Natural Killer (NK) Cell CD Antigen
Related Symbol Search List
- CD38
- DPP4
- L-selectin
- TNFRSF9
- TNFSF9
- CD16a
- FCGR3B
- FCGR4
- CD274
- CD244
- CXCR2
- ITGAM
- CD40
- CD226
- IL10RB
- Pvrl2
- CD160
- CD2
- CD27
- CD276
- CD7
- CLEC1A
- IL18R1
- IL2RB
- NCR3
- TNFSF10
- TNFSF8
- VTCN1
Immunology Background
Available Resources for Natural Killer (NK) Cell CD Antigen Research
Creative BioMart provides a comprehensive resource platform for natural killer (NK) cell CD antigens, providing researchers with valuable information, high-quality products, and customized services. Use the power we give you to understand the role of NK cell CD antigens in immune response, disease, vaccine development, and other research, and stay informed about the latest discoveries and progress in this field.
We provide a comprehensive list of NK cell CD antigens, including CD38, DPP4, L-selectin, TNFRSF9, TNFSF9, CD16a, FCGR3B, FCGR4, CD274, CD244, CXCR2, ITGAM, CD40, CD226, IL10RB, and others.
- Creative BioMart provides a variety of antibodies, recombinant proteins, protein pre-coupled magnetic beads, cell and tissue lysates, chromatography reagents, and more kits targeting different NK cell CD antigens.
- Our experienced team of experts provides the customized tools needed for your NK cell CD antigen research, such as antibody development, protein engineering, recombinant antigen production, and assay development services.
- In addition, we provide rich resources covering multiple aspects of NK cell CD antigens, such as pathways, protein functions, interacting proteins, related articles, research areas, and other related topics. These resources will help researchers better explore different research areas and disease associations related to NK cell CD antigens.
Our Featured Products
| Cat.# | Product name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD38-574H | Active Recombinant Human CD38, Fc-tagged | Human | Human Cell | Fc |
| DPP4-270H | Active Recombinant Human DPP4 protein | Human | HEK293 | N/A |
| TNFRSF9-581H | Recombinant Human TNFRSF9, Fc-His tagged | Human | Human Cell | Fc/His |
| FCGR3B-3869H | Recombinant Human FCGR3B protein(Met18-Gly193) | Human | E.coli | N/A |
| CD244-10930H | Recombinant Human CD244, His-tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
| IL10RB-14142H | Recombinant Human IL10RB, His-tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
| PVRL2-610H | Recombinant Human PVRL2 protein(Met1-Leu360) | Human | HEK293 | N/A |
| CD160-453H | Active Recombinant Human CD160 Protein, His-tagged | Human | HEK293 | His |
| CD2-10922H | Recombinant Human CD2, GST-tagged | Human | E.coli | GST |
| NCR3-815H | Recombinant Human NCR3, Fc-His tagged | Human | Human Cell | Fc/His |
| TNFSF10-2154H | Recombinant Human TNFSF10, His-tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
| VTCN1-3694H | Recombinant Human VTCN1, GST-tagged | Human | E.coli | GST |
About Natural Killer (NK) Cell CD Antigen
Natural Killer (NK) cells are a type of lymphocyte that plays a critical role in the innate immune response against virally infected and cancerous cells. NK cells are able to recognize and kill target cells without prior sensitization, making them an important component of the body's defense against pathogens and abnormal cells.
One of the key distinguishing features of NK cells is the expression of a variety of cell surface markers, including CD antigens. CD antigens are clusters of differentiation molecules that are used to classify cells based on specific proteins expressed on their surface. In the case of NK cells, one important CD antigen is CD56 (NCAM), which serves as a marker for identifying and isolating these cells from other immune cell populations. In addition to CD56, NK cells also express other CD antigens such as CD16 (FcγRIII), CD57, CD94/NKG2A, NKG2D, and NKp46 (NCR1). These CD antigens, along with others not mentioned here, contribute to the development, activation, and effector functions of NK cells. Their expression patterns and interactions with ligands on target cells regulate the balance between NK cell activation and inhibition, ultimately influencing immune responses against infections and tumors. Understanding the roles of NK cell CD antigens provides insights into NK cell biology and their potential therapeutic applications.
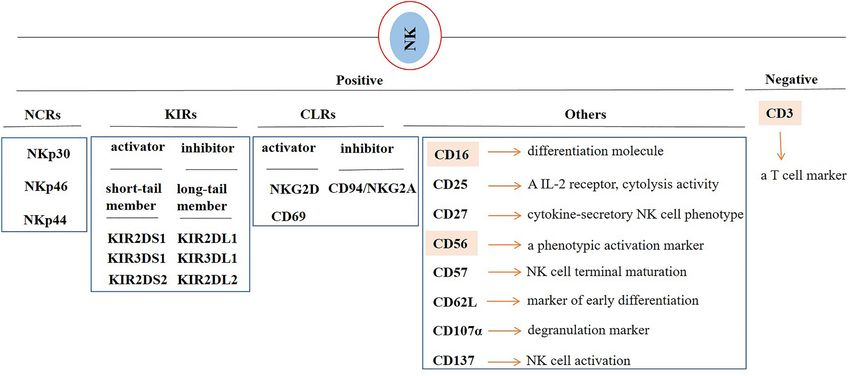 Fig.1 Natural killer (NK) cell markers. (Mortezaee K., et al., 2022)
Fig.1 Natural killer (NK) cell markers. (Mortezaee K., et al., 2022)
In clinic, NK cells are mostly described based on the positive expressions of CD16 and CD56 and the absence of the T cell marker CD3. CD56 is a neural cell adhesion molecule that is known as a phenotypic activation marker. CD16 mediates antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC). Natural killer group 2, member D (NKG2D) and CD16 are markers of NK cell functionality. NKG2D (CD314) is a receptor expressed on surface of NK cells that upon interaction with its cognate receptors promotes cytolysis of tumor cells. CD27 is a marker of NK cell activation, and CD107α (LAMP-1) is a marker of NK cell degranulation. NK cell activation is also evaluated by assessing the expression of CD25 and CD69. Among C-type lectin-like receptors (CLRs), CD94/NKG2A acts as an inhibitor, whereas NKG2D is an activating receptor. NKp46 (NCR1 or CD335), NKp44 (NCR2 or CD336) and NKp30 (NCR3 or CD337) are placed in the class of natural cytotoxicity receptor (NCRs). Killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptors (KIRs) can be both inhibitory (long-tail member) and activator (short-tail member) of NK cell functionality.
The Role of NK Cell CD Antigen in Immune-Related Diseases
NK cell CD antigens have important implications in various immune-related diseases. Here are some examples of their roles in specific conditions:
Cancer
- Downregulation or shedding of NKG2D ligands by tumor cells can impair NK cell recognition and immune surveillance, allowing tumors to evade NK cell-mediated antitumor responses.
- Impaired expression or function of CD16 on NK cells can compromise antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC), an important mechanism for tumor cell killing.
- The interaction of iller-cell Immunoglobulin-like receptors (KIRs) on NK cells with their ligands on tumor cells can influence the susceptibility and progression of certain cancers, including leukemia and colorectal cancer.
Viral Infections
- Upregulation of HLA-E, the ligand for CD94/NKG2A, on virus-infected cells can inhibit NK cell cytotoxicity, allowing viral evasion of the immune response. This mechanism is observed in infections like human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) and HIV.
- Some viruses, such as human papillomavirus (HPV) and hepatitis C virus (HCV), can downregulate NKG2D ligands on infected cells, impairing NK cell recognition and facilitating viral persistence.
Autoimmune Diseases
- Overexpression of HLA-E, the ligand for CD94/NKG2A, on self-tissues can lead to the inhibition of autoreactive NK cells, potentially contributing to the development or progression of autoimmune diseases like multiple sclerosis and psoriasis.
- Genetic variations in killer-cell Immunoglobulin-like receptors (KIRs) genes and their interactions with HLA class I molecules have been associated with autoimmune disorders, including rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus.
Immunodeficiency
- Deficiencies in NK cell CD antigens, such as CD16, NKG2D, or KIRs, can result in impaired NK cell function and compromised immune responses, increasing susceptibility to infections, particularly viral infections.
These examples illustrate how alterations or dysregulation of NK cell CD antigens can have significant implications in immune-related diseases. Understanding the roles of these antigens in specific conditions can provide insights into disease mechanisms and potentially guide the development of targeted therapies.

Creative BioMart is committed to providing researchers with high-quality experimental materials and professional technical support to help them achieve deeper understanding and breakthroughs in the field of NK cell CD antigen-related research. If you have any questions, requirements, or cooperation intentions, please feel free to contact us. We very much look forward to working with you and helping you achieve research and commercial success.
Related References
- Mortezaee K, Majidpoor J. NK and cells with NK-like activities in cancer immunotherapy-clinical perspectives. Med Oncol. 2022;39(9):131.
- Abel AM, Yang C, Thakar MS, Malarkannan S. Natural Killer Cells: Development, Maturation, and Clinical Utilization. Front Immunol. 2018;9:1869.
- Renoux V M, Zriwil A, Peitzsch C, et al. Identification of a human natural killer cell lineage-restricted progenitor in fetal and adult tissues. Immunity, 2015, 43(2): 394-407.

