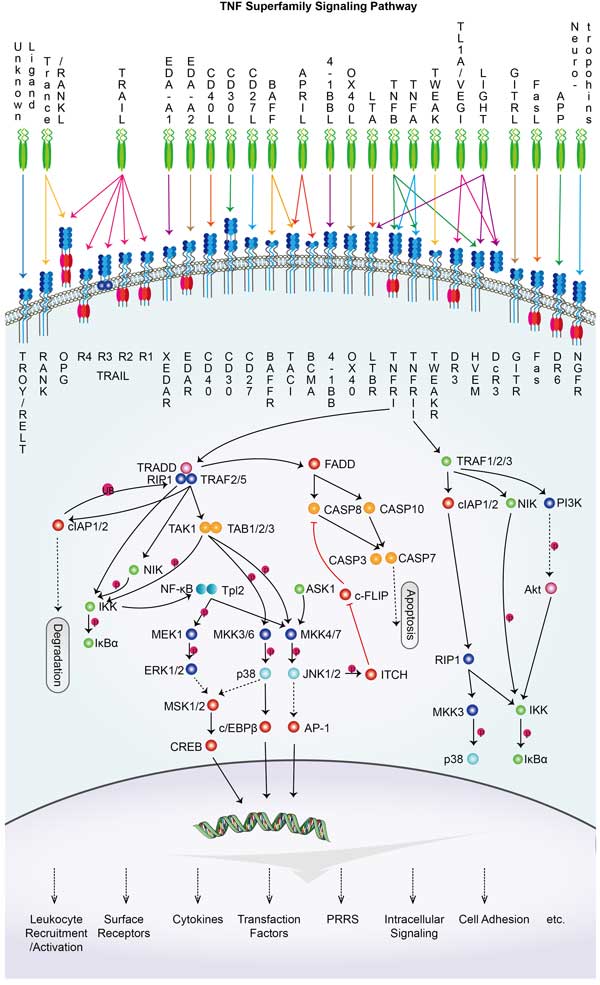
Tnfsf4
-
Official Full Name
tumor necrosis factor (ligand) superfamily, member 4 -
Overview
OX40L (Tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 4; or CD252) is the endogenous ligand of the OX40 receptor. OX40 is localized on activated T-cells and propagates the immune response by promoting division and survival of T-cells, thereby increasing the population of memory CD4 and CD8 T cells produced in response to antigen detection. The OX40/OX40L may also regulate cytokine production and suppress the activity of T-regulatory cells. OX40/OX40L is therefore an important mediator of the immune response. Previous studies have suggested that OX40 signaling maybe involved in the development of autoimmune diseases. -
Synonyms
TNFSF4;tumor necrosis factor (ligand) superfamily, member 4;tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 4;OX40 ligand;atherosclerosis 1;tax-transcriptionally activated glycoprotein 1 ligand;Ath1;gp34;Ath-1;Ox40l;TXGP1;CD134L;OX-40L;Txgp1l;CD134L;CD 252;CD134;CD134 ligand;CD134L;CD252;CD252 antigen;glycoprotein 34 kd;glycoprotein Gp34;GP34;OX-40L;OX40 ligand;OX40L;TAX transcriptionally-activated glycoprotein 1;TNFL4;TNFSF4;tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 4;TXGP1;tumor necrosis factor (ligand) superfamily, member 4
Recombinant Proteins
- Mouse
- Human
- Monkey
- Cynomolgus
- Cynomolgus/Rhesus macaque
- Rat
- Oryctolagus cuniculus
- Rabbit
- Macaca mulatta
- HEK293
- Hi-5 Insect Cells
- Human Cells
- E.coli
- Insect Cells
- Mammalian Cells
- His
- Fc
- mFc
- rFc
- Non
- Flag
- Avi
- DDK
- Myc
Background
What is TNFSF4 protein?
TNFSF4 gene (TNF superfamily member 4) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 1 at locus 1q25. TNFSF4 is a protein that belongs to the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) ligand family. It plays a role in T cell-antigen-presenting cell (APC) interactions and is involved in mediating the adhesion of activated T cells to endothelial cells. This cytokine has the capability to bind to TNFRSF4 and co-stimulates T-cell proliferation and cytokine production. Furthermore, TNFSF4 has been identified as a potential target for immunotherapy, particularly in the context of breast carcinomas, due to its aberrant expression patterns and its association with shorter overall survival and disease-free survival. The TNFSF4 protein is consisted of 183 amino acids and TNFSF4 molecular weight is approximately 21.1 kDa.
What is the function of TNFSF4 protein?
TNFSF4, also known as OX40 Ligand, binds to its receptor TNFRSF4 (OX40), which is predominantly expressed on activated T cells. This interaction provides a co-stimulatory signal that enhances T cell proliferation, survival, and cytokine production. By engaging with its receptor, TNFSF4 helps regulate the immune response, promoting the differentiation of T cells into effector and memory cells, which is critical for long-term immunity. High expression of TNFSF4 is associated with shorter overall survival and disease-free survival, and it is considered a potential target for immunotherapy due to its ability to reactivate the immune response and potentially inhibit cancer stem cells. TNFSF4 has been found to correlate with ALDH1A1 expression, which is associated with cancer stem cells.
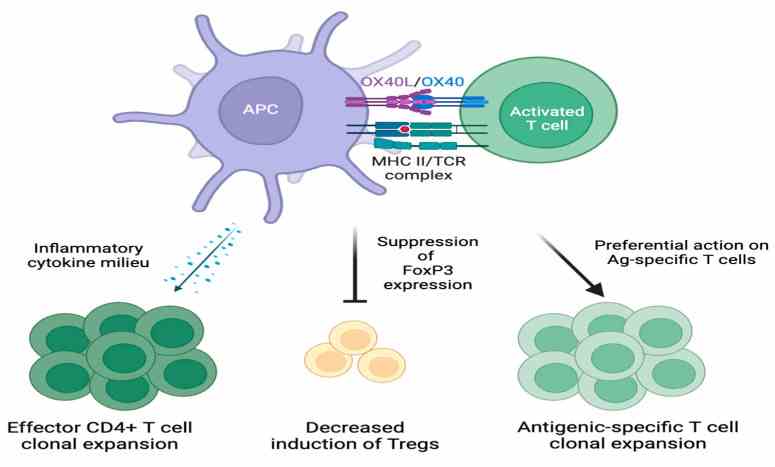
Fig1. Downstream effects of OX40-OX40L signaling. (Kaviyon Sadrolashrafi, 2024)
TNFSF4 Related Signaling Pathway
TNFSF4 binds to its receptor, OX40 (TNFRSF4), which is expressed on the surface of activated T cells. The engagement of TNFSF4 with OX40 can modulate immune responses by enhancing the activity of T cells and potentially reducing the suppressive activity of regulatory T cells (Tregs), which can be important in the context of cancer immunotherapy. TNFSF4 has been implicated in antitumor immunity. Its interaction with OX40 on T cells can enhance T cell-mediated immunity against cancer cells. The signaling through OX40 induced by TNFSF4 can promote cell survival by inhibiting apoptosis and promoting cell proliferation, which is important for maintaining the T cell population during an immune response. TNFSF4 may also interact with other members of the TNF family and their receptors, potentially contributing to a complex network of signals that regulate immune cell function and homeostasis.
TNFSF4 Related Diseases
Abnormal expression or dysfunction of TNFSF4 has been associated with a variety of diseases, especially autoimmune diseases. For example, polymorphisms in the TNFSF4 gene have been linked to Sjogren's syndrome and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). In addition, the expression of TNFSF4 in breast cancer is also of interest to investigators because it may be involved in tumor immune escape and the regulation of anti-tumor immune responses. Overexpression of TNFSF4 was associated with shorter overall survival and disease-free survival, suggesting that it may play a role in tumor development and immune escape.
Bioapplications of TNFSF4
In cancer therapy, TNFSF4 is being investigated as a potential target for immune checkpoint inhibitors to enhance the immune response of T cells against tumors, particularly in the treatment of solid tumors such as breast cancer. In addition, agonist antibodies to TNFSF4 are being evaluated in clinical trials to determine whether they can promote the activation and proliferation of T cells, thereby enhancing the attack on tumors. In the field of cell therapy, the expression of TNFSF4 can enhance the effectiveness of treatments such as T cell therapy by promoting the persistence and function of T cells to improve the effectiveness of treatment for disease. In addition, the signaling pathway of TNFSF4 also shows a potential role in stem cell regulation and the control of cancer stem cells, which offers the possibility of developing new therapeutic approaches.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Jason Roszik, 2019
TNFSF4 is a co-stimulatory checkpoint protein expressed by several types of immune and non-immune cells, and was shown in the past to enhance the anti-neoplastic activity of T cells. Here, researchers assessed its expression in melanoma and its association with outcome in locally advanced and metastatic disease. TNFSF4 mRNA is expressed in melanoma cell lines and melanoma samples, including those with low lymphocytic infiltrates, and is not associated with the ulceration status of the primary tumor. Low expression of TNFSF4 mRNA is associated with worse prognosis in all melanoma patients and in the cohorts of stage III and stage IIIc-IV patients. Low expression of TNFSF4 mRNAs is also associated with worse prognosis in the subgroup of patients with low lymphocytic infiltrates, suggesting that tumoral TNFSF4 is associated with outcome. TNFSF4 expression was not correlated with the expression of other known checkpoint mRNAs. Last, metastatic patients with TNFSF4 mRNA expression within the lowest quartile have significantly worse outcome on anti-PD1 treatment, and a significantly lower response rate to these agents.
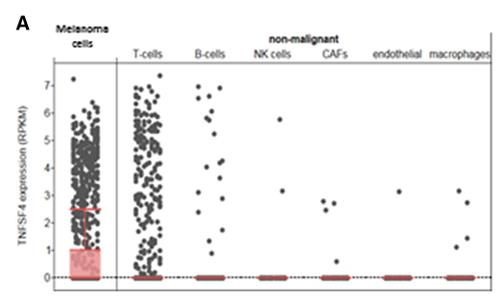
Fig1. The expression of TNFSF4 mRNA.
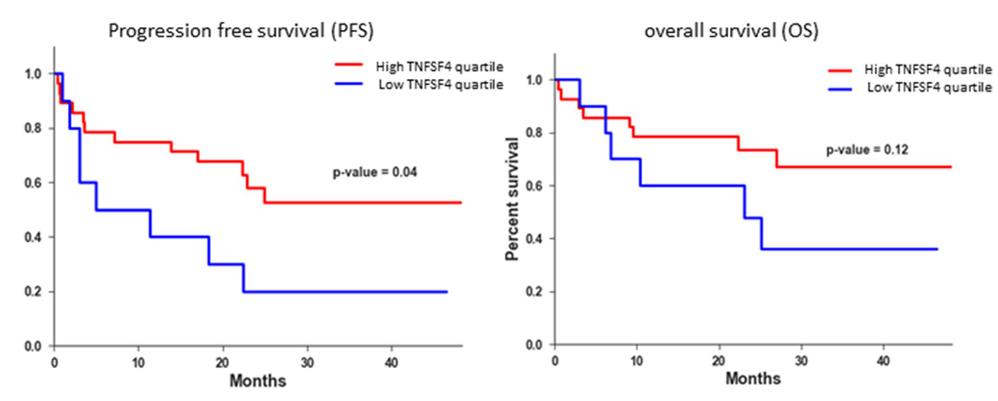
Fig2. Survival of patients with metastatic melanoma treated with anti-PD1 antibodies.
Case Study 2: Trivendra Tripathi, 2019
Graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) is one of the major obstacles for the success of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Here, researchers report that the interaction between OX40L and OX40 is of critical importance for both induction and progression of acute GVHD (aGVHD) driven by human T cells. Anti-human OX40L monoclonal antibody (hOX40L) treatment could thus effectively reduce the disease severity in a xenogeneic-aGVHD (x-aGVHD) model in both preventative and therapeutic modes. Mechanistically, blocking OX40L-OX40 interaction with an anti-hOX40L antibody reduces infiltration of human T cells in target organs, including liver, gut, lung, and skin. It also decreases IL-21- and TNF-producing T cell responses, while promoting regulatory T cell (Treg) responses without compromising the cytolytic activity of CD8+ T cells.
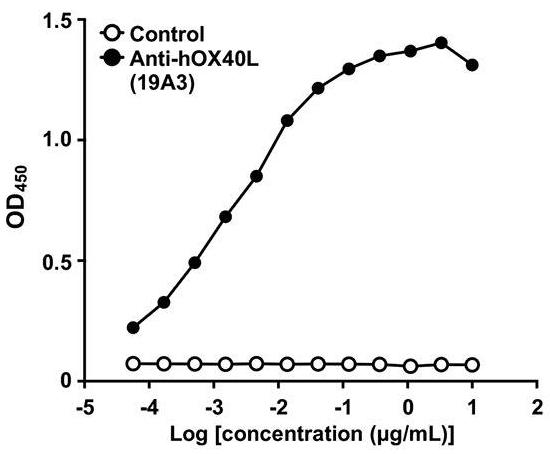
Fig3. Assessment of anti-hOX40L antibody specificity by ELISA using plates coated with hOX40L protein.
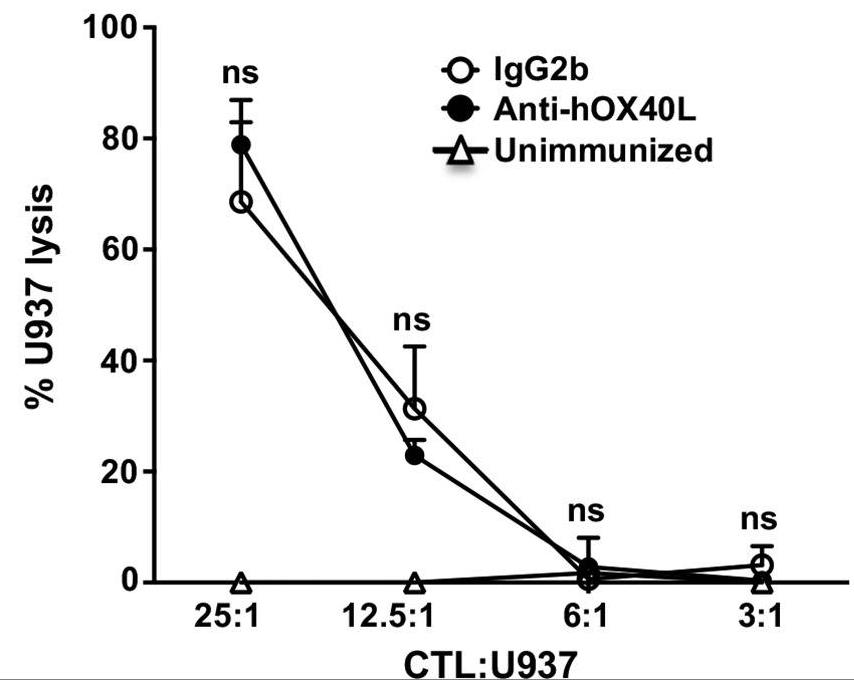
Fig4. Anti-hOX40L treatment does not impair CD8+ T cell functions.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (TNFSF4-490H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (TNFSF4-142H)
Involved Pathway
Tnfsf4 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways Tnfsf4 participated on our site, such as Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with Tnfsf4 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction | CCR3,TNFRSF10D,TGFB2,BMPR2B,TSLP,VEGFB,FLT1,PLEKHO2,IL23,TGFBR1A |
Protein Function
Tnfsf4 has several biochemical functions, for example, cytokine activity,receptor binding,tumor necrosis factor receptor binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by Tnfsf4 itself. We selected most functions Tnfsf4 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with Tnfsf4. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| tumor necrosis factor receptor binding | TNFSF13B,TNFSF13,TRAF1,TNFSF11,TNFB,FADD,TRAP1,TNFSF10L,LTB,EDA |
| cytokine activity | TNFSF15,IFNPHI1,FAM3D,Ccl9,LFT1,IL16,IL8L2,CCL20A.3,INHBAB,SPAW |
| tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily binding | FADD,TNFSF11,TNFSF18,TNFSF9 |
| receptor binding | ALCAM,NPPC,HRG,NPY,TENM2,RASA1,TRDN,LBP,TGFB2,NRG4 |
Interacting Protein
Tnfsf4 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with Tnfsf4 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of Tnfsf4.
Tnfsf4 Related Signal Pathway
Resources
Gene Families
Research Area
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Mahlios, J; De la Herran-Arita, AK; et al. The autoimmune basis of narcolepsy. CURRENT OPINION IN NEUROBIOLOGY 23:767-773(2013).
- Kim, K; Bang, SY; et al. High-density genotyping of immune loci in Koreans and Europeans identifies eight new rheumatoid arthritis risk loci. ANNALS OF THE RHEUMATIC DISEASES 74:-(2015).