Active Recombinant Human ACVR1, Fc-tagged, Biotinylated
| Cat.No. : | ACVR1-526H |
| Product Overview : | The recombinant human ACVR1-Fc fusion protein is expressed as a 331amino acid protein consisting of Met21 - Glu123 region of ACVR1 (UniProt accession #Q04771) and a C-terminal Fc fusion from human IgG1, which exists as a dimer under non-reducing condition. |
| Availability | January 27, 2026 |
| Unit | |
| Price | |
| Qty |
- Specification
- Gene Information
- Related Products
- Citation
- Download
| Species : | Human |
| Source : | Human Cells |
| Tag : | Fc |
| Protein Length : | 21-123 a.a. |
| Form : | Supplied at 0.5 mg/ml in sterile PBSpH7.4 (carrier & preservative free). The purified recombinant protein was labeled with Biotin (3-5 Biotin per molecule). |
| Bio-activity : | Immobilized ACVR1 protein binds human BMP6 in a functional ELISA. Blocks BMP6-mediated signaling activity. |
| Molecular Mass : | Calculated molecular mass (kDa): 37.1; Estimated by SDS-PAGE under reducing condition (kDa): ~45 |
| AA Sequence : | MEDEKPKVNPKLYMCVCEGLSCGNEDHCEGQQCFSSLSINDGFHVYQKGCFQVYEQGKMTCKTPPSPGQAVECC QGDWCNRNITAQLPTKGKSFPGTQNFHLESTGTHTCPPCPAPELLGGPSVFLFPPKPKDTLMISRTPEVTCVVV DVSHEDPEVKFNWYVDGVEVHNAKTKPREEQYNSTYRVVSVLTVLHQDWLNGKEYKCKVSNKALPAPIEKTIS KAKGQPREPQVYTLPPSREEMTKNQVSLTCLVKGFYPSDIAVEWESNGQPENNYKTTPPVLDSDGSFFLYSKLT VDKSRWQQGNVFSCSVMHEALHNHYTQKSLSLSPGK |
| Endotoxin : | <0.1 eu per 1 μg of purified recombinant protein determined by the |
| Purity : | >95% judged by SDS-PAGE under reducing condition |
| Storage : | The product is shipped at 4°C. Upon receipt, centrifuge the product briefly before opening the vial. It is recommended to store small aliquots at the temperature below –20°C for long-term storage and the product is stable for 3 months. The undiluted protein can be stored at 4°C for no more than 2 weeks. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Conjugation : | Biotin |
| Publications : |
| Gene Name | ACVR1 activin A receptor, type I [ Homo sapiens ] |
| Official Symbol | ACVR1 |
| Synonyms | ACVR1; activin A receptor, type I; ACVRLK2; activin receptor type-1; ACVR1A; ALK2; SKR1; activin receptor type I; hydroxyalkyl-protein kinase; activin receptor-like kinase 2; TGF-B superfamily receptor type I; activin A receptor, type II-like kinase 2; serine/threonine-protein kinase receptor R1; FOP; TSRI; ACTRI; |
| Gene ID | 90 |
| mRNA Refseq | NM_001105 |
| Protein Refseq | NP_001096 |
| MIM | 102576 |
| UniProt ID | Q04771 |
| Chromosome Location | 2q23-q24 |
| Pathway | ALK1 pathway, organism-specific biosystem; ALK1 signaling events, organism-specific biosystem; ALK2 signaling events, organism-specific biosystem; Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction, organism-specific biosystem; Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction, conserved biosystem; TGF-beta signaling pathway, organism-specific biosystem; TGF-beta signaling pathway, conserved biosystem; |
| Function | ATP binding; SMAD binding; activin binding; contributes_to activin receptor activity, type I; follistatin binding; metal ion binding; nucleotide binding; protein binding; protein homodimerization activity; protein serine/threonine kinase activity; receptor activity; receptor signaling protein serine/threonine kinase activity; transforming growth factor beta binding; transforming growth factor beta receptor activity, type I; transmembrane receptor protein serine/threonine kinase activity; |
| ◆ Recombinant Proteins | ||
| Acvr1-8719R | Recombinant Rat Acvr1 protein, hFc-tagged | +Inquiry |
| ACVR1-170H | Recombinant Human ACVR1 Protein, His-tagged | +Inquiry |
| ACVR1-239H | Recombinant Human Activin A Receptor, Type I, GST-tagged, Active | +Inquiry |
| ACVR1-32H | Recombinant Human ALK2 (Q207D), GST-tagged | +Inquiry |
| ACVR1-33H | Recombinant Human ALK2 (Q207E), GST-tagged | +Inquiry |
| ◆ Cell & Tissue Lysates | ||
| ACVR1-967CCL | Recombinant Canine ACVR1 cell lysate | +Inquiry |
| ACVR1-1305RCL | Recombinant Rat ACVR1 cell lysate | +Inquiry |
| ACVR1-1232CCL | Recombinant Cynomolgus ACVR1 cell lysate | +Inquiry |
| ACVR1-478HCL | Recombinant Human ACVR1 cell lysate | +Inquiry |
| ACVR1-2686MCL | Recombinant Mouse ACVR1 cell lysate | +Inquiry |
An anti-ACVR1 antibody exacerbates heterotopic ossification by fibro-adipogenic progenitors in fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva mice
Journal: The Journal of Clinical Investigation PubMed ID: 35503416 Data: 2022/6/15
Authors: John B. Lees-Shepard, Sean J. Stoessel, David J. Goldhamer
Article Snippet:The phagemid was used to transform XL1-blue E . coli cells to generate the anti-ACVR1 library.The phagemid was used to transform XL1-blue E . coli cells to generate the anti-ACVR1 library.. The library was panned for 2 rounds on biotinylated ACVR1 ECD (Creative BioMart) that was conjugated to magnetic streptavidin beads (Dynabeads MyOne, Thermo Fisher Scientific, 65601).. Streptavidin beads without ACVR1 were used in deselection steps to remove nonspecific binders.Streptavidin beads without ACVR1 were used in deselection steps to remove nonspecific binders.
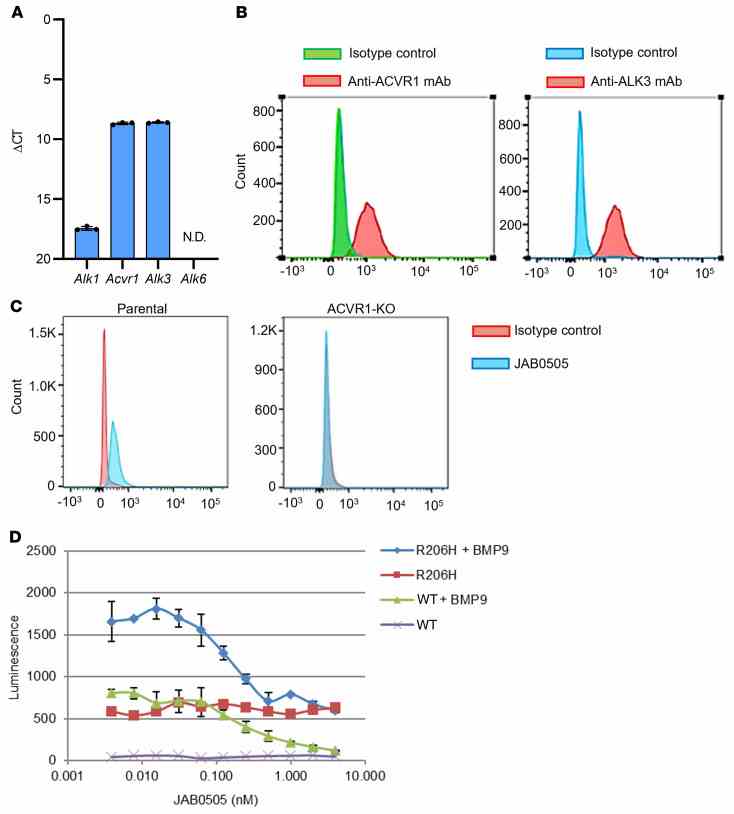
( A ) Mouse C2C12 myoblast cells express similar levels of
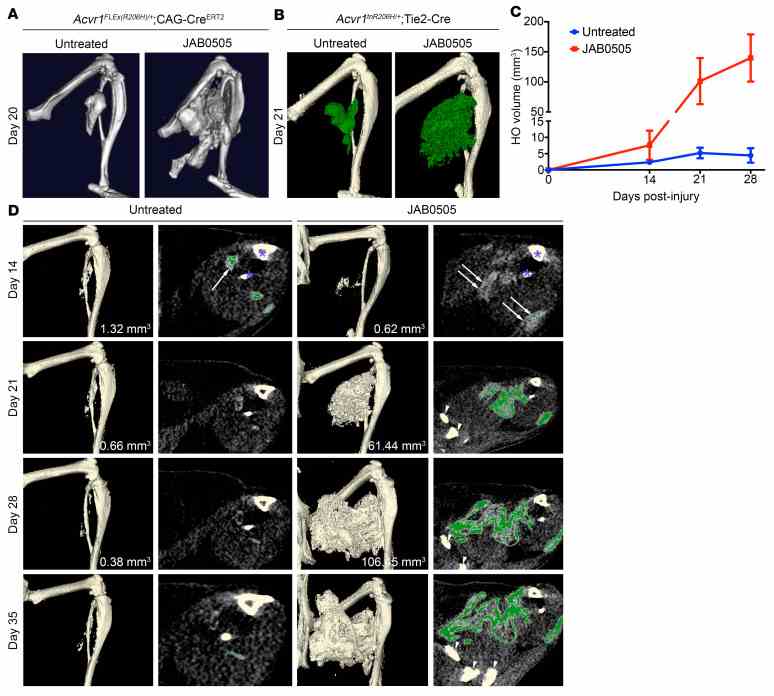
( A ) Representative μCT images of HO in
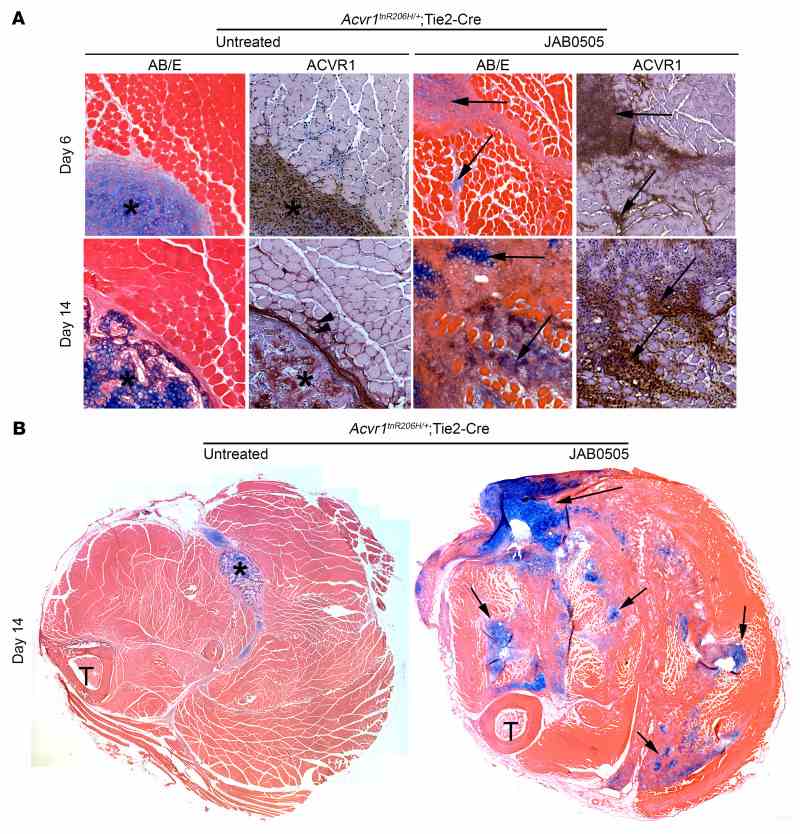
( A ) Transverse sections of muscle from untreated and JAB0505-treated
Not For Human Consumption!
Inquiry
- Reviews (0)
- Q&As (0)
Ask a Question for All ACVR1 Products
Required fields are marked with *
My Review for All ACVR1 Products
Required fields are marked with *



