CD38
-
Official Full Name
CD38 molecule -
Overview
CD38 (cluster of differentiation 38), also known as cyclic ADP ribose hydrolase, is a transmembrane glycoprotein found on the surface of some immune cells including plasma cells, activated or immature T and B cells, monocytes, and natural killer cells. CD38 participates in cell adhesion, signal transduction and calcium signaling. It is expressed at high levels in the plasma cell tumor, prostate cancer, stomach cancer, and neuroblastoma. CD38 is used as one of the plasma cell markers and its ligand is CD31 molecules. -
Synonyms
CD38;CD38 molecule;ADP-ribosyl cyclase 1;CD38H;cADPr hydrolase 1;cyclic ADP-ribose hydrolase 1;CD38 antigen (ADP-ribosyl cyclase / cyclic ADP-ribose hydrolase)
Recombinant Proteins
- Mouse
- Human
- Monkey
- Rat
- Rabbit
- Cynomolgus/Rhesus
- Cynomolgus
- Chicken
- Rhesus macaque
- Mammalian Cells
- Human Cells
- HEK293
- Wheat Germ
- Insect Cells
- E.coli
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- Yeast
- CHO
- His
- Fc
- Avi
- GST
- Non
- Flag
- T7
- lIgG2b
- mIgG2a
Background
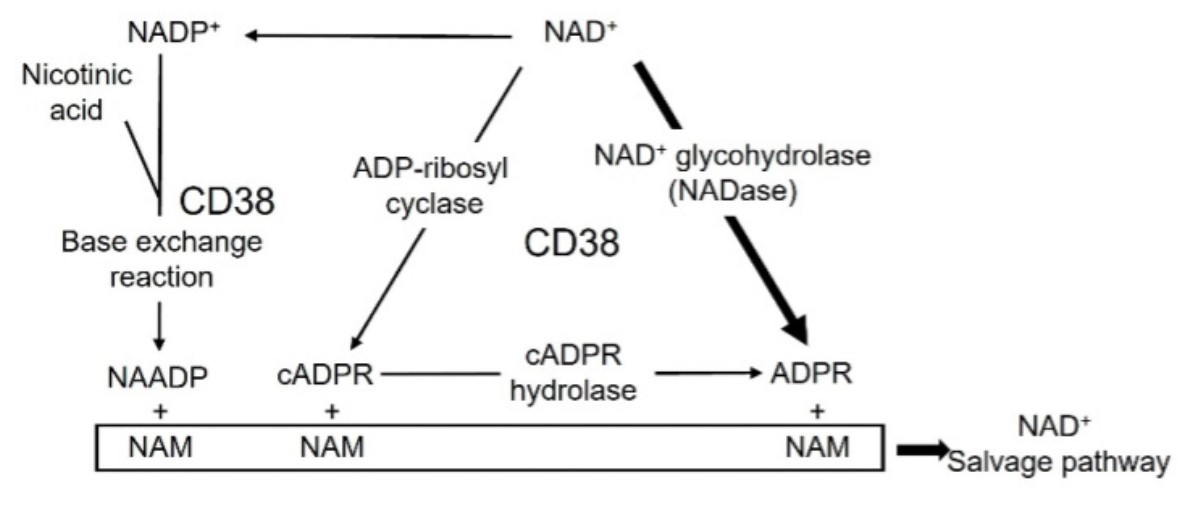
Fig1. Enzymatic activity of CD38. CD38 metabolizes NAD+ to ADPR through its glycohydrolase (NADase) activity or cADPR through its cyclase activity. (Munehiro Kitada, 2023)
What is CD38 protein?
CD38 (CD38 molecule) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the short arm of chromosome 4 at locus 4p15. CD38 (cluster of differentiation 38), also known as cyclic ADP ribose hydrolase, is a transmembrane glycoprotein found on the surface of some immune cells including plasma cells, activated or immature T and B cells, monocytes, and natural killer cells. CD antigen CD38 is also known as ADP-ribosyl cyclase 1, which belongs to the ADP-ribosyl cyclase family. CD38 is expressed at high levels in pancreas, liver, kidney, brain, testis, ovary, placenta, malignant lymphoma and neuroblastoma. CD38 is used as one of the plasma cell markers and its ligand is CD31 molecules. The CD38 protein is consisted of 300 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 34.3 kDa.
What is the function of CD38 protein?
CD38 participates in cell adhesion, signal transduction and calcium signaling. CD38 is a multifunctional ectoenzyme that catalyzes the synthesis and hydrolysis of cyclic ADP-ribose (cADPR) from NAD+ to ADP-ribose. These reaction products are essential for the regulation of intracellular Ca2+. The loss of CD38 function is associated with impaired immune responses, metabolic disturbances, and behavioral modifications. The CD38 protein is a marker of cell activation. It has been connected to HIV infection, leukemias, myelomas, solid tumors, type II diabetes mellitus and bone metabolism. CD38 has been used as a prognostic marker in leukemia.
CD38 Related Signaling Pathway
CD38 can hydrolyze coenzyme NAD+ (nicotinate amine adenine dinucleotide) into nicotinic acid (NADH) and adenosine diphosphate ribose (ADPR), further regulating intracellular calcium ion concentration. At the same time, it can also participate in MAPK signaling pathway, NF-κB signaling pathway, PI3K/AKT signaling pathway, and then regulate cell inflammation, cell growth and other processes. It also affects immune cells: B/T cells. These signaling pathways interact and work together to regulate the function of the immune system.
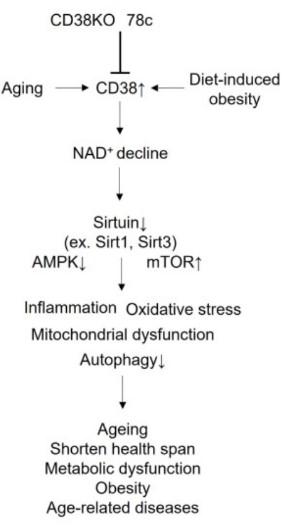
Fig2. Beneficial effect of gene ablation and pharmacological inhibition of CD38 on aging and age-related diseases. (Munehiro Kitada, 2023)
CD38 Related Diseases
Cd38-related diseases involve many fields such as immune system, tumor, infectious disease, blood disease, nervous system disease and cardiovascular disease, and its abnormal expression or dysfunction may lead to abnormal activation of immune cells and inflammatory response, resulting in various diseases. For example: Multiple Myeloma, Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL).
Bioapplications of CD38
CD38 can be used to label and detect a variety of immune cells, such as lymphocytes, monocytes, and macrophages. CD38 is highly expressed on plasma cell surface in patients with multiple myeloma (MM) and can be used as a diagnostic marker for MM. Monoclonal antibody drugs targeting CD38 have been developed, such as daratumumab, isatuximab, etc. CD38 is used in CAR-T cell therapy to improve the function and effectiveness of immune cells.
Case Study
Case study 1: M Tommy Gambles, 2021
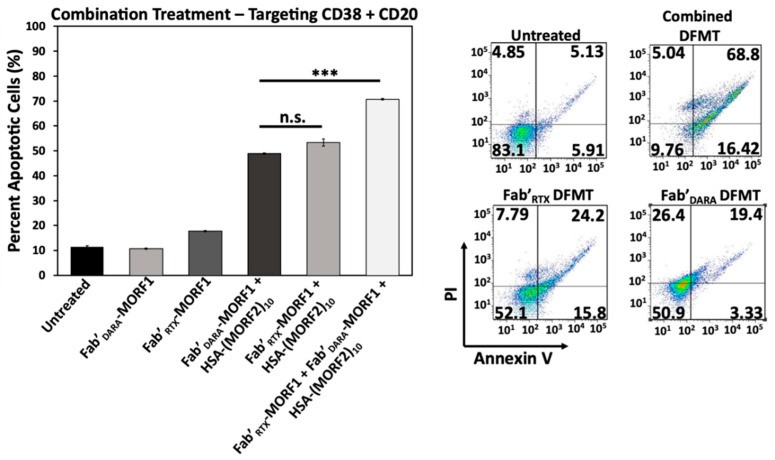
The researchers designed an inventive paradigm in nanomedicine-drug-free macromolecular therapeutics (DFMT). The ability of DFMT to induce apoptosis is based on biorecognition at cell surface, and crosslinking of receptors without the participation of low molecular weight drugs. Here, the researchers intend to demonstrate that DFMT is a platform that will be effective on other receptors than previously validated CD20. We appraised the impact of daratumumab (DARA)- and isatuximab (ISA)-based DFMT to crosslink CD38 receptors on CD38+ lymphoma (Raji, Daudi) and multiple myeloma cells (RPMI 8226, ANBL-6).
The biological properties of DFMTs were determined by flow cytometry, confocal fluorescence microscopy, reactive oxygen species determination, lysosomal enlargement, homotypic cell adhesion, and the hybridization of nanoconjugates. The data revealed that the level of apoptosis induction correlated with CD38 expression, the nanoconjugates meet at the cell surface, mitochondrial signaling pathway is strongly involved, insertion of a flexible spacer in the structure of the macromolecular effector enhances apoptosis, and simultaneous crosslinking of CD38 and CD20 receptors increases apoptosis.
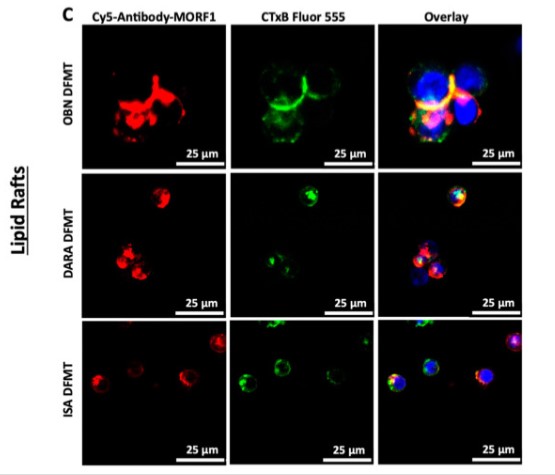
Fig1. Confocal microscopy was employed to observe any redistribution of CD38 receptors into cholesterol-rich lipid rafts.
Case study 2: Long Gao, 2021
It has been recently reported that CD38 expressed on tumor cells of multiple murine and human origins could be upregulated in response to PD-L1 antibody therapy, which led to dysfunction of tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T immune cells due to increasing the production of adenosine. However, the role of tumor expressed-CD38 on neoplastic formation and progression remains elusive. So the researchers aimed to delineate the molecular and biochemical function of the tumor-associated CD38 in lung adenocarcinoma progression.
Using multiple in vitro assays they found that the enzymatic activity of tumor expressed-CD38 facilitated lung cancer cell migration, proliferation, colony formation, and tumor development. And the in vivo results showed that inhibition of the enzymatic activity or antagonizing the enzymatic product of CD38 resulted in the similar inhibition of tumor proliferation and metastasis as CD38 gene knock-out or mutation. These findings suggested that malignant lung cancer cells were capable of using cADPR catalyzed by CD38 to facilitate tumor progression, and blocking the enzymatic activity of CD38 could be represented as an important strategy for preventing tumor progression.
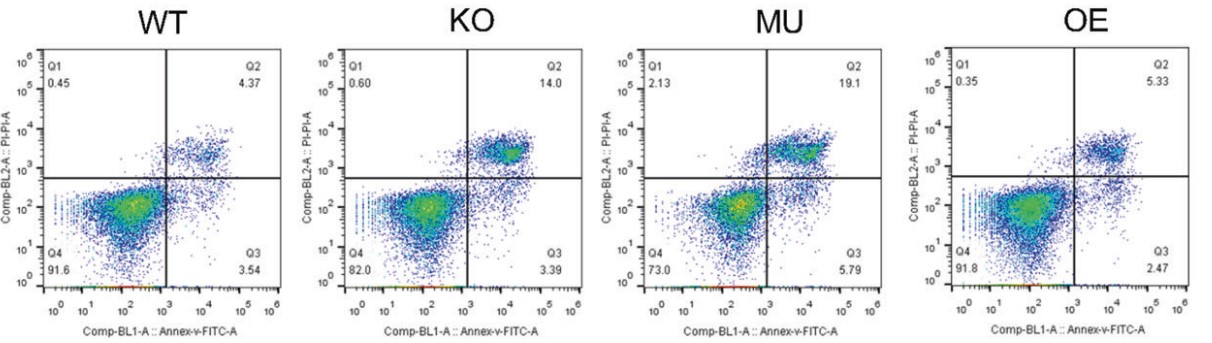
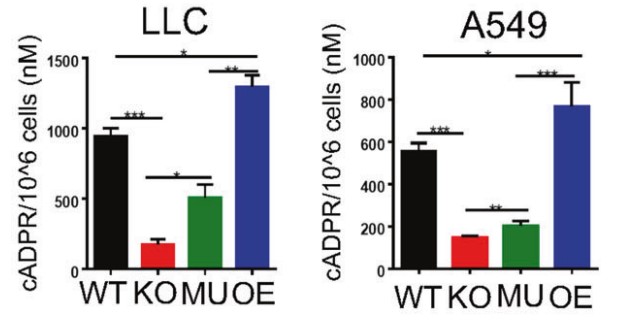
Fig3. Representative FACS plots showing the apoptotic of LLC with different level of CD38 expression.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity

Fig1. SDS-PAGE (CD38-1822H) (PROTOCOL for western blot)
.
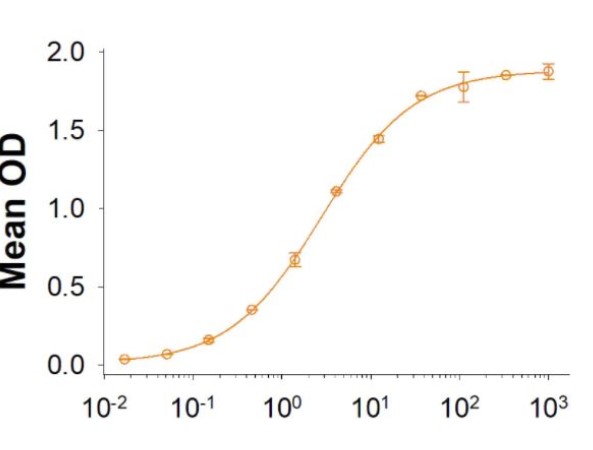
Fig2. Activity Data. (CD38-051H)
Involved Pathway
CD38 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways CD38 participated on our site, such as Nicotinate and nicotinamide metabolism,Metabolic pathways,Calcium signaling pathway, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with CD38 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Salivary secretion | CST3,PRB1,PLCB1,PLCB2,HTN1,MUC5B,KCNN4,NOS1,PRH1,AMY1B |
| Epstein-Barr virus infection | IRAK1,PIK3R1,LYN,ICAM1,MAP2K4,TAB2,HLA-A,SPN,FCER2,SNW1 |
| Nicotinate and nicotinamide metabolism | NT5C2,ENPP1,NT5C,NADK,NT5C2B,KCNG4,NNT,ENPP3,NT5C3A,PNP |
| Calcium signaling pathway | PRKACG,CALM2,PLCD1,PDGFRA,NOS3,CAMK2G,TACR1B,DRD1A,CALM2A,HRH1 |
| Hematopoietic cell lineage | CSF3R,CD7,MS4A1,CD8B1,IL11,CSF1R,ITGA2B,MME,CD36,CD59A |
| Oxytocin signaling pathway | MAPK1,ROCK2,NFATC4,CAMK2B,KCNJ14,PLCB3,PIK3R5,PRKACA,CACNG1,GNAI3 |
| Pancreatic secretion | Slc4a2,PLA2G5,GNAQ,RHOA,CPA2,ATP2B1,CLCA4,PRSS3,CELA2A,PLA2G12B |
| Metabolic pathways | AHCY,MAT2AA,SAT2,UROC1,ACSS2L,IDH3B,ALDH3A2A,NAT1,CHIA.3,ST6GALNAC4 |
Fig1. NAD+-consuming enzymes. CD38 can convert NAD+ or NMN to NAM, and CD157/BST-1 can convert NAD+ or NR to NAM. (Munehiro Kitada, 2023)
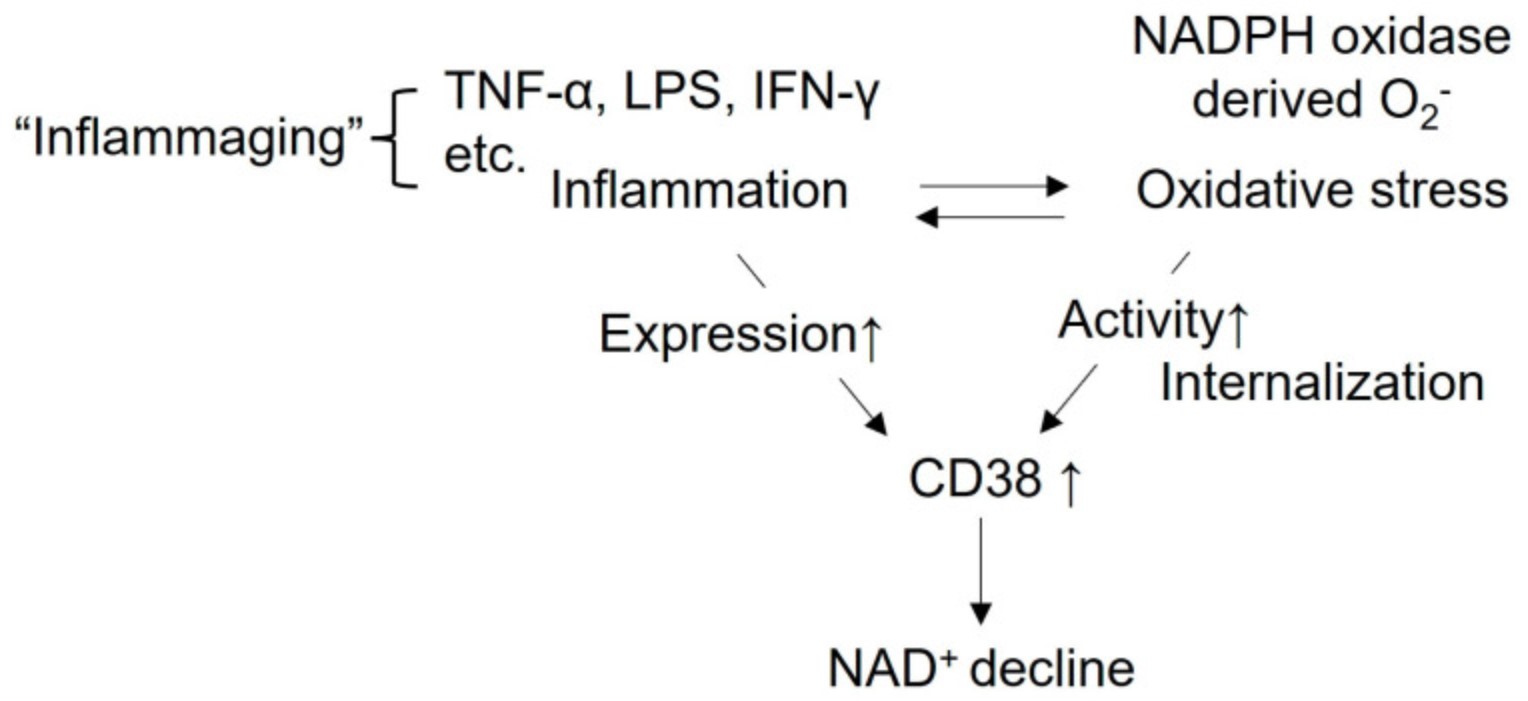
Fig2. Regulation of CD38 by inflammation and oxidative stress. CD38 expression is enhanced by inflammatory cytokines including TNF-α, LPS and IFN-γ, etc., leading to cellular NAD+ decline. (Munehiro Kitada, 2023)
Protein Function
CD38 has several biochemical functions, for example, NAD(P)+ nucleosidase activity,NAD+ nucleosidase activity,phosphorus-oxygen lyase activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by CD38 itself. We selected most functions CD38 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with CD38. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| phosphorus-oxygen lyase activity | ADCY2B,ADCY1B,GUCY2F,GUCY2E,ADCY1A,NPR1A,BST1,GC3,GC2 |
| NAD(P)+ nucleosidase activity | BST1 |
| NAD+ nucleosidase activity | BST1,ART5 |
| transferase activity | TRIO,SULT3ST2,TAOK1,HS6ST1B,BST1,EPHB4B,MAT2AL,ST3GAL3A,GM4952,UGT1AB |
Interacting Protein
CD38 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with CD38 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of CD38.
Resources
Research Area
- Cancer Drug Targets
- Myeloid Lineage Markers
- B Cell CD Antigen
- CD Antigen (Hematopoietic Stem Cell Markers)
- Natural Killer (NK) Cell CD Antigen
- Hematopoietic Stem Cell Markers
- CD Antigen (Regulatory T Cells)
- Leukemia Cancer Stem Cell Markers
- Myeloma Cancer Stem Cell Markers
- Hematopoietic Progenitor Cell Markers
- CAR-T Cell Therapy Targets
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Schubert, RD; Hu, Y; et al. IFN-beta Treatment Requires B Cells for Efficacy in Neuroautoimmunity. JOURNAL OF IMMUNOLOGY 194:2110-2116(2015).
- Franquesa, M; Mensah, FK; et al. Human Adipose Tissue-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Abrogate Plasmablast Formation and Induce Regulatory B Cells Independently of T Helper Cells. STEM CELLS 33:880-891(2015).




