Guide of PCR-assisted Analysis of Protein-DNA Sequence Specificity
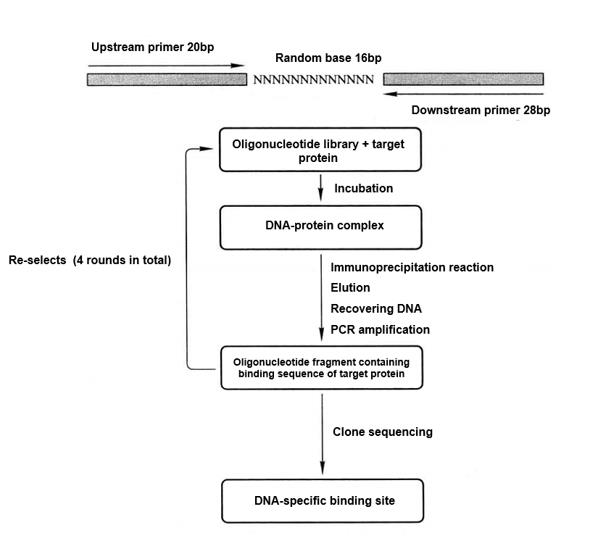
PCR-assisted protein-DNA sequence specificity analysis (random binding sites selection) is a new method for screening the specific sequence that binds to the target protein from the random nucleotide sequence library. Multiple binding screening reactions can be used to clone and sequence the exact nucleotide sequence that binds to the target protein.
The main purpose of this experimental manual is to help scientific researchers understand the principle of PCR-assisted protein-DNA sequence specificity analysis and master the main operating steps and precautions of PCR-assisted protein-DNA sequence specificity analysis.
PCR-assisted protein-DNA sequence specificity analysis (random bind sites selection) is a new technology based on PCR technology to screen DNA sequences that specifically bind to the target protein. The application range of this technology is from confirming the unknown DNA target sequence that specifically binds to a specific protein to providing more information about protein-DNA interactions with known DNA-binding domains.
The basic principle is that random sequences can be used as binding sources of target proteins. After the target protein binds to specific oligonucleotide fragments, the protein-DNA complex is isolated by immunoprecipitation with the antibody of the target protein, and the unbound oligonucleotides are removed by mild washing. The combined oligonucleotides are recovered and amplified by PCR before the next round of binding, recovery and amplification with the target protein. After 4 rounds of screening, the obtained oligonucleotide fragments were sequenced to obtain DNA sequences that specifically bind to the target protein. The schematic diagram is as follows
1. Main Instruments and Equipment
PE 9700 PCR, acrylamide gel electrophoresis system, metal bath, micro dispenser, etc.
2. Material
Specific protein samples to be tested: purified DNA binding protein with GST tag (GST MYB fusion protein is used in this experiment).
3. Main Reagents
Klenow fragment enzyme (E. coli polymerase I).
Promega MagneGSTTM protein purification kit.
R64:5'-TGGAGAAGAGGAGTGGCNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNCTCTTTGCATTCT TCTTCGATTCCGG-3'.
Primer-F: 5'-TGGAGAAGAGGAGGAGTGGC-3'.
Primer-R: 5'-CCCGGAATCGAAGAGAGAATGCAAAAGAG-3'.
Gel washing buffer: 150 mmol/L NaCl, 10 mmol/L Tris-Cl (pH 7.5), 2 mmol/L EDTA, 0.2%SDS.
2×dialysis buffer: 20 mmol/L Tris-HCl(pH 7.5), 100 mmol/L NaCl, 2 mmol/L DTT, 2 mmol/L EDTA, 10% glycerol, 100 μg/mL poly (dI-dC), 200μg/mL BSA.
LA Taq enzyme.
PGM-T vector.
1. Synthesis of Double-stranded Oligonucleotide Library Using Klenow Fragment Enzyme (E. coli polymerase I)
(1) Add the following substances into 0.5mL sterile eppendorf tube (EP tube):
| Single-strand oligonucleotide R64 (50ng/ μL) | 2μL |
| 5 × polymerase buffer | 4μL |
| dNTP mixture (10mmol/L) | 2μL |
| Reverse primer (80ng/ μL) | 2μL |
| Klenow fragment enzyme (20 U/ μL) | 1μL |
| H2O | 9μL |
| Total volume | 20μL |
(2) The total volume is 20 μL. Mix well and centrifuge to make the sample concentrate at the bottom of the tube. React according to the following procedure
2. Purification of Double-stranded Oligonucleotide Library R64*1 by 8% Native Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis
(1) After the above PCR samples were separated by PAGE and stained by EB, the required DNA bands were cut from the gel under the ultraviolet lamp, put into sterile EP tubes, chopped up, and soaked in 200μL in the glue buffer, take a water bath at 50°C for the night.
(2) Centrifuge for 2 min, take the supernatant and add 400μL phenol/chloroform for extraction, put the centrifuge tube into the freezing centrifuge, adjust the temperature to 4°C, 10000g, centrifuge for 5min, and repeat.
(3) Take the supernatant, add 2.5 times the volume of ethanol, and overnight at -20°C. DNA precipitation was collected by centrifugation, washed twice with 70% ethanol, dried in vacuum, and dissolved in a certain volume of sterile water.
3. Binding Reaction Between DNA and Target Protein
Incubate the double-stranded oligonucleotide library R64 purified in the previous step with the target protein containing GST tag:
Add the following substances into 1.5mL sterile EP tube:
| Double-strand oligonucleotide R64 (0.2ng/ μL) | 2μL*2 |
| GST fusion target protein (500 μg/ μL) | 20μL |
| 2×dialysis buffer | 50μL |
| H2O | 28μL |
| Total volume | 100μL |
Place at 4°C for 1h to form DNA-protein complex.
4. Use Promega MagneGSTTM Protein Purification Kit to Purify Oligonucleotide Fragments Binding to Target Protein
(1) A 1.5mL sterile EP tube was added with 400μL MagneGSTTM magnetic beads, transiently centrifuged, and the magnetic frame B/F (solid/ liquid) separated.
(2) Add 1mL MagneGSTTM binding/wash buffer, stir from time to time with a vortex mixer, centrifuge transiently, and separate the magnetic frame B/F (solid/ liquid) and repeat 3 times.
(3) Add 900μL of MagneGSTTM binding/wash buffer, stir from time to time with a vortex mixer, add 100μL of DNA-protein complex, and shake for 30 min at room temperature.
(4) Centrifuge instantly, magnetic rack B/F (solid/ liquid) separation, and remove the supernatant.
(5) Add 1mL of MagneGSTTM binding/wash buffer, broadcast at room temperature for 5 min, magnetic frame B/F (solid/liquid) separation, remove the supernatant, repeat 3 times.
(6) Add 200μL eluent, shake at room temperature for 15 min, magnetic frame B/F (solid/liquid) separation, and remove the supernatant.
(7) Add 400μL H2O, 600μL Tris saturated phenol/chloroform/isoamyl alcohol (25:24:1)*3, invert up and down several times, shake well, and centrifuge at 1000g for 5min.
(8) Take the supernatant, add 600μL Tris saturated phenol/chloroform/isoamyl alcohol (25:24:1), turn up and down several times, shake well, and centrifuge at 1000g for 5 min.
(9) Take the supernatant, add 500μL chloroform/isoamyl alcohol (24:1), turn up and down several times, shake well, and centrifuge at 10000g for 5 min.
(10) Take 300μL of supernatant, add 30μL of 7.5 mol/L NH4AC*4, 825μL of anhydrous ethanol, 1μL of 10 mg/mL glycogen*5, place at 4°C for 30 min, and centrifuge at 10000g for 10 min to precipitate nucleic acid.
(11) Add 70% ethanol to wash the precipitate, centrifuge at 10000g for 5 min at room temperature, and remove the supernatant.
(12) After drying at room temperature, add proper amount of water to dissolve, after electrophoresis detection, store at - 20°C for standby.
5. PCR Amplification Reaction and Target Fragment Recovery
(1) Add the following substances into 0.5mL sterile EP tube:
| Purified single-stranded oligonucleotide R64 (50ng/ μL) | 1μL |
| 10 × LA Taq buffer | 5μL |
| DNTP mixture (10mmol/L) | 5μL |
| Forward primer (80 ng/ μL) | 2μL |
| Reverse primer (80 ng/ μL) | 2μL |
| LA Taq enzyme (20U/μL) | 1μL |
| H2O | 34μL |
| Total volume | 50μL |
(2) The total volume is 50μL. Mix well and centrifuge to make the sample concentrate at the bottom of the tube. Follow the procedure below.

The gel recovery kit recovers the PCR product and dilutes it with water to a concentration of 50ng/μL.
6. Rebinding Reaction Between Target Fragment and Protein
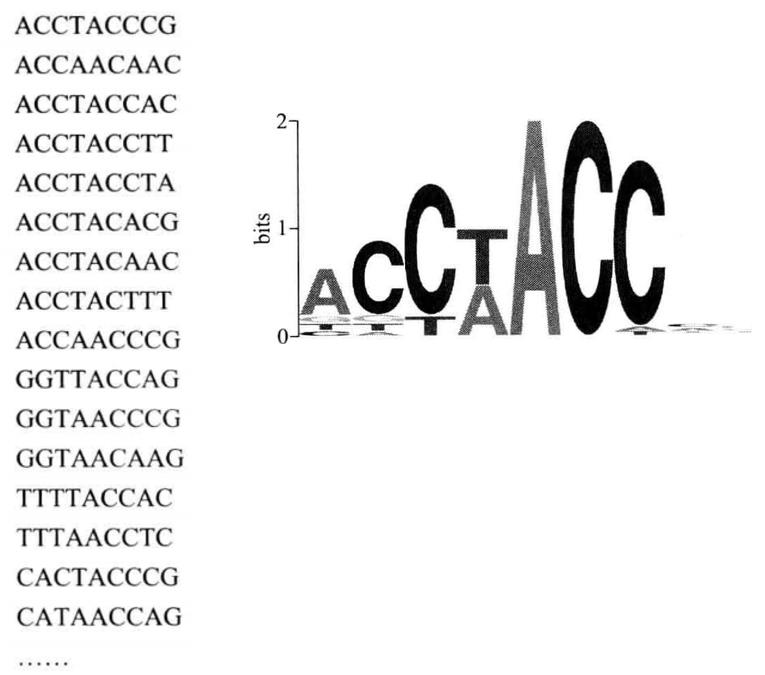
Combine the recovered target oligonucleotide fragment with the target protein with the GST tag again, repeat steps (3) to (6), after four rounds of screening, connect the obtained sequence to the T-vector, clone, and sequence to obtain the DNA sequence specifically binding with the target protein.
1. All operations shall be carried out at 4°C. The selected target protein should maintain its activity during the purification process and not lose its natural conformation.
2. In the process of protein-DNA binding reaction, the concentration of double-stranded oligonucleotides should be operated in strict accordance with the indicated concentration. Too high concentration will cause the folding of DNA double-stranded molecules and the non-specific binding of the target protein.
*1 Double-stranded oligonucleotide R64 can also be prepared by annealing the forward primer and extending the Klenow fragment of Escherichia coli DNA polymerase 1.
*2 Phenol/chloroform extraction to remove proteins bound to dsDNA molecules.
*3 Ammonium acetate has the function of precipitating, and its interaction with 95% ethanol leads to the precipitation of dsDNA molecules.
*4 Glycogen solution is used as the indicator of precipitation.
*5 In one round of screening, 0.4 ng probe was used for each reaction, and the amount of probe was 0.2 ng in the second, third and fourth rounds of screening.

