SMAD3
-
Official Full Name
SMAD family member 3 -
Overview
The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the SMAD, a family of proteins similar to the gene products of the Drosophila gene mothers against decapentaplegic (Mad) and the C. elegans gene Sma. SMAD proteins are signal transducers and transcriptional modulators that mediate multiple signaling pathways. This protein functions as a transcriptional modulator activated by transforming growth factor-beta and is thought to play a role in the regulation of carcinogenesis. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2009] -
Synonyms
SMAD3;SMAD family member 3;LDS3;LDS1C;MADH3;JV15-2;HSPC193;HsT17436;mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 3;mad3;hMAD-3;hSMAD3;MAD homolog 3;mad homolog JV15-2;mad protein homolog;mothers against DPP homolog 3;SMA- and MAD-related protein 3;SMAD, mothers against DPP homolog 3;MAD, mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 3
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Rhesus macaque
- Mouse
- Rat
- Chicken
- Human/Mouse/Rat
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cells
- Human
- Insect Cells
- HEK293
- GST
- His
- MBP
- Non
- Avi
- Fc
- Flag
- SUMO
- DDK
- Myc
Background
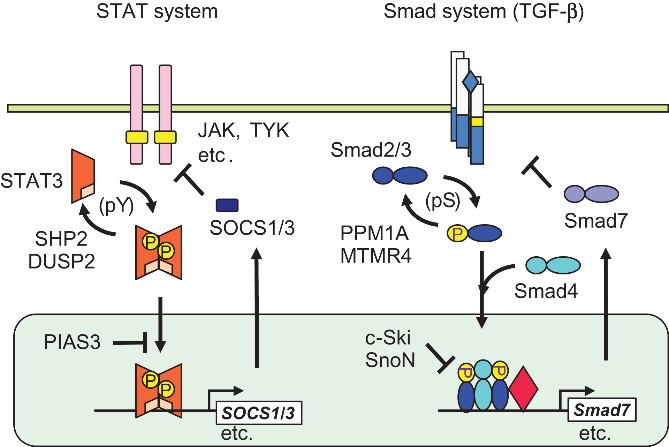
Fig1. Signal transduction through STAT3 and Smad2/3. (Yuka Itoh, 2018)
What is SMAD3 protein?
SMAD3 (SMAD family member 3) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 15 at locus 15q22. The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the SMAD, a family of proteins similar to the gene products of the Drosophila gene mothers against decapentaplegic (Mad) and the C. elegans gene Sma. SMAD proteins are signal transducers and transcriptional modulators that mediate multiple signaling pathways. The SMAD3 protein is consisted of 425 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 48.1 kDa.
What is the function of SMAD3 protein?
SMAD3 is a direct mediator of transcriptional activation by the TGF receptor. The activity of SMAD3 is regulated by the TGF receptors, and SMAD3 is phosphorylated and associated with the ligand-bound receptor complex. TGF stimulation leads to phosphorylation and activation of SMAD3, which form a complex with SMAD4 that accumulate in the nucleus and regulate transcription of target genes such as CDK inhibitor. SMAD3 containing a C-terminal truncation acts as a dominant-negative inhibitor of the normal TGF response. SMAD3 is a major physiologic substrate of the G1 cyclin-dependent kinases CDK4 and CDK2.
SMAD3 Related Signaling Pathway
SMAD3 protein is a key transcription factor in transforming the growth factor-β (TGF-β) superfamily signaling pathway. In the TGF-β signaling pathway, when TGF-β ligand binds to its receptor, SMAD3 is activated and forms a complex with SMAD2 or SMAD4, which then moves into the nucleus to regulate the expression of target genes. In addition to the TGF-β signaling pathway, SMAD3 is also involved in signaling other members of the TGF-β superfamily, such as bone morphogenetic proteins (BMP), activins, and statins.
SMAD3 Related Diseases
Abnormal activation of SMAD3 is associated with the occurrence of many diseases, including cancer, cardiovascular disease and pulmonary fibrosis. In cancer, overactivation of SMAD3 can promote the growth and metastasis of tumor cells. In cardiovascular disease, abnormal activation of SMAD3 may lead to cardiac hypertrophy and heart valve disease. In pulmonary fibrosis, overactivation of SMAD3 can promote the occurrence of pulmonary interstitial fibrosis.
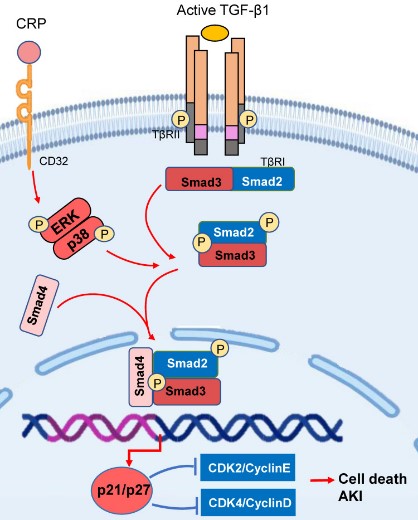
Fig2. Smad3 triggers the cell death pathways in acute kidney injury. (Wenjing Wu, 2022)
Bioapplications of SMAD3
At present, research on small molecule inhibitors or activators of SMAD3 is ongoing, with a view to developing novel drugs or therapies to treat related diseases. In addition, SMAD3 is also used as a biomarker to diagnose certain types of cancer or other diseases.
Case Study
Case study 1: Chen Yang, 2021
Macroautophagy/autophagy dysregulation has been noted in diabetic nephropathy; however, the regulatory mechanisms controlling this process remain unclear. In this study, the researchers showed that SMAD3 (SMAD family member 3), the key effector of TGFB (transforming growth factor beta)-SMAD signaling, induces lysosome depletion via the inhibition of TFEB-dependent lysosome biogenesis. The pharmacological inhibition or genetic deletion of SMAD3 restored lysosome biogenesis activity by alleviating the suppression of TFEB, thereby protecting lysosomes from depletion and improving autophagic flux in renal tubular epithelial cells in diabetic nephropathy. Mechanistically, they found that SMAD3 directly binds to the 3'-UTR of TFEB and inhibits its transcription. Silencing TFEB suppressed lysosome biogenesis and resulted in a loss of the protective effects of SMAD3 inactivation on lysosome depletion under diabetic conditions. In conclusion, SMAD3 promotes lysosome depletion via the inhibition of TFEB-dependent lysosome biogenesis; this may be an important mechanism underlying autophagy dysregulation in the progression of diabetic nephropathy.
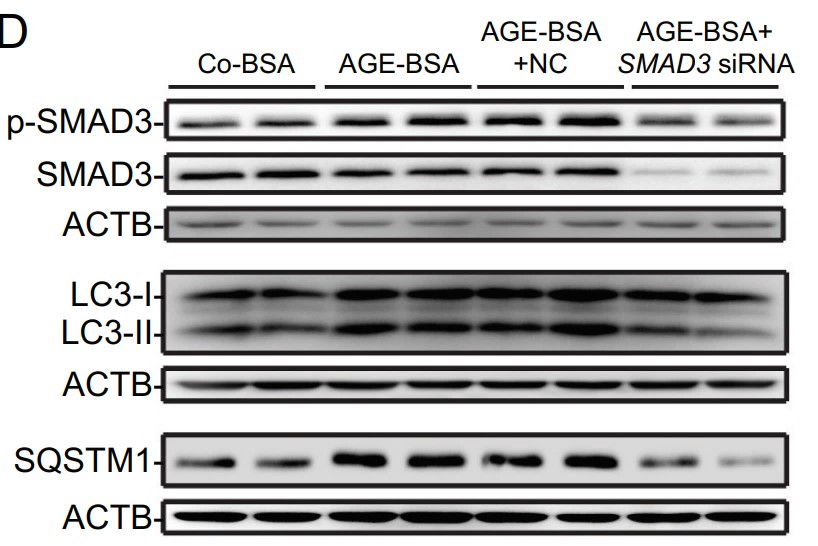
Fig1. Western blot analysis of phospho-SMAD3, LC3, and SQSTM1 expression in AGE-BSA or Co-BSA-treated HK-2 cells.
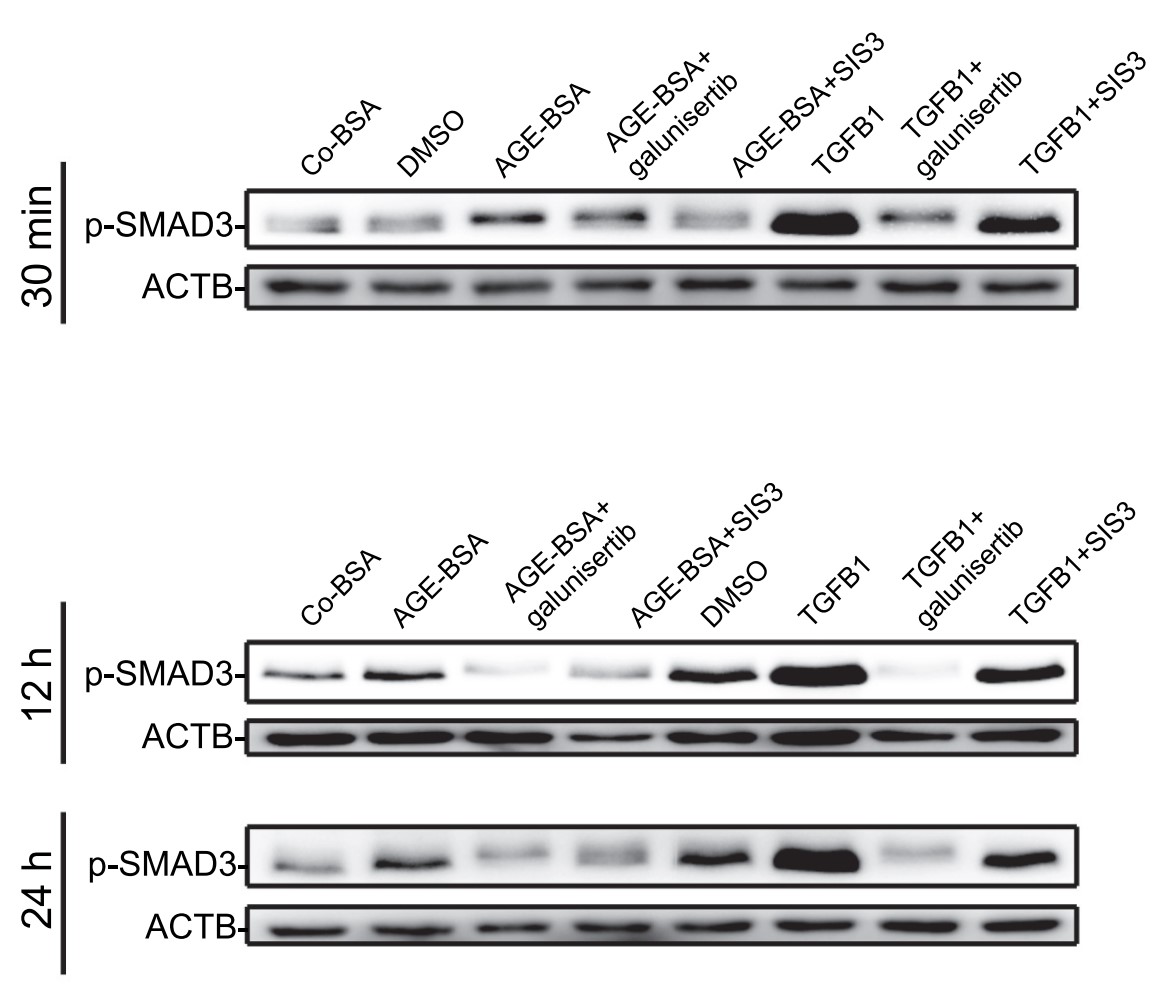
Case study 2: Heeseog Kang, 2020
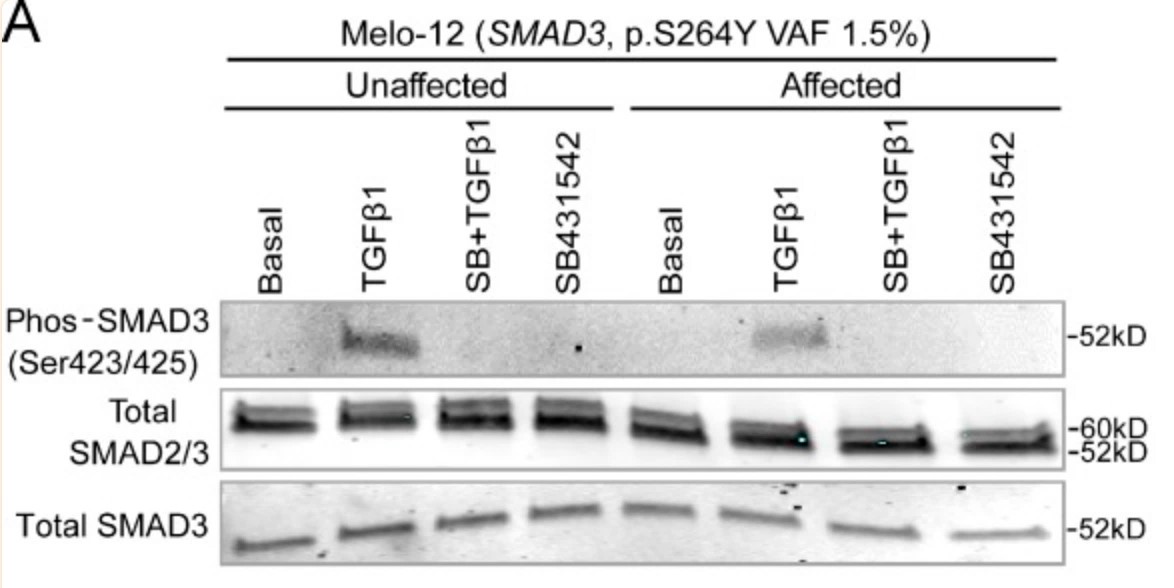
Melorheostosis is a rare sclerosing dysostosis characterized by asymmetric exuberant bone formation. Recently, the researchers reported that somatic mosaicism for MAP2K1-activating mutations causes radiographical "dripping candle wax" melorheostosis. They now report somatic SMAD3 mutations in bone lesions of four unrelated patients with endosteal pattern melorheostosis. In vitro, the SMAD3 mutations stimulated the TGF-β pathway in osteoblasts, enhanced nuclear translocation and target gene expression, and inhibited proliferation. Osteoblast differentiation and mineralization were stimulated by the SMAD3 mutation, consistent with higher mineralization in affected than in unaffected bone, but differing from MAP2K1 mutation-positive melorheostosis. Conversely, osteoblast differentiation and mineralization were inhibited when osteogenesis of affected osteoblasts was driven in the presence of BMP2. Transcriptome profiling displayed that TGF-β pathway activation and ossification-related processes were significantly influenced by the SMAD3 mutation. Co-expression clustering illuminated melorheostosis pathophysiology, including alterations in ECM organization, cell growth, and interferon signaling. These data reveal antagonism of TGF-β/SMAD3 activation by BMP signaling in SMAD3 mutation-positive endosteal melorheostosis, which may guide future therapies.
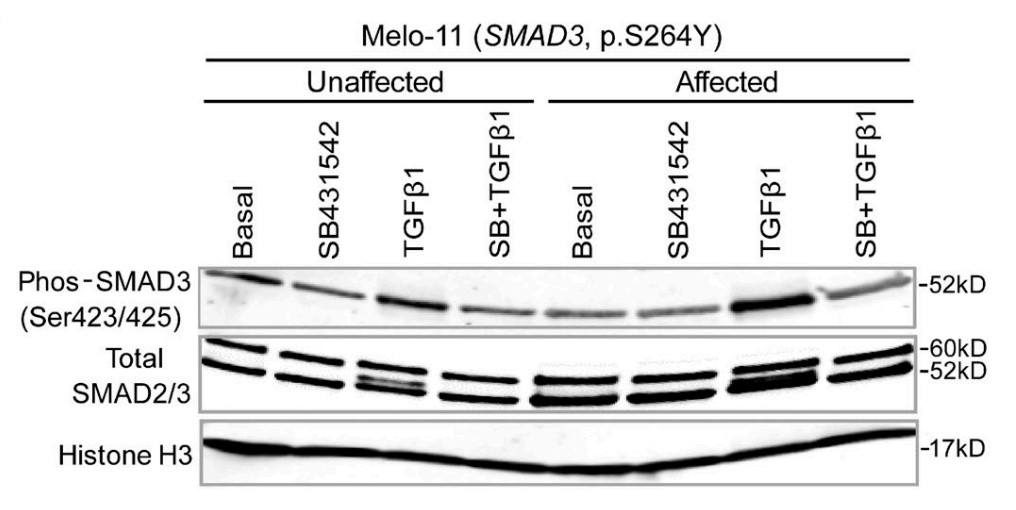
Fig3. SMAD3 phosphorylation upon TGF-β stimulation with or without TGFβRI inhibitor (SB431542) pretreatment was assessed by Western blotting (Melo-11, SMAD3 p.S264Y).
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
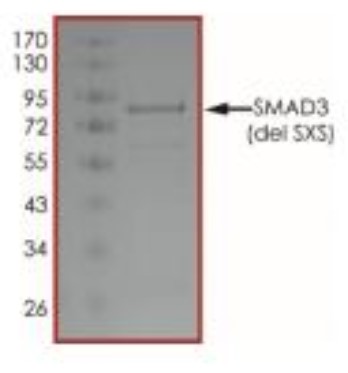
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (SMAD3-295H) (PROTOCOL for western blot)
.
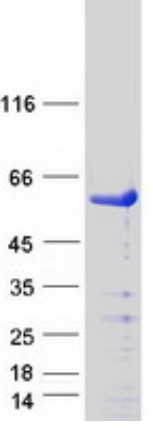
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (SMAD3-4788H) (PROTOCOL for western blot)
Involved Pathway
SMAD3 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways SMAD3 participated on our site, such as FoxO signaling pathway,Cell cycle,Endocytosis, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with SMAD3 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
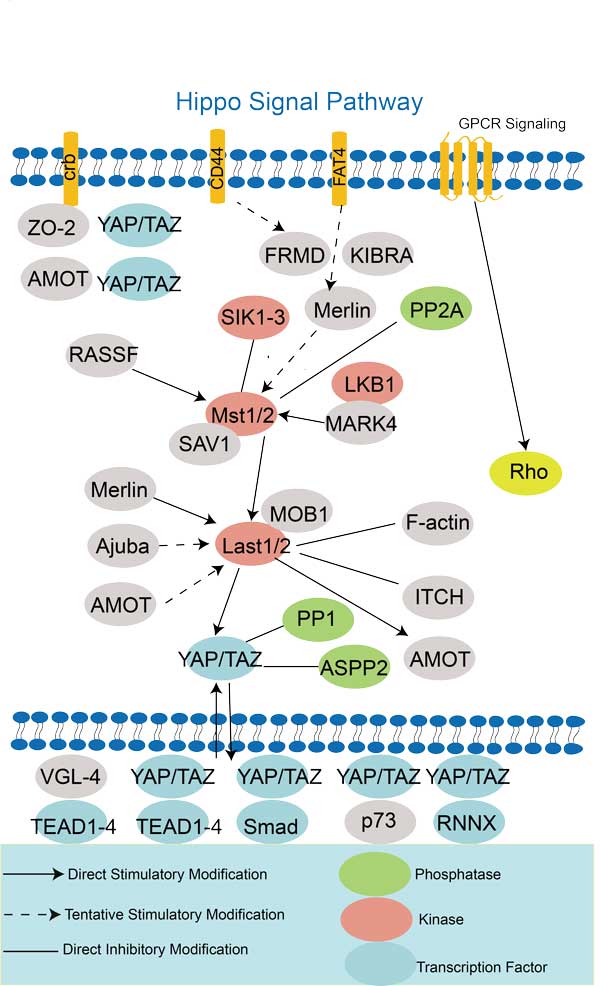
| Hippo signaling pathway | BMP8B,FZD10,AJUBA,ID1,LIMD1,ACTG1,JUB,CRB1,DLG1,PPP2CA |
| Cell cycle | OFD1,CDC25C,TGFB1A,SMAD4,TCTN2,SPDL1,TERF1,ESCO1,SMC1A,ANAPC5 |
| FoxO signaling pathway | STK11,STK4,FOXO6,FOXO1A,GRM1,HOMER1,INS2,PTEN,PRKAG3B,NLK2 |
| Pancreatic cancer | RB1,RALBP1,RALGDS,ERBB2,BRAF,MAP2K1,IKBKB,RAC1,PIK3R1,PIK3R2 |
| Pathways in cancer | FGF9,GLI3,MLH1,PTGS2,MAP2K1,PPARG,BIRC8,BCR,PAX8,LAMA4 |
| Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) | IL4,IL1B,IL6,Il23a; Il12b,HLA-DRA,HLA-DOA,TBX21,HLA-DMB,IFNGR2,TLR4 |
| Hepatitis B | EP300,SMAD4,TLR2,CYCS,HBXIP,ATP6AP1,IFNA13,TLR3,PIK3CB,IKBKB |
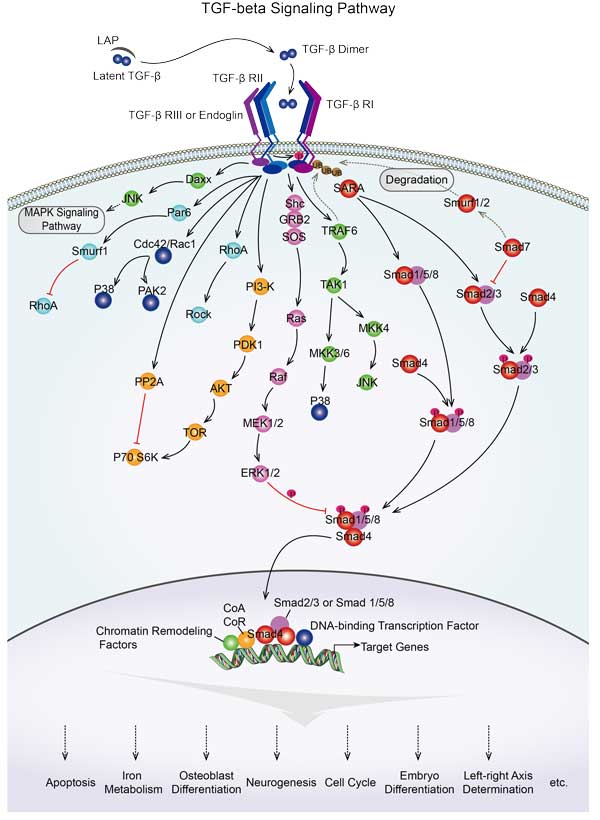
| TGF-beta signaling pathway | EP300,INHBAB,ACVR2A,ID1,RPS6KB1B,LFT1,SMAD7B,CHRD,TGFB2,RBX1 |
| Chronic myeloid leukemia | MDM2,TRP53,TGFB1,RELA,TGFB3,PIK3CG,RAF1,STAT5A,IKBKB,AKT1 |
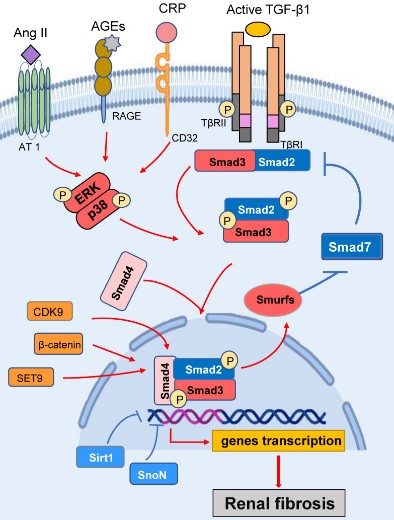
Fig1. Smad3 signaling and crosstalk pathways in renal fibrosis. (Wenjing Wu, 2022)
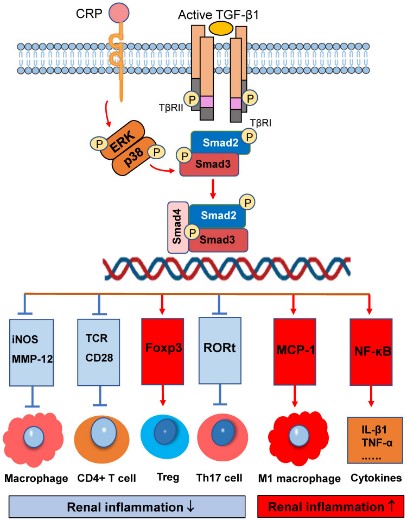
Fig2. Smad3 signaling and crosstalk pathways in renal inflammation. (Wenjing Wu, 2022)
Protein Function
SMAD3 has several biochemical functions, for example, R-SMAD binding,RNA polymerase II activating transcription factor binding,RNA polymerase II core promoter proximal region sequence-specific DNA binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by SMAD3 itself. We selected most functions SMAD3 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with SMAD3. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| protein homodimerization activity | HPGD,NETO2,CADM3,VOX,PVRL4,SYT16,DPYD,ODZ4,TG,GABPB2 |
| phosphatase binding | CTSC,SLC9A3R1,ELL,PPP1R37,PPP1R26,CSRNP2,ELFN2,PPP1R35,SLC9A3R2,CRY1 |
| protein heterodimerization activity | VEGFA,H3F3A,DMRT3,MAPK6,DMRTA2,ALX4,Fzd4,PPARD,PIK3R2,BCL2 |
| R-SMAD binding | ANKRD1,MEN1,FOXH1,TRIM33,FOS,C18orf1,PARP1,PAX6,SMURF1,PPM1A |
| co-SMAD binding | FOXH1,SMAD6,CITED1,GATA4,SMAD1,SMAD2,USP9X,TRIM33,TGIF1 |
| transcription regulatory region DNA binding | Arid4b,TBP,CTCFL,ZFP382,KLF11,SNCA,JUN,SALL1A,HMGB2,HHEX |
| zinc ion binding | RYBPB,NR5A2,CHMP1A,ESR2,TLL2,TRIM35-30,VPS8,LONRF2,KDM5BA,ADH5 |
| ubiquitin binding | NUP62,KCNS1,C6orf106,IDE,USP5,BRAP,D17WSU92E,TOP2A,UCHL3,TOM1L1 |
| transcription factor binding | PPARGC1B,ERCC3,HEY1,RNF222,JUNB,TRIB2,APBB2,HEYL,TRP53,APBB3 |
Interacting Protein
SMAD3 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with SMAD3 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of SMAD3.
SMAD4;SKI
SMAD3 Related Signal Pathway
Resources
Gene Families
Research Area
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Smithrithee, R; Niyonsaba, F; et al. Human beta-defensin-3 increases the expression of interleukin-37 through CCR6 in human keratinocytes. JOURNAL OF DERMATOLOGICAL SCIENCE 77:46-53(2015).
- McMillin, M; Galindo, C; et al. Gli1 activation and protection against hepatic encephalopathy is suppressed by circulating transforming growth factor beta 1 in mice. JOURNAL OF HEPATOLOGY 61:1260-1266(2014).