of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). -
Synonyms
FASLG;Fas ligand (TNF superfamily, member 6);FASL;CD178;CD95L;CD95-L;TNFSF6;APT1LG1;tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 6;APTL;CD95 ligand;OTTHUMP00000032708;fas antigen ligand;apoptosis antigen ligand;apoptosis (APO-1) antigen ligand 1;tumor necrosis factor (ligand) superfamily, member 6;soluble form;APO1L;Apoptosis antigen ligand 1;CD178 antigen;CD95;L CD95L protein;Fas L;Fas ligand;Fasl Fas ligand (TNF superfamily member 6);Generalized lymphoproliferative disease;Gld;TNF superfamily member 6;TNFL6_HUMAN;Fas-L
Recombinant Proteins
- Mouse
- Human
- Rhesus macaque
- Rat
- Chicken
- Zebrafish
- Cynomolgus
- Pig
- Macaca fascicularis
- Macaca nemestrina
- CHO
- HEK293
- E.coli
- Yeast
- Human Cells
- Mammalian Cells
- Wheat Germ
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- HA
- Fc
- His
- T7
- Non
- Flag
- S
- GST
- Avi
- SUMO
- MBP
Background
What is FASLG protein?
FASLG gene (Fas ligand) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 1 at locus 1q24. The primary function of the encoded transmembrane protein is the induction of apoptosis triggered by binding to FAS. The FAS/FASLG signaling pathway is essential for immune system regulation, including activation-induced cell death (AICD) of T cells and cytotoxic T lymphocyte induced cell death. It has also been implicated in the progression of several cancers. Defects in this gene may be related to some cases of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). The FASLG protein is consisted of 281 amino acids and FASLG molecular weight is approximately 31.5 kDa.
What is the function of FASLG protein?
FASLG is a protein that plays a critical role in the regulation of the immune system, particularly in the process of apoptosis or programmed cell death. It is expressed on the surface of activated T cells and binds to the Fas receptor on target cells, triggering a cascade of events that lead to cell death. This interaction is essential for maintaining immune homeostasis by eliminating infected or damaged cells and for preventing autoimmunity. Dysregulation of FASLG has been implicated in various diseases, including autoimmune disorders and cancer, and it is a key factor in the pathogenesis of certain lymphoproliferative syndromes.
FASLG related signaling pathway
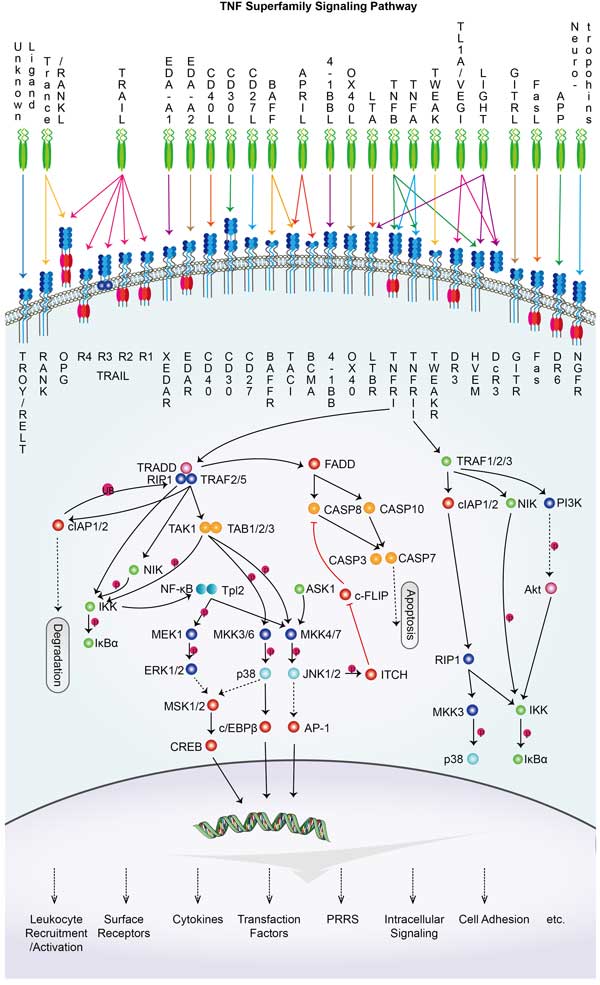
The FASLG (Fas Ligand)-related signaling pathway is a critical component in the regulation of programmed cell death, or apoptosis. This pathway involves the interaction between FASLG, a cell surface protein, and its receptor, Fas (CD95), which triggers a cascade of intracellular signals leading to apoptosis. The engagement of Fas by FASLG activates the receptor, resulting in the recruitment of adaptor proteins like FADD (Fas-associated via death domain) and procaspase-8. This complex formation leads to the activation of caspase-8, an initiator caspase that cleaves and activates downstream effector caspases such as caspase-3, ultimately resulting in cellular demolition. This pathway plays a crucial role in maintaining immune system homeostasis, eliminating autoreactive lymphocytes, and mediating cytotoxic T-cell-induced target cell death. Dysregulation of this pathway can contribute to various disease states, including autoimmune disorders, cancer, and inflammatory conditions.
FASLG related diseases
FASLG related diseases encompass a range of pathological conditions characterized by dysregulation of the Fas/FasL apoptotic signaling pathway. This pathway is crucial for maintaining immune system homeostasis and eliminating unwanted or damaged cells. When this pathway is disrupted, it can lead to various diseases. For instance, insufficient FasL activity or expression can impair apoptosis, contributing to autoimmune disorders such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) by allowing autoreactive lymphocytes to escape deletion. Conversely, overexpression or hyperactivity of FasL can lead to excessive apoptosis, implicated in conditions like liver disease (e.g., alcoholic hepatitis) due to uncontrolled killing of hepatocytes. Additionally, deregulation of this pathway can facilitate tumor progression and resistance to chemotherapy in cancers by enabling malignant cells to evade immune surveillance and apoptosis. Therefore, the balance and proper functioning of the FASLG-related signaling pathway are essential for preventing these diverse diseases associated with abnormal cell survival or death.
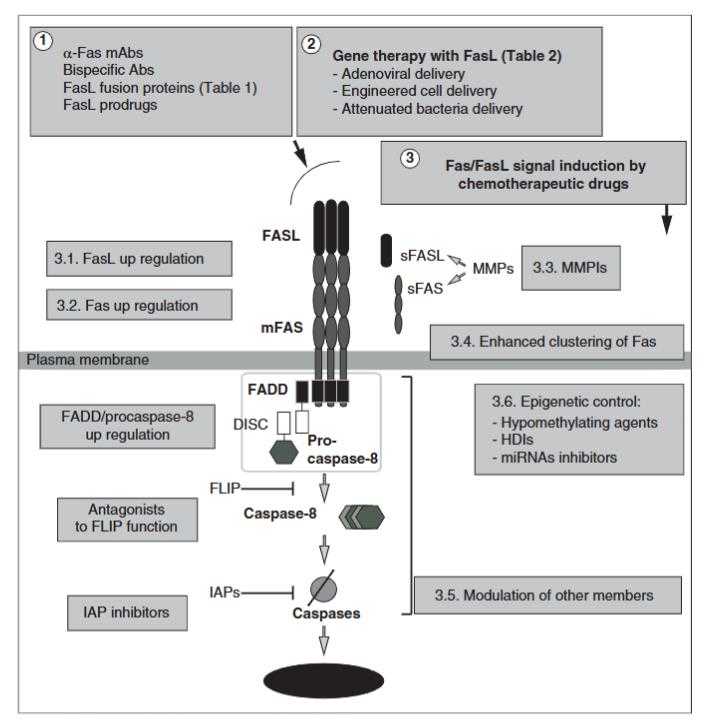
Fig1. Approaches targeting the Fas/FasL signaling for cancer therapy. (María Villa-Morales, 2012)
Bioapplications of FASLG
FASLG primarily functions by binding to the Fas receptor, triggering a caspase cascade that leads to apoptosis in target cells. It is crucially involved in immune regulation, including T-cell homeostasis and cytotoxicity. FasL is highly expressed on activated T cells and natural killer cells, promoting apoptosis of infected or altered cells and maintaining immune response balance. Deregulation of FasL can lead to autoimmune diseases and tumor development.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Li-Jie Li, 2022
Oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) often leads to death due to pulmonary metastasis from circulating cancer stem cells. This research reveals that the FAS receptor, known for inducing apoptosis, also promotes OSCC metastasis and stemness. FAS receptor knockout in OSCC cells reduced their ability to form metastases and invasion, and was linked to poor prognosis in patients. Here a new FAS-ERK-JAG1-NOTCH1 signaling pathway: FAS receptor activation increased JAG1 and NOTCH1, which are crucial for cancer stem cell properties. Targeting this pathway could offer a new therapeutic strategy for OSCC by inhibiting pulmonary metastasis.
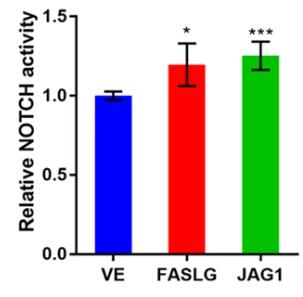
Fig1. rhJAG1 or rhFASLG treatment promotes NOTCH1 signaling activation.
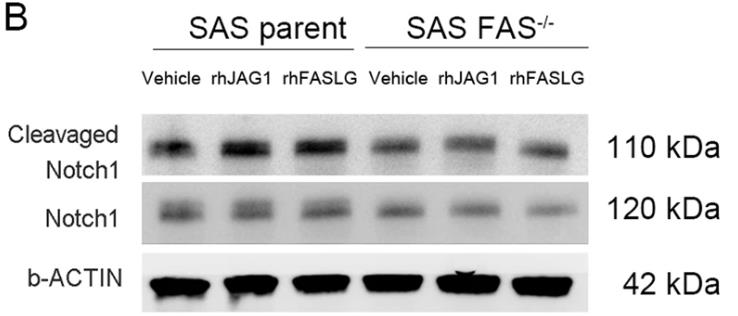
Fig2. NOTCH signaling pathway activation analysis by cleavage NOTCH1 expression under rhJAG1 or rhFASLG treatment.
Case Study 2: Barbara Łasut-Szyszka, 2024
Usually, cancer cells are resistant to the apoptotic effects of FAS ligand (FASLG). However, treating cancer cells with a combination of actinomycin D (ActD) and nutlin-3a (Nut3a) sensitizes them to FASLG, leading to rapid cell death. This drug combination activates both extrinsic and intrinsic apoptotic pathways and is dependent on functional p53. Notably, normal human fibroblasts are less susceptible to this treatment. This strategy could potentially revitalize the use of recombinant FASLG in cancer immunotherapy.
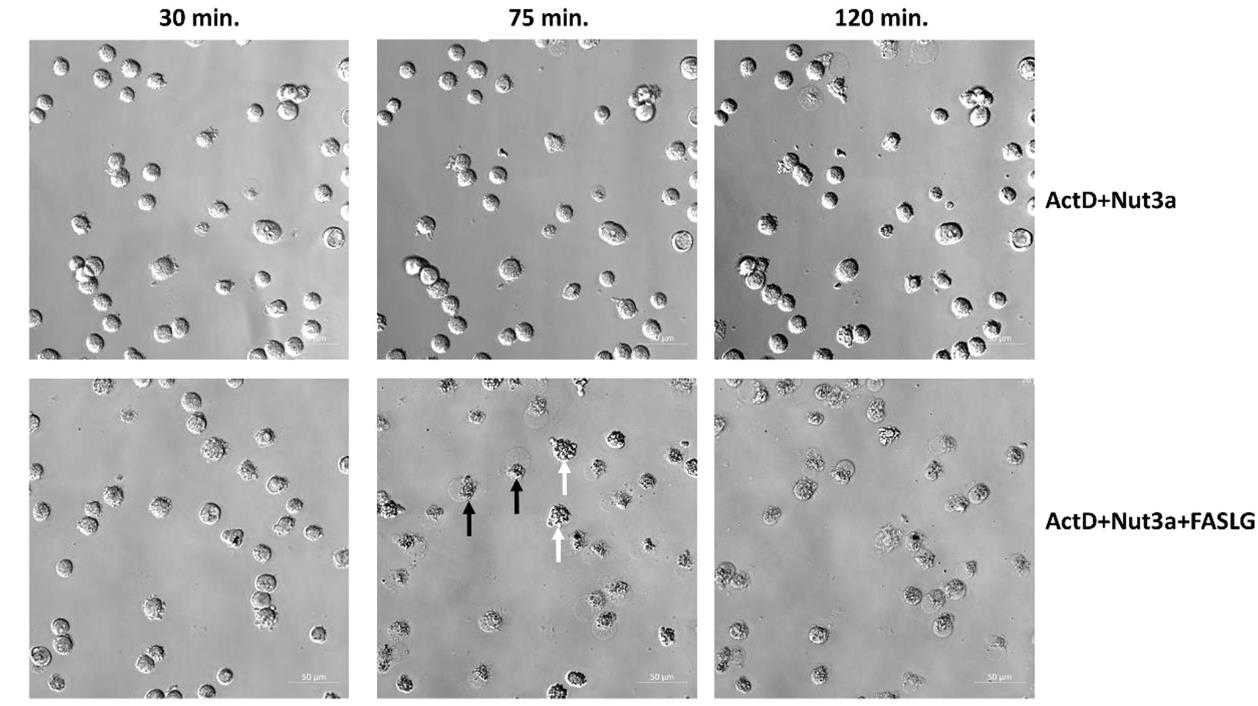
Fig3. Microscope observations reveal frequent death of cells pre-exposed to actinomycin D and nutlin-3a and subsequently incubated with FASLG.
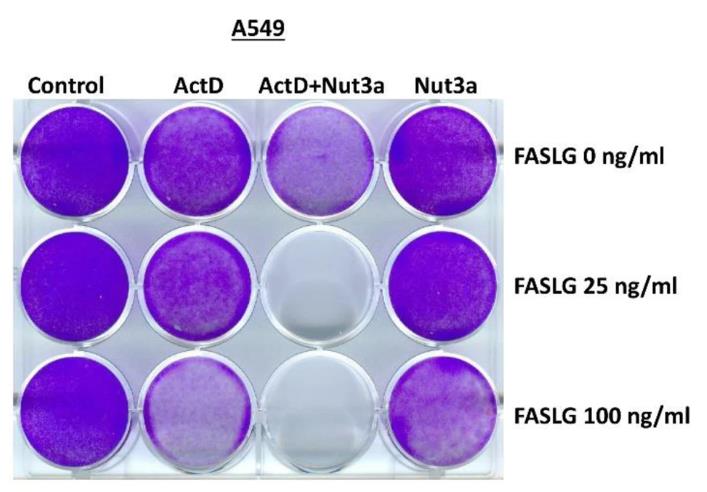
Fig4. Cells attached to the wells of the culture plate (stained by crystal violet) following the indicated treatment regimen.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (FASLG-624H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (FASLG-3857H)
Involved Pathway
FASLG involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways FASLG participated on our site, such as MAPK signaling pathway,Ras signaling pathway,Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with FASLG were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| FoxO signaling pathway | GABARAPL2,INSRB,PIK3R3A,IL7R,CDKN1BA,PCK2,PLK2,HRASA,SOS1,MAPK10 |
| PIK-Akt signaling pathway | ITGB7,NRAS,YWHAZ,ANGPT1,VEGFA,PKN2,PRL,IFNAR1,INS,EIF4E2 |
| Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) | NDUFB5,RXRA,CDC42,NDUFA11,UQCR10,PIK3R5,NDUFA4,NDUFB9,NR1H3,NDUFB3 |
| Autoi | CD28,H2-AB1,GZMB,IFNA14,Ifna15,IFNA8,HLA-DMB,IFNA16,FAS,CD80 |
| Influenza A | IFN-a,XPO1,MAPK8,RAF1,STAT2,DNAJB1,TBK1,HLA-DOA,IFIH1,PRSS2 |
| Natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity | BID,PPP3R1,KRAS,CD244,PPP3R2,VAV1,SAMD3,MICB,RAET1L,NFATC1 |
| Measles | NFKBIA,IFNAR1,IL6,PIK3CB,IFNA21,IL1B,MYD88,CCND1,IFNA4,IFNA2 |
| Type I diabetes mellitus | HLA-DPA1,Il2,HLA-DRB3,HLA-F,H2-Q10,HLA-C,HLA-DRA,H2-AA,TNF,INS2 |
| Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction | FIGF,CCL15,BMPR1AA,PRL2,EDA2R,TNFRSF19,CCL19,CRLF2,ACVR1,Ifna11 |
Protein Function
FASLG has several biochemical functions, for example, cytokine activity,death receptor binding,protein binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by FASLG itself. We selected most functions FASLG had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with FASLG. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| cytokine activity | GPI1,MSTNB,AREG,TIMP1,IFNA21,IL17A/F3,IL17B,IFNA10,IL37,SECTM1 |
| receptor binding | FGF12B,GCG,AMN,IFNL3,FYB,POMC,APOF,CD58,NCR3,FZD1 |
| death receptor binding | CASP8,NOL3,PIDD1,Fasl,FADD,RIPK1,PRDM4,TNFSF15,FEM1B,TMBIM1 |
| tumor necrosis factor receptor binding | TNFSF10L3,LTB,EDA,TNFSF10,TNFSF13,TRIM37,BRE,TRAF6,LTA,TNFB |
| protein binding | RAB11B,ABCD2,TET3,FKBP6,PRDM4,MYH10,PALB2,CRABP1,Apba1,PAX8 |
Interacting Protein
FASLG has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with FASLG here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of FASLG.
PSTPIP1;FAS;FADD;CASP8;SRGAP2;FYN
FASLG Related Signal Pathway
Resources
Research Area
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Senapati, S; Gutierrez-Achury, J; et al. Evaluation of European coeliac disease risk variants in a north Indian population. EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF HUMAN GENETICS 23:530-535(2015).
- Barathan, M; Gopal, K; et al. Chronic hepatitis C virus infection triggers spontaneous differential expression of biosignatures associated with T cell exhaustion and apoptosis signaling in peripheral blood mononucleocytes. APOPTOSIS 20:466-480(2015).