CLEC10A
-
Official Full Name
C-type lectin domain family 10, member A -
Overview
ASGPR/MGL (asialoglycoprotein / macrophage galactose lectin receptor) / CD301 is a Ca2+ dependent type II transmembrane lectin. Immunoprecipitation from DCs using anti-DC-ASGPR Monoclonal Antibody yields a major 40-kDa protein. ASGPR mRNA is observed predominantly in immune tissues (DCs and granulocytes), but not in T, B, or NK cells, or monocytes. ASGPR species are restricted to the CD14- derived DCs obtained from CD34+ progenitors, while absent from the CD1a-derived subset. Accordingly, both monocyte-derived DCs and tonsillar interstitial-type DCs express ASGPR protein, while Langerhans-type cells do not. ASGPR is a feature of immaturity, as its expression is lost upon CD40L activation. In agreement with the presence of tyrosine-based and dileucine motifs in the intracytoplasmic domain, Monoclonal Antibody against DC-ASGPR is rapidly internalized by DCs at 37°C. Finally, intracellular ASGPR is localized in early endosomes, suggesting that the receptor recycles to the cell surface following internalization of ligand. ASGPR/HML is a feature of immature DCs and a subtype of macrophages, and likely important for the specialized antigen-capture function of DCs. -
Synonyms
HML;MGL;HML2;CD301;CLECSF13;CLECSF14;C-type lectin domain family 10 member A;macrophage lectin 2 (calcium dependent);C-type (calcium dependent, carbohydrate-recognition domain) lectin, superfamily member 13 (macrophage-derived);C-type (calcium dependent, carbohydrate-recognition domain) lectin, superfamily member 14 (macrophage-derived);CD301 antigen;CLEC10A;C-type lectin superfamily member 14;Macrophage lectin 2;macrophage C-type lectin
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Rhesus macaque
- HEK293
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cells
- Wheat Germ
- Human Cells
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- Fc
- His
- Non
- GST
- T7
- Avi
- DDK
- Myc
- rFc
Background
What is CLEC10A protein?
CLEC10A gene (C-type lectin domain containing 10A) is a protein coding gene which situated on the short arm of chromosome 17 at locus 17p13. This gene encodes a member of the C-type lectin/C-type lectin-like domain (CTL/CTLD) superfamily. Members of this family share a common protein fold and have diverse functions, such as cell adhesion, cell-cell signalling, glycoprotein turnover, and roles in inflammation and immune response. The encoded type 2 transmembrane protein may function as a cell surface antigen. The CLEC10A protein is consisted of 316 amino acids and CLEC10A molecular weight is approximately 35.4 kDa.
What is the function of CLEC10A protein?
CLEC10A plays a role in the maturation of dendritic cells and may be involved in regulating the activation and migration of dendritic cells to lymphoid tissue, thereby presenting antigens to T cells. CLEC10A acts as an endocytic receptor of antigen-presenting cells and binds to ligands to activate immune responses, for example by promoting the maturation of dendritic cells and activating T cells. CLEC10A may play a role in regulating adaptive and innate immune responses, interacting with the sugar domain by binding to calcium-dependent ions. CLEC10A is a pathogen recognition receptor that is able to specifically recognize structures containing terminal N-acetylgalactosamine (GalNAc), which are expressed in a variety of cancer cells.
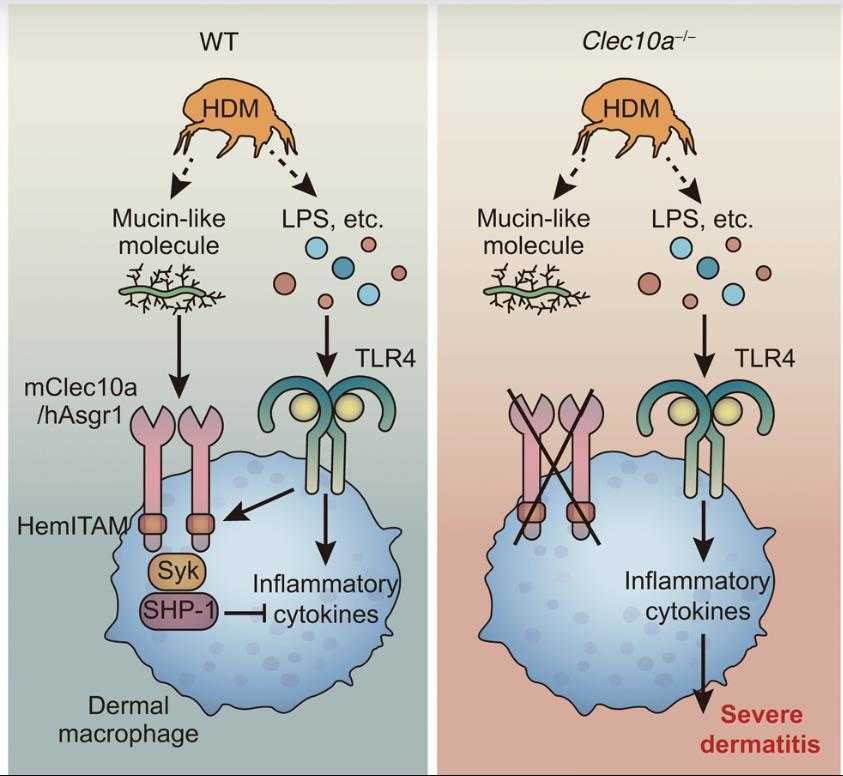
Fig1. A hypothetical model of the role of Clec10a in skin homeostasis upon HDM exposure. (Kazumasa Kanemaru, 2019)
CLEC10A Related Signaling Pathway
Activation of CLEC10A can trigger intracellular signaling events, such as through Syk kinase and downstream molecules such as PLCγ and PKCδ, thereby affecting the physiological function of cells. CLEC10A activates immune cells that bind to it, such as dendritic cells and macrophages, by recognizing specific carbohydrate structures, such as tumor-associated Tn antigens (GalNAc structures). CLEC10A plays a role in antigen presentation by bringing bound antigens into cells through endocytosis and presenting antigen peptides to T cells via MHC molecules, thereby activating T-cell-mediated immune responses. CLEC10A is involved in the regulation of immune responses, including promoting the proliferation and differentiation of T cells, and regulating the activity of natural killer (NK) cells and dendritic cells.
CLEC10A Related Diseases
CLEC10A is a molecule closely related to the immune response, and abnormal expression levels have been associated with a variety of diseases. In the field of cancer, especially lung cancer (LUAD) and breast cancer (BC). In addition, functional abnormalities of CLEC10A are also associated with tumor immune escape and the regulation of anti-tumor immune responses, suggesting a potential role in tumor development and metastasis. In autoimmune diseases, CLEC10A may be involved in regulating the activity of immune cells, affecting inflammation and immune response processes.
Bioapplications of CLEC10A
Reduced expression levels of CLEC10A in a variety of cancers, such as lung and breast cancer, are associated with poor prognosis, making it a potential target for cancer therapy. CLEC10A plays a role in the activation and regulation of immune cells, and its agonists, or antagonists, may be used to treat autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. CLEC10A plays a role in the antigen presentation of dendritic cells and may affect the immunogenicity of vaccines, and the study of its mechanism will help design more effective vaccines. In cell therapies such as CAR-T cell therapy, the expression of CLEC10A may affect the efficacy and safety of cells, and its optimization may improve the specificity and effectiveness of treatment.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Mingyuan Zou, 2022
CLEC10A has attracted attention because of its important role in improving the antitumor activity of immune cells. However, to our knowledge, no study has evaluated the role of CLEC10A in HNSCC prognosis, progression, and immune microenvironment. In the present study, researchers comprehensively analyzed expression profiles of CLEC10A and its association with tumor progression, HPV status, and survival of patients. Moreover, they explored the association between CLEC10A expression relative to immune infiltration and the response to immunotherapy. They explored the association between the timing of the receipt of palliative care relative to cancer diagnosis and survival. The results revealed that CLEC10A has decreased expression in HNSCC compared with normal tissues, and that low expression of CLEC10A was associated with an advanced clinical stage and poor prognosis. Furthermore, a higher level of CLEC10A expression correlated with immune infiltration presence and response to immunotherapy in HNSCC.
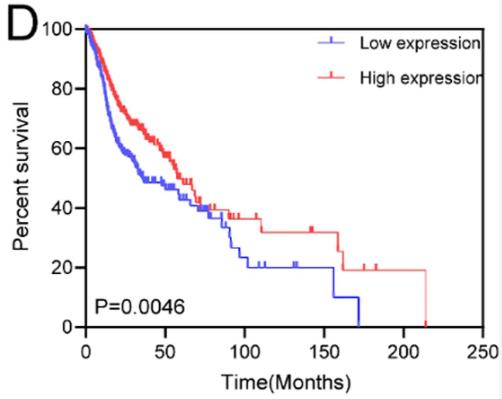
Fig1. Kaplan-Meier analysis was used to compare the CLEC10A high expression group to the CLEC10A low expression.
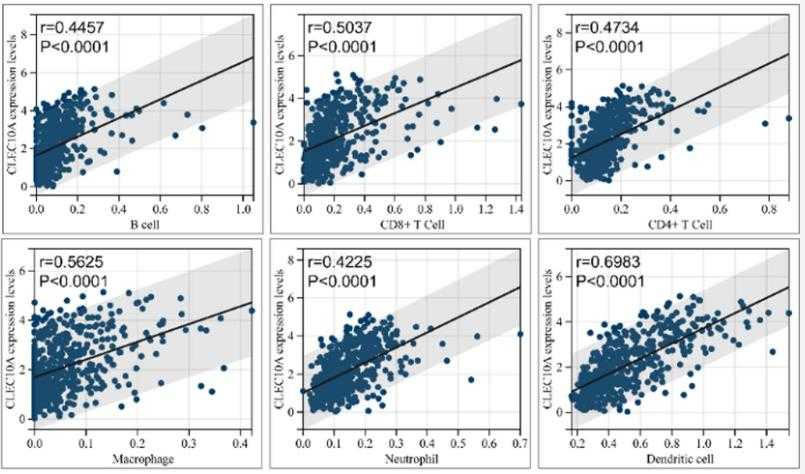
Fig2. Scatterplot of correlation analysis results for the CLEC10A expression levels and immune infiltration level of six immune cell types.
Case Study 2: Yan Qin, 2022
CLEC10A is expressed in a variety of cells. However, the role of CLEC10A from a pan-cancer perspective has not yet been analyzed, and its role in human cancer prognosis and immunology remains largely unclear. Researchers studied the expression levels of CLEC10A and investigated its prognostic value in various cancers across distinct datasets including Oncomine, cBioPortal, and TCGA, and conducted immunohistochemical experiments using fresh bladder cancer and breast cancer samples to verify the results. In addition, they also performed GSEA of CLEC10A and explored the relationship between CLEC10A expression and immune infiltration, immune checkpoints, immune activation genes, immunosuppressive genes, chemokines and chemokine receptors. The results showed that the expression of CLEC10A was significantly related to the immunomodulatory interaction between lymph and non-lymphocytes. Importantly, the analysis of the relationship between CLEC10A and TMB and MSI also confirmed the speculation that CLEC10A may influence antitumor immunity by regulating the composition and immune mechanisms of the tumor microenvironment.
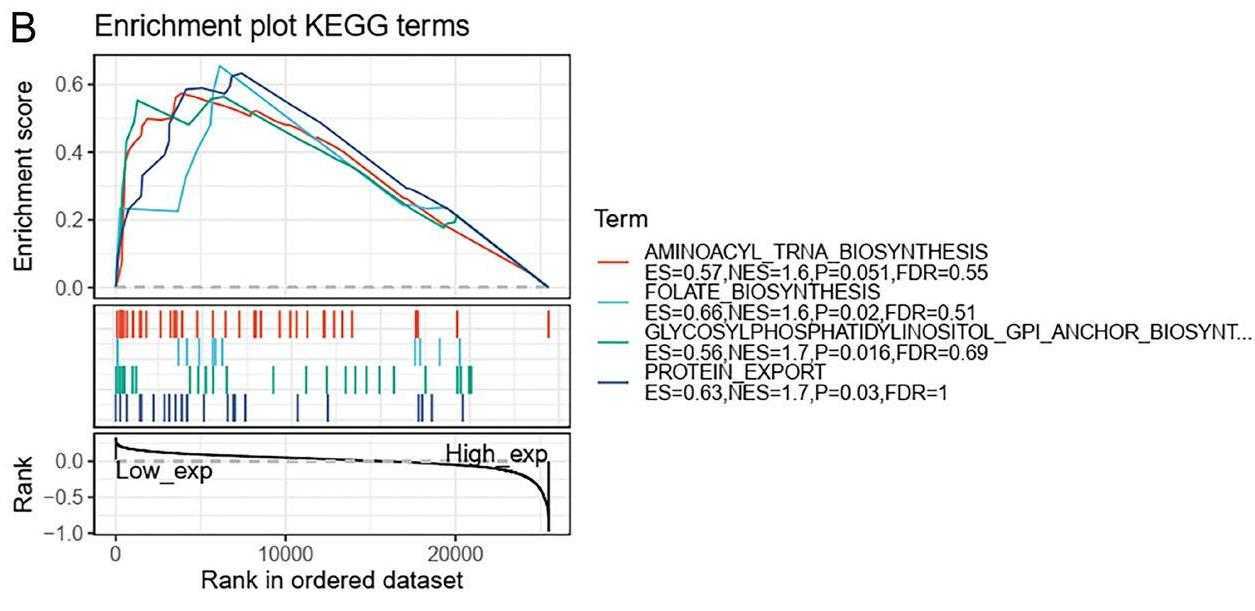
Fig3. Analysis of KEGG pathway in CLEC10A low-expression group.
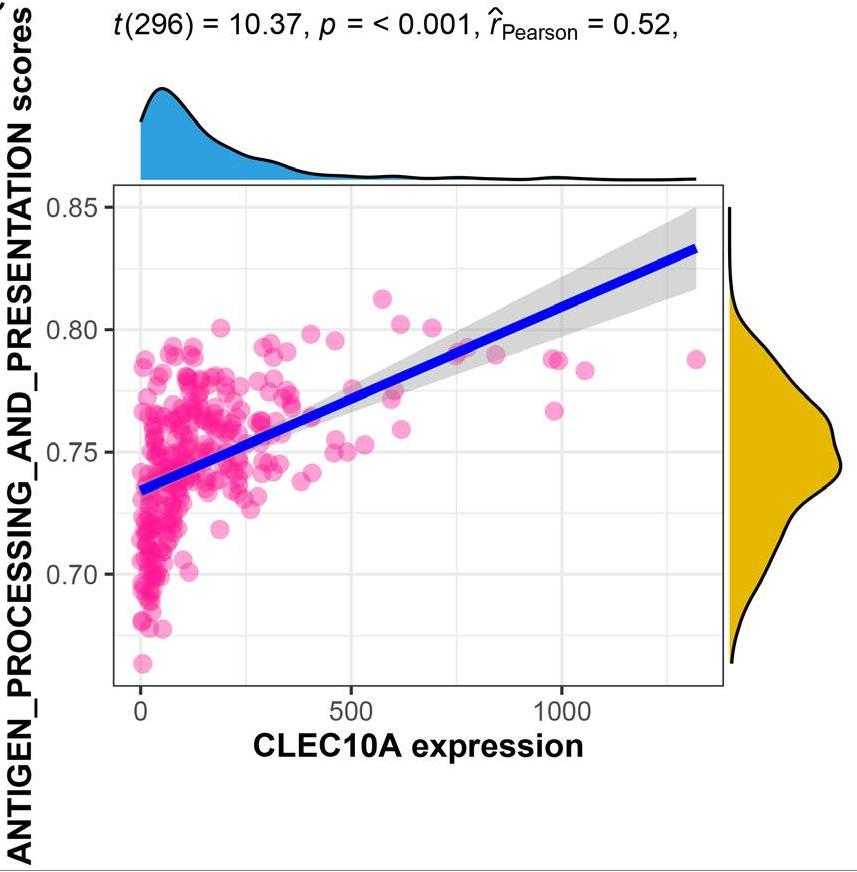
Fig4. The correlation between CLEC10A expression and the enrichment scores of Antigen processing and presentation pathway.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (CLEC10A-1856H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (CLEC10A-1451H)
Involved Pathway
CLEC10A involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways CLEC10A participated on our site, such as , which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with CLEC10A were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|
Protein Function
CLEC10A has several biochemical functions, for example, carbohydrate binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by CLEC10A itself. We selected most functions CLEC10A had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with CLEC10A. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| carbohydrate binding | CLC,CNTN1,REG3B,GALNT3,GFPT1,ZG16,WBSCR17,ILLR4,Clec4n,FBXO6 |
Interacting Protein
CLEC10A has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with CLEC10A here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of CLEC10A.
sSL2
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References



