Th22 Cells
Related Symbol Search List
- CCRL2
- CD4
- TNFa
- CD3e
- IL-10
- IL-13
- IL22
- Il6
- CD3G
- IL21
- IL21R
- Il6ra
- STAT3
- CNOT6
- Tgfb1
- TGFBR2
- ACKR2
- AHR
- CCL15
- CCL7
Immunology Background
Available Resources Related to Th22 Cells
Creative BioMart is dedicated to supporting and advancing Th22 cell research. We provide a comprehensive range of high-quality products, customized services, and valuable resources to facilitate scientific investigations focused on Th22 cells. Our commitment is to empower researchers with the tools and knowledge necessary for understanding the biology, functions, and therapeutic potential of Th22 cells in various diseases.
| We offer a wide range of high-quality research products designed specifically for the study of Th22 cells, including recombinant proteins, GMP proteins, cell and tissue lysates, chromatography reagents, antibodies, and small molecules targeting key Th22 cell markers, cytokines, and signaling pathways. Use our specialized tools and knowledge to unravel the molecular mechanisms behind Th22 cell differentiation, function, and regulation. | |
| Our team of experienced scientists provides customized services to meet specific research needs. We offer custom protein expression and purification, antibody production, and more. These services ensure reliable and reproducible results for your Th22 cell research. | |
| We have collected a range of resources related to Th22 cell research to promote a deeper understanding of Th22 cell biology, including protein functions, protein interactions, involved pathways, and other valuable information. Our dedicated customer support team is always available to answer questions, provide technical assistance, and guide you in selecting the most appropriate products and services for your Th22 cell research program. |
About Th22 Cells
Th22 cells are a subset of T helper cells that have distinct characteristics and functions in the immune system. They were identified more recently compared to other T helper cell subsets, such as Th1, Th2, and Th17 cells. Th22 cells are primarily characterized by their production of the cytokine interleukin-22 (IL-22). Here is an introduction to Th22 cells and their role in immune responses:
Origin of Th22 Cells
Th22 cells are derived from naïve CD4+ T cells that differentiate into Th22 cells under specific cytokine and signaling conditions. The differentiation of Th22 cells is influenced by several factors:
- Cytokines: Th22 cell differentiation is driven by a combination of cytokines, including IL-6, tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), IL-1β, and IL-23. These cytokines promote the expression of the transcription factor aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR) and the lineage-specific transcription factor RORγt, which are crucial for Th22 cell development.
- Signal Transduction: Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) signaling pathway is involved in Th22 cell differentiation. IL-6 and IL-23 activate STAT3, which supports the expression of RORγt and the subsequent commitment to the Th22 cell lineage.
Functions of Th22 Cells
- Cytokine Production: Th22 cells are characterized by their ability to produce interleukin-22 (IL-22), which is their signature cytokine. IL-22 acts on various target cells, including epithelial cells, fibroblasts, and immune cells, to mediate diverse effects. It promotes tissue repair, barrier function maintenance, and the production of antimicrobial peptides. However, excessive IL-22 production can contribute to tissue inflammation and pathology.
- Tissue Homeostasis: Th22 cells are involved in maintaining tissue homeostasis, particularly at barrier surfaces such as the skin and mucosal linings. IL-22 produced by Th22 cells helps preserve epithelial integrity, regulate tissue regeneration, and support antimicrobial defense mechanisms.
- Inflammation and Immunity: Th22 cells have pro-inflammatory properties and can contribute to immune responses in various diseases. They can recruit and activate other immune cells, including neutrophils and macrophages, and regulate the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines.
Regulatory Mechanisms
Several regulatory mechanisms control the development, maintenance, and function of Th22 cells:
- Transcriptional Regulation: Transcription factors, such as RORγt and AHR, are key regulators of Th22 cell differentiation and function. They control the expression of genes associated with Th22 cell identity and cytokine production.
- Cytokine Cross-Talk: The cytokine environment influences Th22 cell development and function. IL-23, IL-1β, and TNF-α are critical for Th22 cell differentiation, while other cytokines, such as interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) and IL-17A, can negatively regulate Th22 cell responses.
- Immune Cell Interactions: Th22 cells interact with other immune cells, such as dendritic cells, regulatory T cells (Tregs), and Th17 cells, through cell-to-cell contact and cytokine signals. These interactions can modulate Th22 cell differentiation and function.
- Epigenetic Regulation: Epigenetic modifications, including DNA methylation and histone modifications, play a role in Th22 cell differentiation and stability. They can influence the accessibility of key genes involved in Th22 cell development and function.
Understanding the regulatory mechanisms of Th22 cells is crucial for targeting their function and developing therapeutic strategies in various diseases. Modulating Th22 cell responses, cytokine signaling, and immune cell interactions may offer potential avenues for the treatment of autoimmune diseases, inflammatory disorders, and other conditions where Th22 cells are implicated.
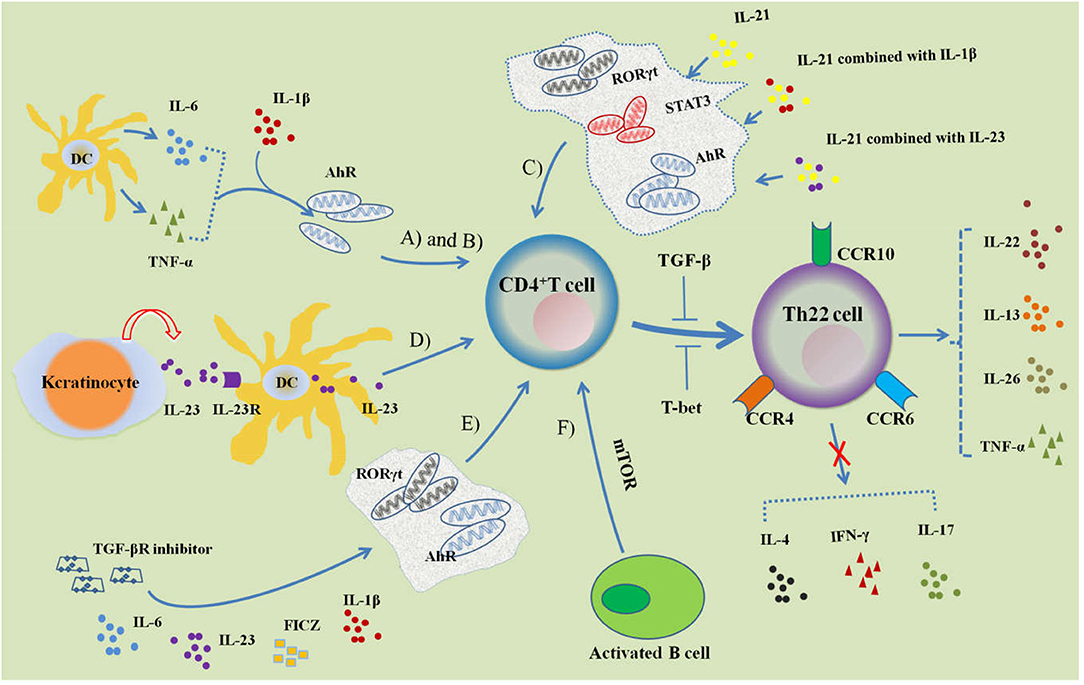 Fig.1 Regulation of Th22 cell differentiation. (Gong J, et al., 2021)
Fig.1 Regulation of Th22 cell differentiation. (Gong J, et al., 2021)
Key Molecules Involved in the Function of Th22 Cells
Th22 cells secrete certain cytokines such as IL-22, IL-13, and TNF-α, but not others, such as IL-17, IL-4, or interferon-γ (IFN-γ), and they express chemokine receptors CCR4, CCR6, and CCR10.
Several molecules play crucial roles in the regulation and function of Th22 cells. These molecules include cytokines, chemokines, transcription factors, and cell surface receptors. Here is a listing and description of some key molecules related to Th22 cells:
| Key molecules type | Functions |
|---|---|
| Interleukin-22 (IL-22) | IL-22 is the signature cytokine produced by Th22 cells. It plays a vital role in maintaining epithelial barrier integrity and defense against pathogens. IL-22 stimulates the production of antimicrobial peptides, mucins, and tight junction proteins, contributing to tissue repair and protection. |
| Interleukin-17 (IL-17) | While primarily associated with Th17 cells, IL-17 is also produced by Th22 cells in certain contexts. IL-17 contributes to the recruitment of immune cells, chronic inflammation, and tissue damage in autoimmune diseases and infections. |
| Interleukin-23 (IL-23) | IL-23 is an important cytokine involved in the differentiation and expansion of Th22 cells. It promotes the production of IL-22 and other Th22-related cytokines. IL-23 signaling is crucial for the maintenance and activation of Th22 cells in various immune responses. |
| Chemokine Receptor CCR4 | Th22 cells express the chemokine receptor CCR4, which guides their migration to specific tissues. CCR4 is involved in the recruitment of Th22 cells to the skin, lungs, and other sites of inflammation. |
| Chemokine Receptor CCR6 | Similar to CCR4, Th22 cells express CCR6, which is associated with their migration to specific tissues. CCR6 plays a role in the recruitment of Th22 cells to the skin, gut, and other mucosal tissues. |
| Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor (AhR) | AhR is a transcription factor that is important for Th22 cell differentiation and function. Activation of AhR by specific ligands promotes the production of IL-22 by Th22 cells. |
| Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 (STAT3) | STAT3 is a transcription factor that is critical for Th22 cell differentiation and maintenance. It is activated by IL-6 and IL-23 signaling, leading to the production of IL-22 and the acquisition of Th22 cell phenotype. |
| Retinoic Acid Receptor-Related Orphan Receptor Gamma T (RORγt) | RORγt is a transcription factor that controls the differentiation of Th22 cells. It is involved in the regulation of IL-22 production and the development of Th22 cell phenotype. |
These molecules collectively contribute to the development, maintenance, and function of Th22 cells. Their intricate regulation and interactions play crucial roles in immune responses, tissue homeostasis, and the pathogenesis of various diseases, including autoimmune disorders, infections, and tissue repair processes. Further research on these molecules and their signaling pathways will deepen our understanding of Th22 cell biology and pave the way for potential therapeutic interventions.
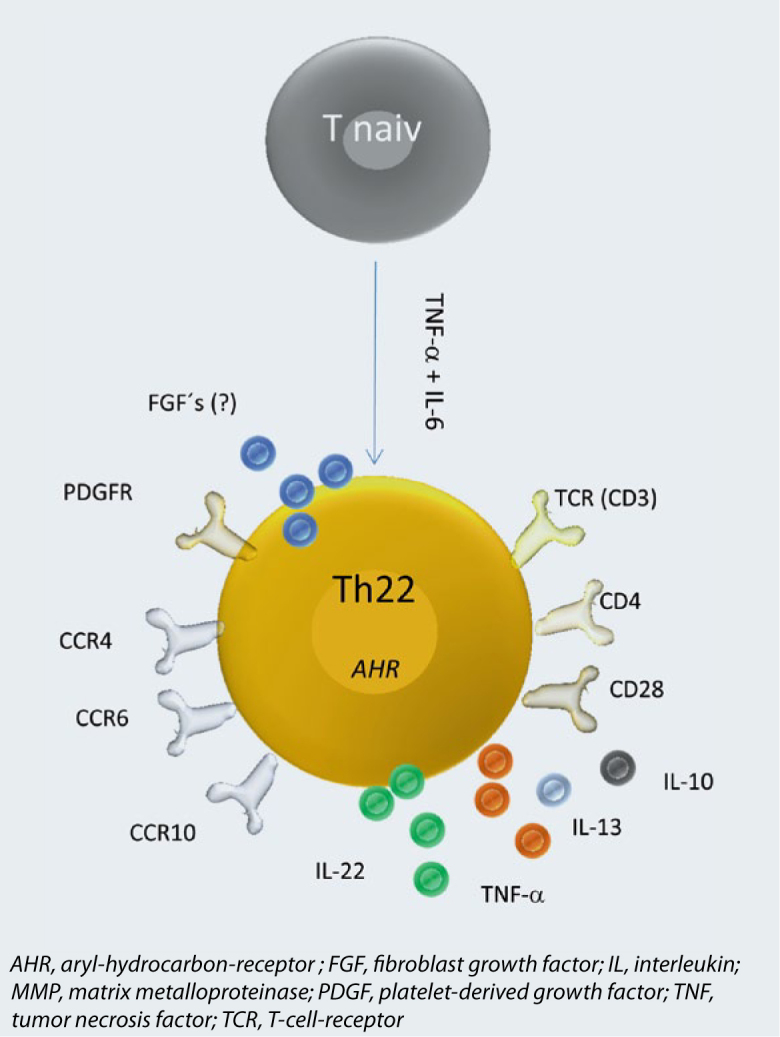 Fig.2 Phenotype of Th22 cells. (Eyerich K, et al., 2015)
Fig.2 Phenotype of Th22 cells. (Eyerich K, et al., 2015)
The Role of Th22 Cells and Related Molecules in Various Diseases
The role of Th22 cells and related molecules in various diseases is multifaceted, and their dysregulation can contribute to disease development and progression. Here is a detailed introduction to their role in different disease contexts:
Autoimmune Diseases
Th22 cells and IL-22 have been implicated in several autoimmune diseases. In psoriasis, Th22 cells are abundant in skin lesions and contribute to the development of the disease. IL-22 produced by Th22 cells promotes keratinocyte hyperproliferation and the formation of psoriatic plaques. Similarly, Th22 cells and IL-22 play a role in rheumatoid arthritis, where they contribute to chronic inflammation and joint damage. Inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) such as Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis also involve Th22 cells and IL-22, which contribute to intestinal inflammation and tissue damage.
Allergic Disorders
In atopic dermatitis, Th22 cells contribute to skin inflammation and impaired barrier function. IL-22 promotes epidermal hyperplasia and disrupts skin barrier integrity, contributing to the characteristic eczematous lesions. In asthma, Th22 cells have been detected in the lungs of asthmatic patients. IL-22 produced by Th22 cells may contribute to airway hyperresponsiveness, mucus production, and tissue remodeling.
Infectious Diseases
In fungal infections, such as Candida albicans, Th22 cells help control fungal growth and promote epithelial defense mechanisms. IL-22 enhances antimicrobial responses and tissue repair processes. Th22 cells and IL-22 also participate in the immune response against certain bacterial pathogens, including Staphylococcus aureus and Klebsiella pneumoniae.
Cancer
The role of Th22 cells and IL-22 in cancer is complex and still being elucidated. IL-22 can have both pro-tumor and anti-tumor effects depending on the specific context. It can promote tumor growth by inducing angiogenesis and suppressing anti-tumor immune responses. Conversely, IL-22 can enhance anti-tumor immune responses by activating immune cells and promoting the production of other cytokines. The involvement of Th22 cells and IL-22 in tumor immunity is an area of active research.
Other Diseases
Th22 cells and IL-22 have been implicated in other diseases as well. In chronic rhinosinusitis, Th22 cells and IL-22 contribute to persistent inflammation of the nasal and sinus passages. In liver diseases, including hepatitis B and C infections and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), Th22 cells and IL-22 may play a role in the immune response and tissue damage.
Understanding the role of Th22 cells and related molecules in various diseases provides insights into disease mechanisms and potential therapeutic targets. Modulating the activity of Th22 cells or targeting IL-22 signaling pathways may offer new strategies for the treatment of autoimmune diseases, allergic disorders, infectious diseases, and cancer. However, further research is needed to fully understand the complex roles of Th22 cells in different disease contexts and to develop targeted therapeutic interventions.
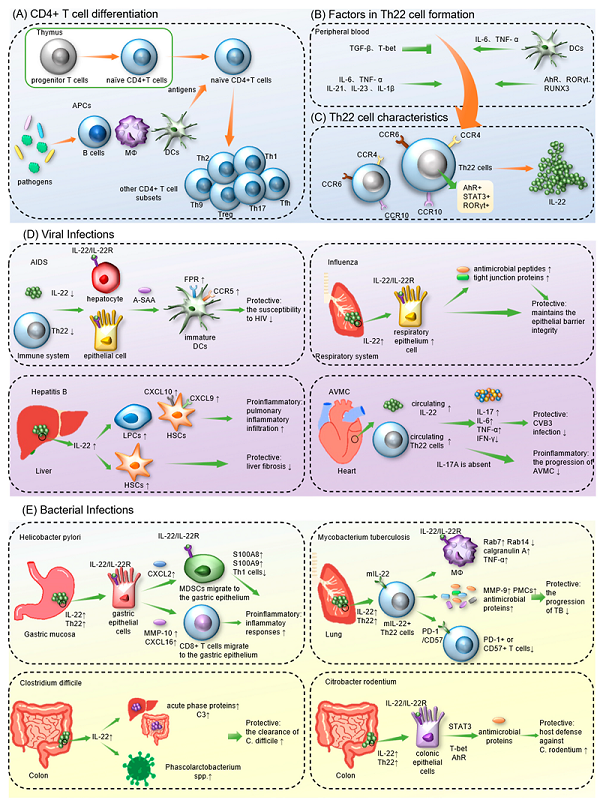 Fig.3 Formation of Th22 cells and IL-22 and the role of Th22/IL-22 in infectious diseases. (Zhang K, et al., 2023)
Fig.3 Formation of Th22 cells and IL-22 and the role of Th22/IL-22 in infectious diseases. (Zhang K, et al., 2023)
Creative BioMart is your trusted partner in advancing Th22 cell research. With our high-quality products, tailored services, and valuable resources, we aim to empower researchers to gain a deeper understanding of Th22 cell biology and their roles in various diseases. Together, we can pave the way for innovative therapies and treatments targeting Th22 cells, ultimately improving human health and well-being.
Visit our website or contact us today to learn more about our Th22 cell research resources and how we can support your scientific endeavors.
Related References
- Jia L, Wu C. The Biology and Functions of Th22 Cells. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2014;841:209-230.
- Gong J, Zhan H, Liang Y, He Q, Cui D. Role of Th22 Cells in Human Viral Diseases. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021;8:708140.
- Zhang K, Chen L, Zhu C, Zhang M, Liang C. Current Knowledge of Th22 Cell and IL-22 Functions in Infectious Diseases. Pathogens. 2023; 12(2):176.
- Eyerich K, Eyerich S. Th22 cells in Allergic Disease. Allergo J Int. 2015;24(1):1-7

