Th9 Cells
Related Symbol Search List
- SPI1
- CD4
- Ifng
- CD3e
- IL-10
- IL2
- IL-4
- Il6
- CD3G
- IL17RA
- IL21
- IL4R
- IL1B
- Tgfb1
- TGFBR2
- IL17RB
- Il25
- IL9
- STAT6
- ADAM11
- CCL17
- Ifna1
Immunology Background
Available Resources Related to Th9 Cells
Creative BioMart is committed to supporting Th9 cell research by providing high-quality products, customized services, and informative resources. We strive to empower researchers worldwide in their pursuit of understanding the intricate biology of Th9 cells and their implications in diseases. Partner with us to advance your Th9 cell research and make significant contributions to scientific knowledge and therapeutic developments.
| We offer a wide range of high-quality products specifically tailored for Th9 cell research. Our product portfolio includes recombinant proteins, GMP proteins, protein-coupled magnetic beads, cell and tissue lysates, antibodies, chromatography reagents, assay kits, and more. | |
| we understand that every research project is unique. Therefore, we offer customized services to meet your specific research needs. Our team of experienced scientists is ready to assist you in designing and executing experiments related to Th9 cell research. Our customized services include custom protein, protein analysis, discovery and translational, and others. | |
| To support researchers in staying up-to-date with the latest advancements in Th9 cell research, we offer a range of informative resources, including protein functions, protein interactions, involved pathways, and other essential data. These valuable tools serve to empower researchers by offering robust support for the progression of their research initiatives and experiments. |
About Th9 Cells
Th9 cells are a subset of CD4+ T helper cells that have distinct functions and cytokine profiles. They were initially identified as a separate Th cell subset in the early 2000s and are characterized by their production of interleukin-9 (IL-9), a cytokine with diverse roles in immune responses and inflammation.
Th9 cells differentiate from naïve CD4+ T cells under specific conditions and are primarily associated with allergic and autoimmune diseases. Here is an introduction to Th9 cells:
Differentiation and Transcription Factors
- Th9 cells differentiate from naïve CD4+ T cells in response to specific cytokine cues. The differentiation process involves the activation of the transcription factors PU.1 and interferon regulatory factor 4 (IRF4), along with the suppression of other lineage-specific transcription factors such as GATA3 and T-bet.
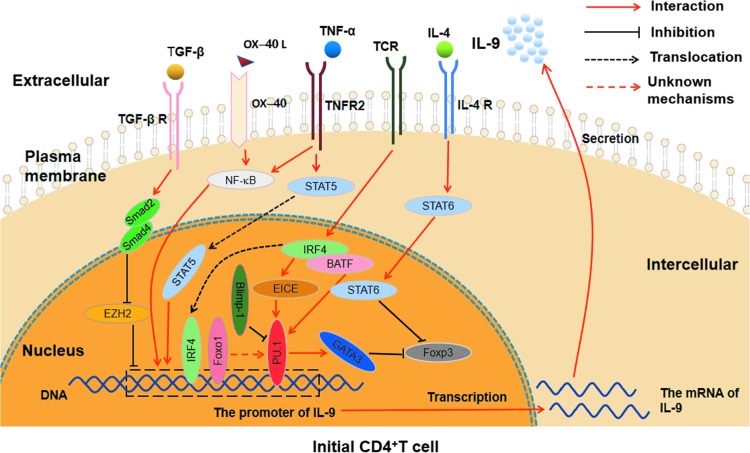 Fig.1 The related cytokine signaling pathways and transcription factors involved in Th9 cell differentiation. (Chen J, et al., 2019)
Fig.1 The related cytokine signaling pathways and transcription factors involved in Th9 cell differentiation. (Chen J, et al., 2019)
PU.1 can directly combine with the IL-9 promoter region and enhance the inhibition of GATA3 on Foxp3; IRF4, which is induced by TCR signaling, regulates the differentiation of Th9 cells through combining with IL-9 promoter region and promoting the interaction between EICE and PU.1, as well as coregulating with BATF and STAT6; Foxo1 affects the differentiation of Th9 cells by combining with the IL-9 promoter region and indirectly regulating PU.1; Blimp-1 represses the Th9 cell differentiation and IL-9 production through binding to PU.1. TGF-β-Smad2/4 signaling regulates IL-9 expression by displacement of EZH2 to promote the differentiation of Th9 cells; IL-4 signaling promotes Th9 differentiation by activating STAT6 to repress Foxp3; TNF-α influences Th9 cell differentiation through TNFR2-STAT5 signaling pathway and NF-κB signaling pathway; OX40/OX40L axis affects the differentiation and IL-9 expression of Th9 cells by activating the NF-κB pathway.
Cytokine Profile
- Th9 cells are characterized by their production of IL-9, which is their signature cytokine. IL-9 is a pleiotropic cytokine that exerts various effects on different immune cells. It can act as both a pro-inflammatory and an anti-inflammatory cytokine depending on the context. IL-9 can influence the function of mast cells, eosinophils, T cells, B cells, and epithelial cells.
Roles and Functions of Th9 Cells
Th9 cells have been primarily associated with allergic and autoimmune diseases, as well as certain types of cancers. The functions of Th9 cells include:
- Promotion of allergic responses: Th9 cells contribute to the development of allergic inflammation by enhancing mast cell activation, eosinophil recruitment, and IgE production.
- Autoimmunity: Th9 cells have been implicated in autoimmune diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), multiple sclerosis (MS), and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). They may contribute to tissue damage and inflammation in these conditions.
- Tumor immunity: Th9 cells have shown potential in anti-tumor immune responses. IL-9 produced by Th9 cells can enhance the activation and cytotoxicity of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) and promote anti-tumor immune responses.
Interactions with Other Cells
Th9 cells can interact with other immune cells and influence their functions. For example:
- Mast cells: IL-9 produced by Th9 cells can stimulate mast cell activation and degranulation, leading to the release of allergic mediators.
- Eosinophils: Th9-derived IL-9 can promote eosinophil recruitment and activation, contributing to eosinophilic inflammation seen in allergic diseases.
- B cells: IL-9 can influence B cell differentiation and antibody production, particularly IgE class switching.
Transdifferentiation and Plasticity of Th9 Cells
- Th9 cells can exhibit plasticity and differentiate into other Th cell subsets under certain conditions. For example, they can convert into Th2 cells or Th17 cells, depending on the inflammatory milieu and the presence of specific cytokines.
Understanding the biology of Th9 cells is crucial for unraveling their roles in immune responses, allergic diseases, autoimmunity, and cancer. Further research is needed to fully characterize Th9 cell differentiation, plasticity, and their interactions with other immune cells. This knowledge may provide insights into potential therapeutic strategies targeting Th9 cells for the treatment of various diseases.
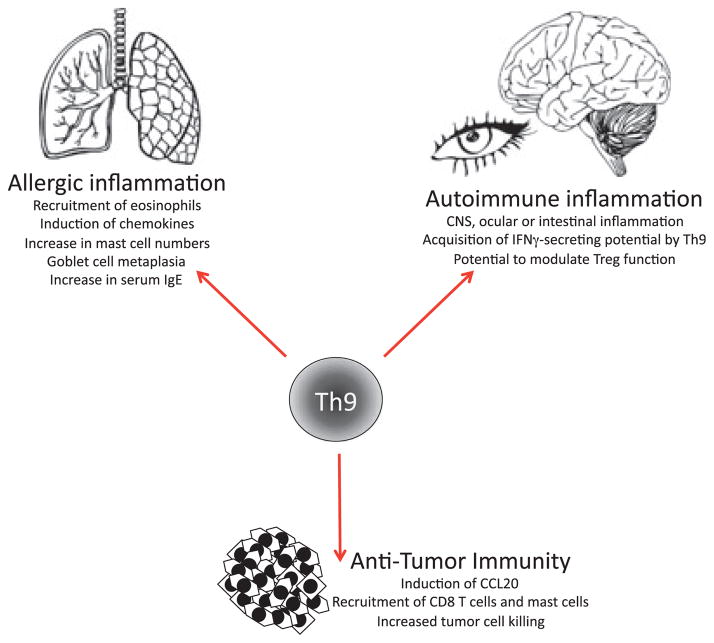 Fig.2 Functions of Th9 cells. (Kaplan MH, 2013)
Fig.2 Functions of Th9 cells. (Kaplan MH, 2013)
Molecules Associated with Th9 Cells Functions
Several molecules are associated with the functions of Th9 cells. These molecules play important roles in Th9 cell differentiation, maintenance, and effector functions. Here are some key molecules associated with Th9 cells (These molecules are just examples.):
| Key molecules type | Key molecules and functions |
|---|---|
| Interleukin-9 (IL-9) | IL-9 is the signature cytokine produced by Th9 cells. It plays a central role in Th9 cell-mediated immune responses. IL-9 has pleiotropic effects on various immune cells and has been implicated in allergic inflammation, autoimmunity, and anti-tumor immune responses. IL-9 promotes mast cell activation, eosinophil recruitment, B cell differentiation, and tissue remodeling. |
| PU.1 and IRF4 | These transcription factors are critical for Th9 cell differentiation. PU.1 and IRF4 are activated during Th9 cell differentiation, driving the expression of Th9-associated genes, including IL-9. They work cooperatively to promote Th9 cell lineage commitment and suppress the expression of other T helper cell lineage-specific transcription factors. |
| Transforming Growth Factor-beta (TGF-β) | TGF-β is a cytokine that plays a crucial role in Th9 cell differentiation. It acts as a key inducer of Th9 cells when combined with IL-4 or IL-1β. TGF-β signaling promotes the expression of PU.1 and IRF4, facilitating Th9 cell commitment and IL-9 production. |
| IL-4 | IL-4 can synergize with TGF-β to induce Th9 cell differentiation. IL-4 signaling through the IL-4 receptor promotes the activation of STAT6 (Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 6), leading to the expression of Th9-associated genes, including IL-9. IL-4 can also enhance Th2 cell plasticity, influencing the balance between Th2 and Th9 cell differentiation. |
| Interferon Regulatory Factor 8 (IRF8) | IRF8 is a transcription factor that negatively regulates Th9 cell differentiation. It inhibits Th9 cell development by directly suppressing the expression of PU.1 and IRF4. Loss of IRF8 enhances Th9 cell differentiation, leading to increased IL-9 production. |
| Notch Signaling Pathway Moleclars | Activation of the Notch signaling pathway has been implicated in Th9 cell differentiation. Notch ligands expressed on antigen-presenting cells, such as dendritic cells, can interact with Notch receptors on CD4+ T cells, promoting Th9 cell differentiation. Notch signaling regulates the expression of PU.1 and IRF4, contributing to Th9 cell commitment. |
| Epigenetic Regulators | Epigenetic modifications, such as DNA methylation and histone acetylation, play a crucial role in Th9 cell differentiation and maintenance. Enzymes involved in epigenetic regulation, including DNA methyltransferases (DNMTs) and histone deacetylases (HDACs), can modulate the expression of key Th9-associated genes, influencing Th9 cell functions. |
Understanding the molecular basis of Th9 cell functions and the interplay between these molecules is essential for deciphering the mechanisms underlying Th9 cell-mediated immune responses. Targeting these molecules or their signaling pathways may offer potential therapeutic strategies for modulating Th9 cell responses in various diseases, including allergic disorders, autoimmunity, and cancer.
Role of Th9 Cell-Associated Molecules in Disease Onset and Progression
Th9 cell-associated molecules play significant roles in the onset and progression of various diseases. Here are some examples of how these molecules contribute to disease pathogenesis:
Allergic Diseases
Th9 cells and their associated molecules have been implicated in the development of allergic diseases, such as asthma, allergic rhinitis, and atopic dermatitis. Excessive Th9 cell differentiation and IL-9 production can lead to enhanced allergic inflammation. IL-9 promotes mast cell activation, eosinophil recruitment, and IgE production, which contribute to the allergic cascade. Additionally, Th9-associated molecules, including TGF-β, IL-4, and Notch signaling, play crucial roles in promoting Th9 cell differentiation and amplifying allergic responses.
Autoimmune Diseases
Th9 cells and their associated molecules have been implicated in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases, including systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), multiple sclerosis (MS), and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Th9 cells can contribute to autoimmunity through IL-9-mediated effects on immune cells and tissues. IL-9 can promote B cell activation and antibody production, leading to the generation of autoantibodies in SLE. In MS and IBD, Th9 cells and IL-9 may contribute to tissue inflammation and damage.
Cancer
Th9 cells and their associated molecules have shown potential in anti-tumor immune responses. IL-9 produced by Th9 cells can enhance the activation and cytotoxicity of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs), promoting anti-tumor immune responses. Th9 cells can also recruit and activate other immune cells, such as eosinophils, which have been associated with anti-tumor effects. Modulating Th9 cell-associated molecules, such as IL-9 and TGF-β, may hold promise for developing immunotherapeutic strategies against cancer.
Inflammatory Disorders
Th9 cells and their associated molecules have been implicated in various inflammatory disorders, such as chronic rhinosinusitis, psoriasis, and ulcerative colitis. Th9 cells and IL-9 have been detected in inflamed tissues in these conditions. IL-9 can promote tissue inflammation, immune cell recruitment, and tissue remodeling, contributing to disease pathogenesis.
Infectious Diseases
Th9 cells and their associated molecules may play roles in the immune response against certain infectious agents. For example, Th9 cells have been observed in the context of helminth infections, where IL-9 can contribute to the expulsion of parasites. However, the role of Th9 cells in infectious diseases is still an area of active research and requires further investigation.
Understanding the role of Th9 cell-associated molecules in disease onset and progression provides insights into the underlying mechanisms of immune dysregulation and inflammation. Targeting these molecules or their signaling pathways may offer potential therapeutic strategies for modulating Th9 cell responses and controlling disease pathogenesis. However, it is important to note that the precise roles of Th9 cells and their associated molecules in specific diseases can vary and may be influenced by the complex interplay of other immune cells and factors within the disease microenvironment.
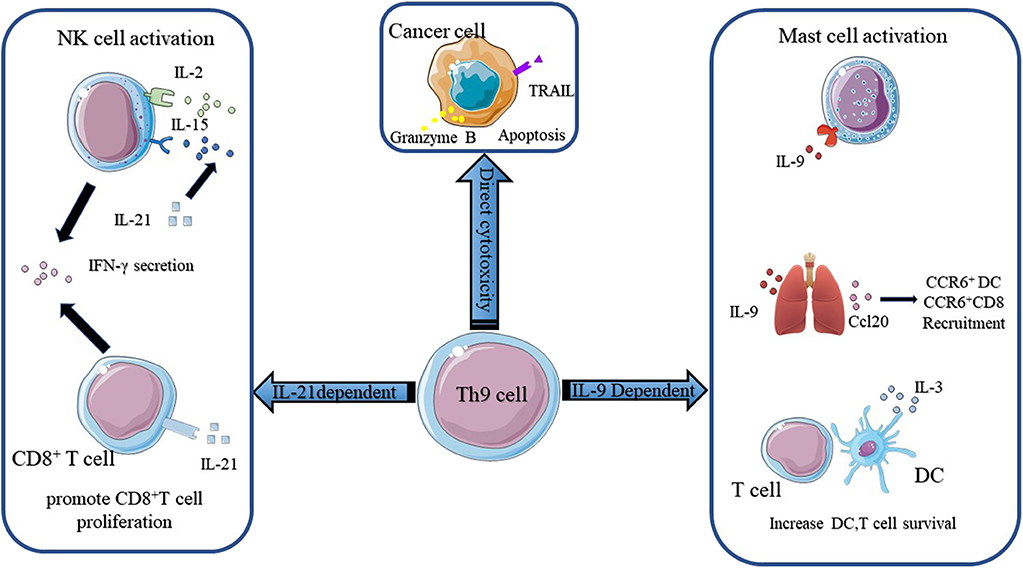 Fig.3 The mechanisms of Th9 cells in anti-tumor immunity. The anti-tumor function of Th9 cells mainly relies on IL-9 and IL-21. (Chen T, et al., 2020)
Fig.3 The mechanisms of Th9 cells in anti-tumor immunity. The anti-tumor function of Th9 cells mainly relies on IL-9 and IL-21. (Chen T, et al., 2020)
For more information, please explore our website or contact us today to learn more about how we can support your research endeavors.
Related References
- Chen J, Guan L, Tang L, et al. T Helper 9 Cells: A New Player in Immune-Related Diseases. DNA Cell Biol. 2019;38(10):1040-1047.
- Kaplan MH. Th9 cells: differentiation and disease. Immunol Rev. 2013;252(1):104-115.
- Chen T, Guo J, Cai Z, et al. Th9 Cell Differentiation and Its Dual Effects in Tumor Development. Front Immunol. 2020;11:1026.

