Inflammasome
Related Symbol Search List
- AIM2
- Bcl-2
- BCL2L1
- BRCC3
- CARD16
- CARD17
- CARD18
- CASP1
- CASP12
- COP1
- RFWD2
- GBP5
- HSP90AA1
- IL1B
- NAIP
- NLRC4
- NLRP1
- NLRP10
- NLRP7
- NOD2
- POP1
- PRKCD
- PYCARD
- PYDC2
- SUGT1
Immunology Background
Available Resources for Inflammasome Research
Creative BioMart is committed to being at the forefront of research in the field of inflammasomes, continuously updating our product portfolio and resources to provide researchers with the latest tools and information, driving progress in this important area of knowledge.
- Our product portfolio includes recombinant proteins and other crucial products, offering vital support for understanding the function and mechanisms of inflammasomes.
- Our team of experts possesses rich knowledge and professional experience in inflammasome research, dedicated to providing personalized solutions to meet the specific needs of each researcher.
- In addition, we provide extensive resource support covering involved pathways, protein functions, interacting proteins, and other valuable information, aimed at helping researchers gain a comprehensive understanding of the relationship between inflammasomes and inflammation, ultimately enhancing their research outcomes.
Our Featured Products
- Recombinant Human AIM2 protein(Met1-Thr343), GST-tagged
- Recombinant Human AIM2 Protein, His-tagged
- Recombinant Human BCL2 protein, GST-tagged
- Recombinant Human BCL2L1, His tagged
- Recombinant Human BRCC3, His-tagged
- Recombinant Human CASP1 protein, His-tagged
- Recombinant Human CASP1, GST-tagged
- Recombinant Human COP1 protein, His-tagged
- Recombinant Human GBP5, GST-tagged
- Recombinant Human HSP90AA1 protein (Glu535-Asp732)
- Recombinant Human IL1B protein
- Active Recombinant Human IL1B Protein
- Recombinant Rat IL1B, His tagged
- Active Recombinant Cynomolgus IL1B Protein
- Recombinant Human NLRP10 protein, His-tagged
- Recombinant Human NLRP10 protein, GST-tagged
- Recombinant Human NLRP7, His-tagged
- Recombinant Human PRKCD, His-tagged
Whether you are studying the role of inflammasome in inflammation, disease pathology, drug discovery, or therapeutic development, Creative BioMart is here to support your research. We are dedicated to helping researchers achieve their scientific goals and make meaningful contributions to the field of inflammasome research. Contact us today to learn more about our products and resources.
About Inflammasome
The inflammasome is a crucial component of the innate immune system that plays a central role in initiating and regulating inflammation. It is a multiprotein complex that functions as a sensor for various danger signals, such as microbial components and host-derived molecules associated with cellular stress or damage. The activation of the inflammasome leads to the production and release of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as interleukin-1β (IL-1β) and interleukin-18 (IL-18), and can contribute to the development of inflammatory diseases.
Understanding the inflammasome and its role in inflammation provides valuable insights into the mechanisms underlying inflammatory diseases. Therapeutic interventions targeting the inflammasome pathway hold promise for the development of novel treatments to modulate inflammation and potentially alleviate the symptoms of inflammatory disorders.
Structure of the Inflammasome
- Sensor proteins: The inflammasome is composed of cytoplasmic sensor proteins, which recognize specific danger signals. These sensor proteins include NOD-like receptors (NLRs), such as NLRP1, NLRP3, and NLRC4, as well as absent in melanoma 2 (AIM2) and pyrin.
- Adapter protein: In addition to the sensor proteins, the inflammasome contains an adapter protein called ASC (apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a caspase recruitment domain). ASC bridges the interaction between the sensor proteins and the effector protein caspase-1.
- Effector protein: Caspase-1 is the effector protein of the inflammasome. Once activated, caspase-1 cleaves pro-IL-1β and pro-IL-18 into their active forms, which are then secreted to initiate the inflammatory response.
Activation of the Inflammasome
- Priming signal: The activation of the inflammasome requires a priming signal, usually provided by pattern recognition receptors (PRRs), such as Toll-like receptors (TLRs), which recognize microbial components or endogenous danger signals. This priming signal induces the transcription and synthesis of inflammasome components, including the sensor proteins and pro-IL-1β and pro-IL-18.
- Activation signal: The inflammasome is activated by specific danger signals that are recognized by the sensor proteins. These danger signals can include pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs), damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs), or other cellular stress signals. Upon recognition of the danger signal, the sensor proteins undergo conformational changes, leading to the recruitment and assembly of the inflammasome complex.
- Assembly and activation: The sensor proteins oligomerize and recruit ASC, forming a large molecular complex known as the inflammasome. This assembly allows the activation of caspase-1 within the inflammasome, leading to the cleavage and maturation of pro-IL-1β and pro-IL-18 into their active forms. Active IL-1β and IL-18 are then released from the cell to trigger inflammation.
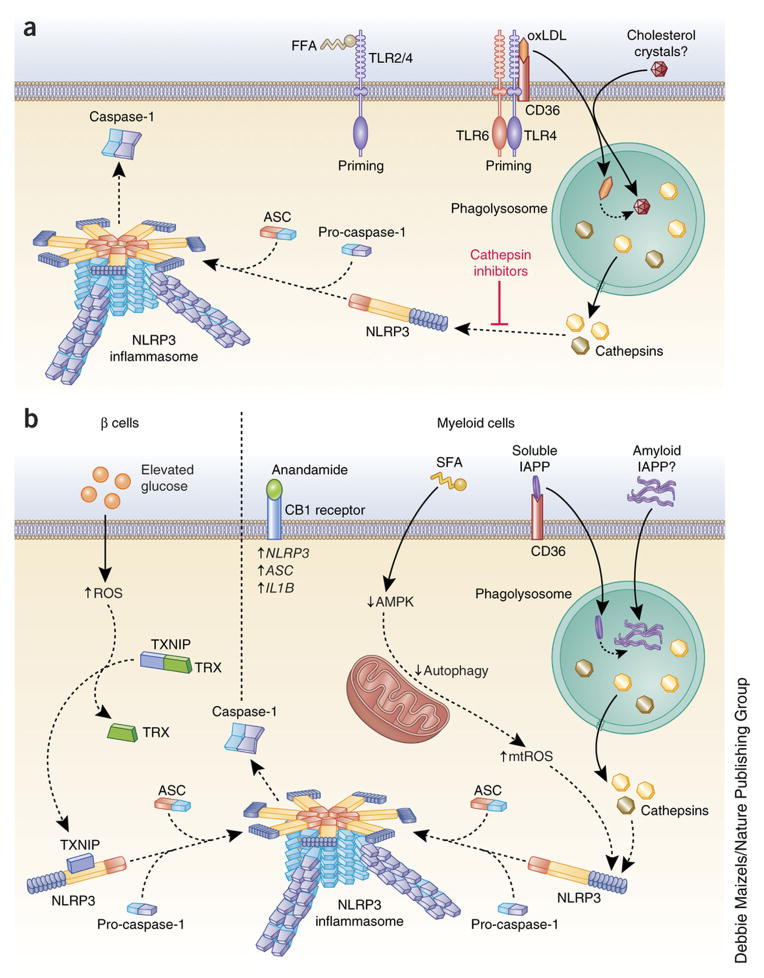 Fig.1 Mechanism of inflammasome activation in inflammatory disease. (Guo H, et al., 2015)
Fig.1 Mechanism of inflammasome activation in inflammatory disease. (Guo H, et al., 2015)
Functions of the Inflammasome
- Pro-inflammatory cytokine production: The main function of the inflammasome is to promote the production and release of pro-inflammatory cytokines, particularly IL-1β and IL-18. These cytokines play crucial roles in initiating and amplifying the inflammatory response by activating immune cells, promoting the recruitment of immune cells to the site of inflammation, and inducing the production of other inflammatory mediators.
- Pyroptosis: In addition to cytokine production, inflammasome activation can lead to a form of programmed cell death called pyroptosis. Pyroptosis is a highly inflammatory form of cell death that helps to eliminate infected cells and promote the clearance of pathogens.
- Role in disease: Dysregulation of the inflammasome has been implicated in the pathogenesis of various inflammatory disorders, including autoinflammatory diseases, infectious diseases, metabolic disorders, and neurodegenerative diseases. Excessive or prolonged activation of the inflammasome can contribute to chronic inflammation and tissue damage.
Inflammasomes and Innate Immunity
- Sensing danger signals: Inflammasomes are cytoplasmic multiprotein complexes that function as sensors for danger signals, including microbial components and host-derived molecules associated with cellular stress or damage. The activation of inflammasomes occurs in response to the recognition of these danger signals by specific sensor proteins, such as NLRs.
- Pro-inflammatory cytokine production: Upon activation, inflammasomes lead to the activation of caspase-1, which cleaves pro-IL-1β and pro-IL-18 into their active forms. These cytokines, IL-1β and IL-18, are potent pro-inflammatory mediators that play crucial roles in initiating and amplifying the inflammatory response. They activate immune cells, promote the recruitment of immune cells to the site of inflammation, and induce the production of other inflammatory mediators.
- Pyroptosis: In addition to cytokine production, inflammasome activation can also trigger a form of programmed cell death called pyroptosis. Pyroptosis is a highly inflammatory form of cell death that helps to eliminate infected cells and promote the clearance of pathogens. It involves the release of cytoplasmic contents, including pro-inflammatory cytokines, which further contribute to the immune response.
The Role of Inflammasomes in Host Defense and Disease
- Pathogen clearance: Inflammasome activation and subsequent cytokine production contribute to the recruitment and activation of immune cells, such as neutrophils and macrophages, which are essential for pathogen clearance. These immune cells phagocytose and eliminate invading pathogens, helping to control infections.
- Inflammatory diseases: Dysregulation of inflammasome activation or excessive cytokine production can lead to chronic inflammation and contribute to the development of inflammatory diseases. Inflammasome dysfunction has been implicated in a range of conditions, including autoinflammatory disorders, infectious diseases, metabolic disorders, and neurodegenerative diseases.
References:
- de Zoete MR, Palm NW, Zhu S, Flavell RA. Inflammasomes. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2014;6(12):a016287. Published 2014 Oct 16. doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a016287.
- Guo H, Callaway J B, Ting J P Y. Inflammasomes: mechanism of action, role in disease, and therapeutics[J]. Nature medicine, 2015, 21(7): 677-687.
- Zheng D, Liwinski T, Elinav E. Inflammasome activation and regulation: toward a better understanding of complex mechanisms[J]. Cell discovery, 2020, 6(1): 36.
- Jamilloux Y, Henry T. The inflammasomes: platforms of innate immunity[J]. Medecine Sciences: M/S, 2013, 29(11): 975-984.

