VEGFC
-
Official Full Name
vascular endothelial growth factor C -
Overview
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the platelet-derived growth factor/vascular endothelial growth factor (PDGF/VEGF) family. The encoded protein promotes angiogenesis and endothelial cell growth, and can also affect the permeability of blood vessels. The proprotein is further cleaved into a fully processed form that can bind and activate VEGFR-2 and VEGFR-3 receptors. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2014] -
Synonyms
VEGFC;vascular endothelial growth factor C;VRP;Flt4-L;FLT4 ligand DHM;vascular endothelial growth factor-related protein;VEGF-C;AW228853
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse/Rat
- Zebrafish
- Mouse
- Rat
- Rhesus macaque
- Cattle
- Dog
- Chicken
- Rabbit
- HEK293
- CHO
- Mammalian Cells
- Insect Cells
- E.coli
- Sf9 Cells
- Insect cells
- Human
- Human Cells
- Yeast
- His
- Fc
- Avi
- Non
- T7
- GST
- Flag
- SUMO
Background
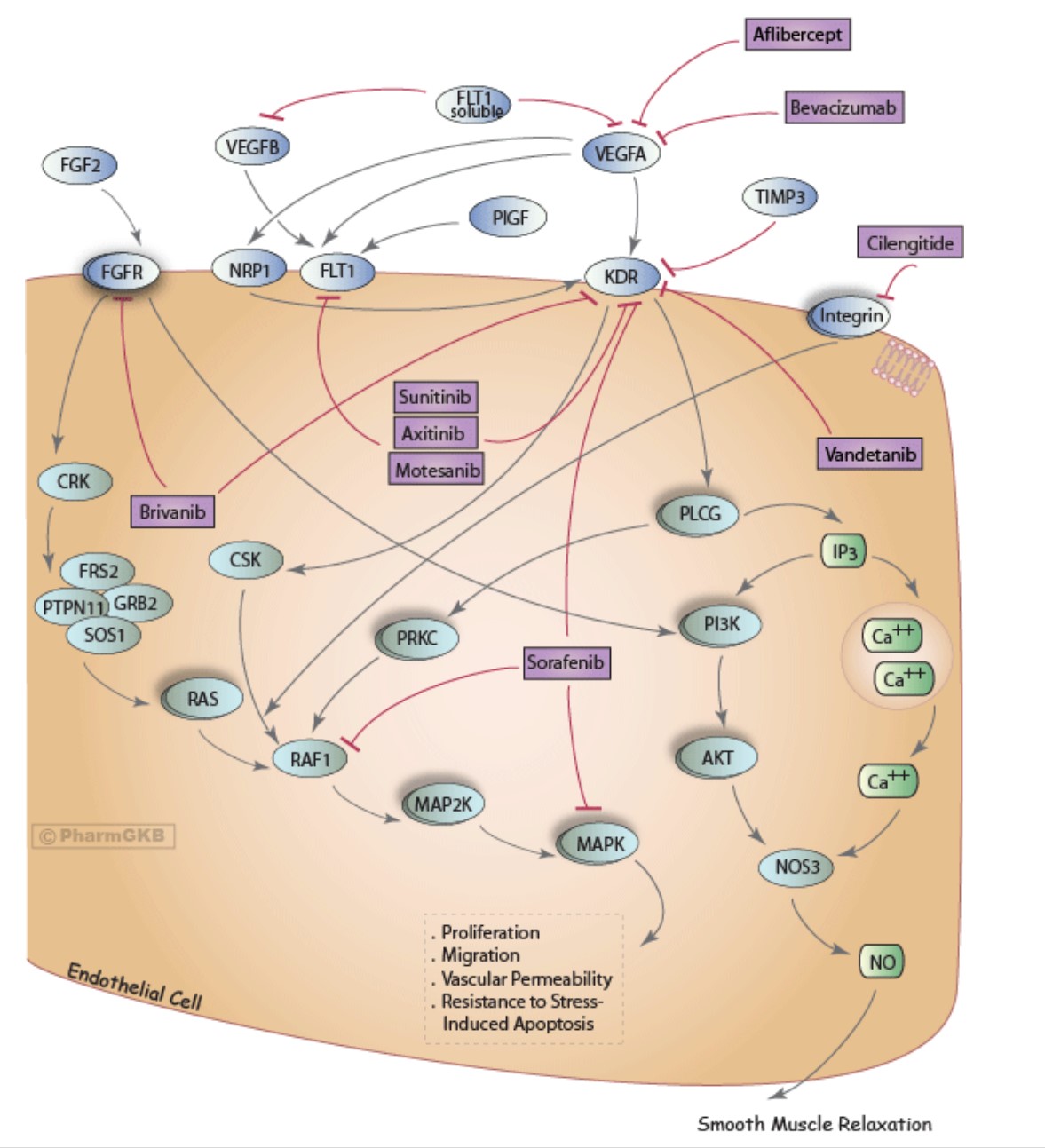
Fig1. Model endothelial cell displaying genes of the VEGF signalling pathway and the sites at which bevacizumab, sorafenib, sunitinib, brivanib and cilengitide are known to act. (Pictures from PHARMGKB)
What is VEGFC protein?
VEGFC (vascular endothelial growth factor C) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 4 at locus 4q34. The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the platelet-derived growth factor/vascular endothelial growth factor (PDGF/VEGF) family. The encoded protein promotes angiogenesis and endothelial cell growth, and can also affect the permeability of blood vessels. The proprotein is further cleaved into a fully processed form that can bind and activate VEGFR-2 and VEGFR-3 receptors. The VEGFC protein is consisted of 419 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 46.9 kDa.
What is the function of VEGFC protein?
VEGFC act as a growth factor in angiogenesis, and endothelial cell growth, stimulating their proliferation and migration and also has effects on the permeability of blood vessels. It may has functions in angiogenesis of the venous and lymphatic vascular systems during embryogenesis, and also in the maintenance of differentiated lymphatic endothelium in adults.
VEGFC Related Signaling Pathway
The VEGFR-2/3 signaling pathway, when combined with it, can activate the pathway, thereby promoting lymphangiogenesis and tumor metastasis. In the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway, VEGFC activates phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) through VEGFR-2, and then activates Akt, which is involved in the regulation of cell proliferation, survival and vascular permeability. In addition, there are MAPK/ERK signaling pathways, Notch signaling pathways and so on.
VEGFC Related Diseases
Overexpression of VEGFC is associated with angiogenesis and metastasis of malignant tumors, such as breast cancer, lung cancer, and colorectal cancer. It is also associated with lymphangiogenesis and lymph node metastasis, and overexpression of VEGFC can lead to abnormal lymphangiogenesis and lymph node enlargement. In addition, some other vascular diseases are associated, such as generalized vasodilatation, congenital lymphedema and so on.
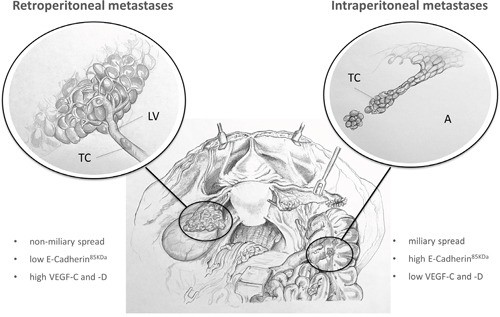
Fig2. Expression patterns determining different types of metastases in EOC Tumour cells of patients with 'predominant retroperitoneal' metastases are characterised by a mesenchymal tumour type with low E-Cadherin and high VEGF-C and –D expression. (Sascha Kuerti, 2017)
Bioapplications of VEGFC
Using VEGFC's anti-angiogenic effect, researchers are exploring its use in the treatment of tumors, inhibiting tumor angiogenesis and stopping tumor growth and metastasis. At the same time, there are also some studies on the treatment of cardiovascular diseases such as myocardial infarction and arterial disease.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Omar García-Pérez, 2023
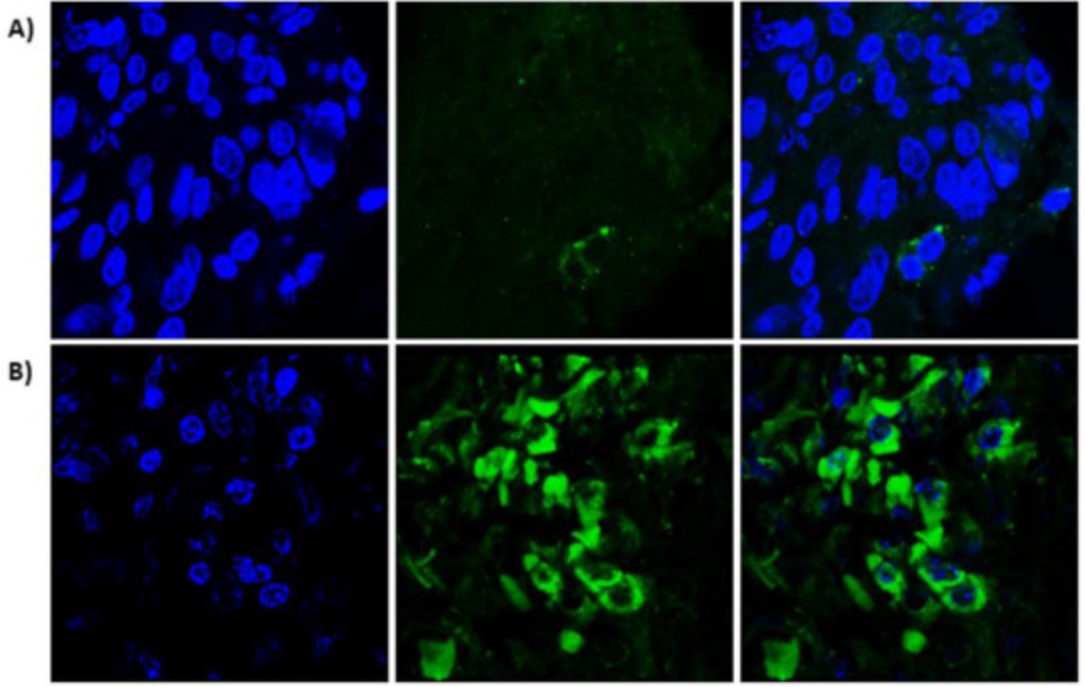
Fig1. VEGFC protein in CSCC tumors detected by immunofluorescence.
Case Study 2: Zhengmin Wang, 2021
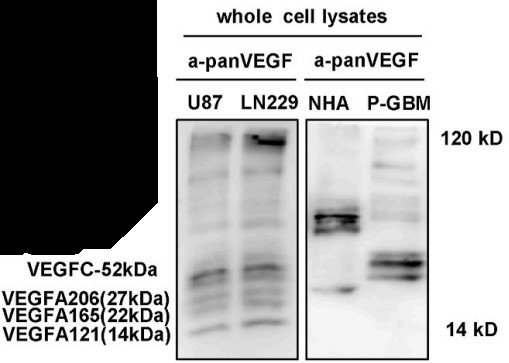
Fig2. Various VEGF-positive bands in the GBM cell lysates were detected by pan-VEGF antibody, and the molecular weight ranged from 15 to 120 kDa.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
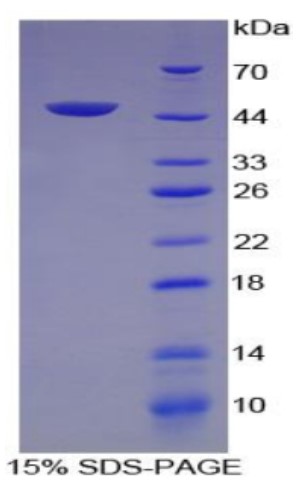
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (VEGFC-604H) (PROTOCOL for western blot)
.
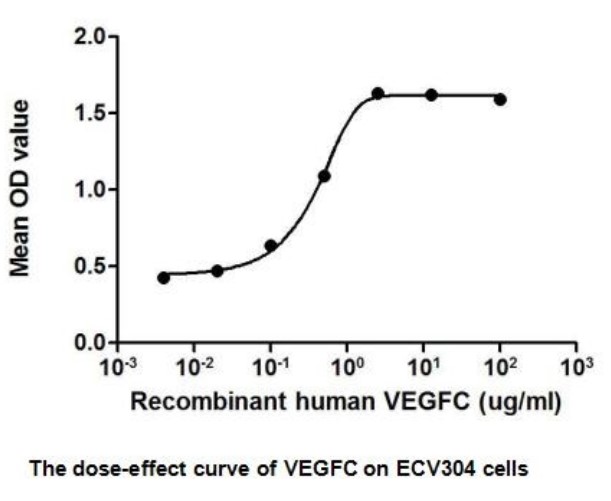
Fig2. Activity Data. (VEGFC-566H)
Involved Pathway
VEGFC involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways VEGFC participated on our site, such as Ras signaling pathway,Rap signaling pathway,Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with VEGFC were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Ras signaling pathway | BCL2L1,PGF,PDGFA,PLCG2,PAK6,SOS1,INS2,FGF2,STK4,RALB |
| PIK-Akt signaling pathway | ITGB5,SGK3,IGF1R,Il4ra,PRKAA1,TCL1B1,TNC,IFNA7,LAMC2,FASLG |
| Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction | GHRA,TNFRSF12A,TNFSF10,IFNW1,CCL20B,Ccl27a,CXCL2,IFNA7,GM13304,TNFRSF11A |
| Rap signaling pathway | MAPK12,SIPA1L2,ITGB3,Itgam&Itgb2,INS2,GRIN2A,MAGI1,IGF1,ITGAM,NGFR |
| TNF signaling pathway | PIK3R5,MAP2K3,TRADD,TRAF5,NFKBIA,CASP7,PIK3CD,BIRC2,MAPK11,IL18R1 |
| Focal adhesion | PIP5K1C,PRKCBA,ACTN3B,CCND1,PTENA,VAV3,LAMB3,VTNA,RAP1AA,ACTN4 |
| Pathways in cancer | MET,FGFR2,MECOM,GNB3,BRCA2,LPAR3,TCF7L2,CDC42,IGF1,PDGFA |
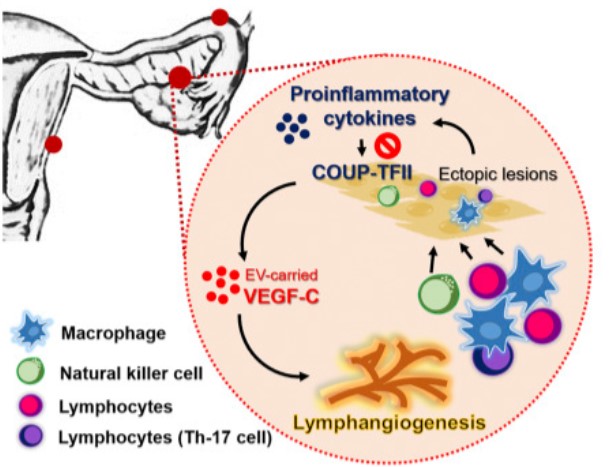
Fig2. Blocking VEGF-C signaling reduces immune cells infiltration to endometriotic tissues. (Wan-Ning Li, 2020)
Protein Function
VEGFC has several biochemical functions, for example, chemoattractant activity,growth factor activity,protein binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by VEGFC itself. We selected most functions VEGFC had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with VEGFC. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| protein binding | EFCAB4B,TYROBP,SAP30,SEPT5,TRAK1,ACY3,BBS7,NCAM1A,PRKCB,DYRK2 |
| vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 binding | FIGF,VHL |
| growth factor activity | GFER,BMP5,GDF2,NOV,NRG1,KLK1B3,MDKA,IL11,FGF3,BTC |
| chemoattractant activity | SAA1,HMGB1,PDGFB,SAA2,MIF,BMP4,CXCL12B,FIGF,VEGFA,CCL16 |
Interacting Protein
VEGFC has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with VEGFC here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of VEGFC.
FLT4
Resources
Gene Families
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Ma, J; Zhou, D; et al. Keratocytes Create Stromal Spaces to Promote Corneal Neovascularization Via MMP13 Expression. INVESTIGATIVE OPHTHALMOLOGY & VISUAL SCIENCE 55:-(2014).
- Ikeda, K; Oki, E; et al. Intratumoral Lymphangiogenesis and Prognostic Significance of VEGFC Expression in Gastric Cancer. ANTICANCER RESEARCH 34:3911-3915(2014).



