CCL21
-
Official Full Name
chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 21 -
Overview
Recombinant Mouse Chemokine (C-C Motif) Ligand 21A (Serine) -
Synonyms
SLC protein, Exodus 2, Exodus-2 protein, 6Ckine protein, Exodus-2 protein, Exodus 2, Exodus 2 protein, Exodus-2, CCL21 protein
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Rhesus macaque
- Cynomolgus
- Rat
- Insect Cells
- E.coli
- CHO
- Mammalian Cells
- Human
- HEK293
- Human Cells
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- Non
- GST
- Fc
- His
- Avi
- Flag
Background
What is CCL21 protein?
CCL21 (C-C motif chemokine ligand 21) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the short arm of chromosome 9 at locus 9p13. This antimicrobial gene is one of several CC cytokine genes clustered on the p-arm of chromosome 9. Cytokines are a family of secreted proteins involved in immunoregulatory and inflammatory processes. The CC cytokines are proteins characterized by two adjacent cysteines. The CCL21 protein is consisted of 134 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 14.6 kDa.
What is the function of CCL21 protein?
Similar to other chemokines the protein encoded by this gene inhibits hemopoiesis and stimulates chemotaxis. This protein is chemotactic in vitro for thymocytes and activated T cells, but not for B cells, macrophages, or neutrophils. The cytokine encoded by CCL21 gene may also play a role in mediating homing of lymphocytes to secondary lymphoid organs. It is a high affinity functional ligand for chemokine receptor 7 that is expressed on T and B lymphocytes and a known receptor for another member of the cytokine family (small inducible cytokine A19).
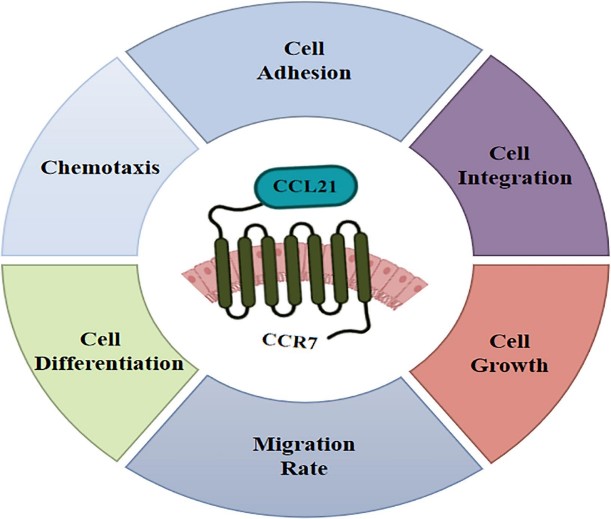
Fig1. Biological functions of CCL21/CCR7 axis. (Le Han, 2023)
CCL21 Related Signaling Pathway
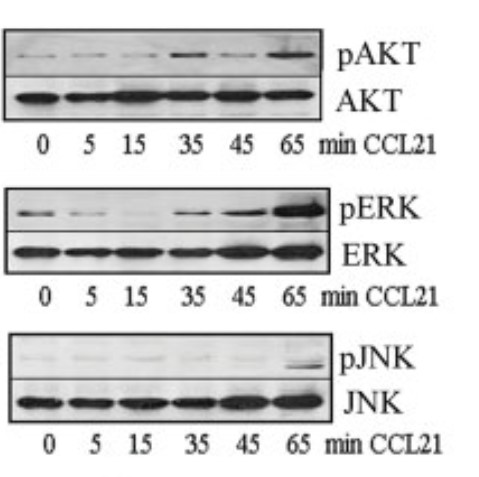
The signaling pathway of CCL21 involves the CCR7 signaling pathway, which regulates cell migration and survival mainly through the activation of PI3K/Akt, MAPK and NF-κB. In addition, CCL21 can chemotactic T cells, B lymphocytes, mature dendritic cells (DC) and NK cells, and participate in the homing process of lymphocytes. In addition, tumor cells secrete immunosuppressive factors such as CCL21 to block the host's anti-tumor immune response, thus achieving immune escape.
CCL21 Related Diseases
It has attracted much attention because of its important role in immune cell migration and inflammation regulation. Diseases associated with CCL21 include inflammatory diseases, autoimmune diseases, and tumors, and its secretion in some aggressive tumor cells may promote tumor development.
Bioapplications of CCL21
Some relevant studies have explored its potential role in cancer treatment, including improving the effectiveness of immunotherapy by modulating the activity of immune cells in the tumor microenvironment, and there are also studies trying to exploit the biological role of CCL21 to develop new drugs or therapies targeting immunotherapy.
Case Study
Case study 1: C Y Hong, 2014
The potential use of lymphoid chemokines to generate a dendritic cell (DC) cancer vaccine is not yet clear. The researchers investigated the effect of lymphoid chemokines on DC function and on the production of effective cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) for application of cancer vaccine using monocyte-derived mature DCs (mDCs) prestimulated with lymphoid chemokines.
mDCs exposed to a secondary lymphoid organ chemokine (SLC/CCL21) dramatically induced CTL response by increasing cytolytic activity without any significant alterations on expression of cell surface markers. mDCs prestimulated with CCL21 showed higher levels of CXCL10 (IP-10) production, but not the production of CCL22, compared with untreated mDCs. IP-10 treatment during CTL generation with DCs dramatically enhanced tumour-specific CTL response compared with untreated CTLs, and these enhanced CTL-inducing functions of CCL21-treated DCs were inhibited by anti-IP-10 treatment.
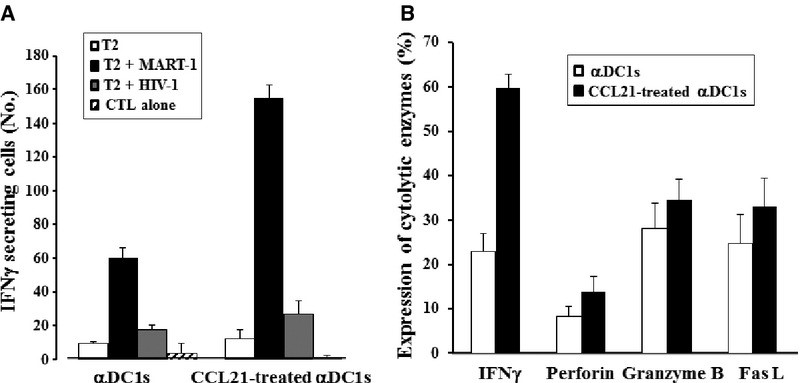
Fig1. Enhanced cytotoxicity of CTLs by CCL21-treated αDC1s. The increased number of IFNγ-secreting cells in CCL21-treated αDC1s.
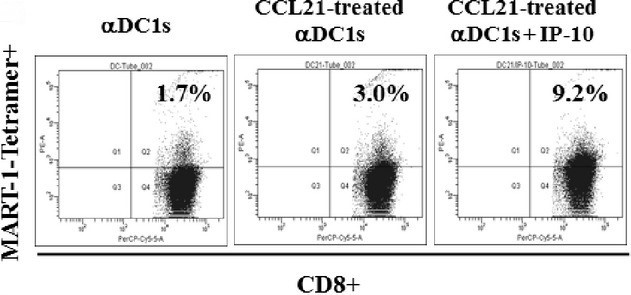
Case study 2: Sarah R Pickens, 2012
To determine the role of CCL21 and its receptor CCR7 in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). The role of CCL21 and/or CCR7 in angiogenesis was examined using in vitro chemotaxis, tube formation, and in vivo Matrigel plug assays. Finally, the mechanism by which CCL21 mediates angiogenesis was determined by Western blot analysis and endothelial cell chemotaxis and tube formation assays.
CCL21, but not CCL19, at concentrations present in the RA joint, induced human microvascular endothelial cell (HMVEC) migration that was mediated through CCR7 ligation. Suppression of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway markedly reduced CCL21-induced HMVEC chemotaxis and tube formation. Neutralization of either CCL21 in RA synovial fluid or CCR7 in HMVECs significantly reduced the induction of HMVEC migration and/or tube formation by RA synovial fluid.
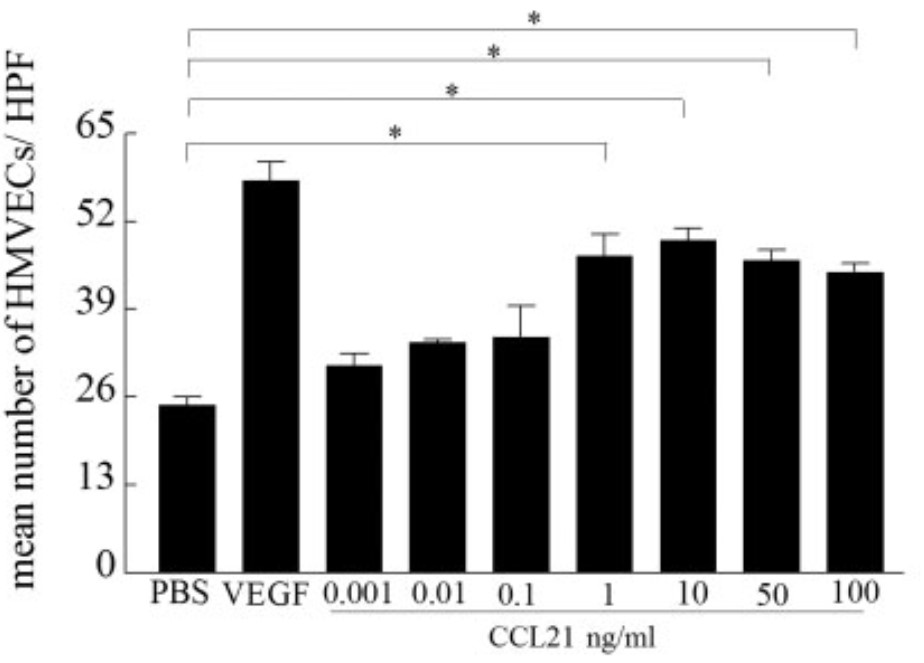
Fig3. CCL21-induced HMVEC chemotaxis showed that CCL21 induced cell migration.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
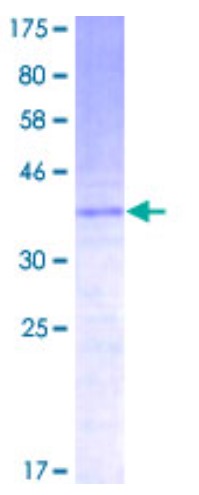
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (CCL21-0626H) (PROTOCOL for western blot)
High Bioactivity
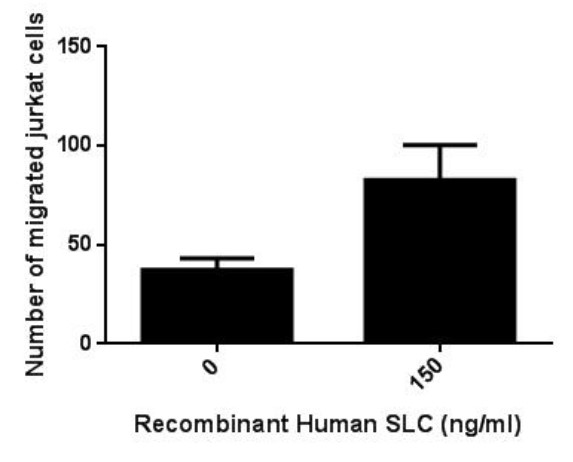
Fig2. Activity Data. (CCL21-2148H)
Involved Pathway
CCL21 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways CCL21 participated on our site, such as Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction,Chemokine signaling pathway,NF-kappa B signaling pathway, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with CCL21 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| NF-kappa B signaling pathway | TNF,LTA,IRAK4,UBE2I,GADD45B,NFKB1,BCL2,CCL13,TNFRSF13C,TAB2 |
| Chemokine signaling pathway | CX3CR1,GNG5,LOC100033925,PLCB3,GNB2,GNG13,CX3CL1,PREX1,CCL4L1,CCR3 |
| Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction | FLT1,TNFRSF4,IFNW1,IL15RA,IFNA13,IL3,IL23R,IL9,GH1,IFNAR1 |
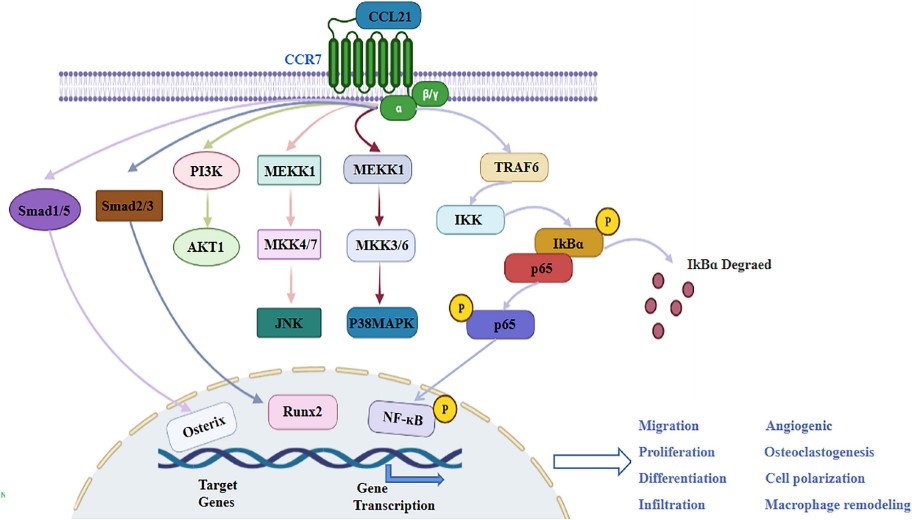
Fig1. Schematic diagram of possible signaling pathways involved by CCL21/CCR7 axis. (Le Han, 2023)
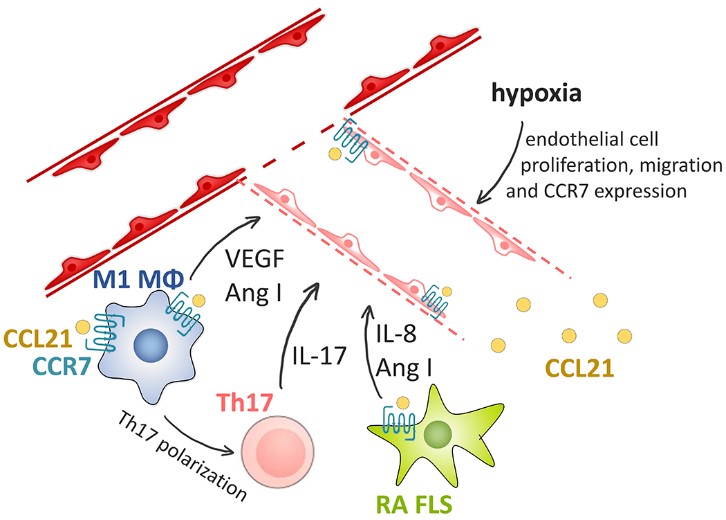
Fig2. The direct and indirect angiogenic impact of CCL21 in RA. (Katrien Van Raemdonck, 2020)
Protein Function
CCL21 has several biochemical functions, for example, CCR chemokine receptor binding,CCR7 chemokine receptor binding,chemokine activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by CCL21 itself. We selected most functions CCL21 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with CCL21. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| CCR chemokine receptor binding | CCL17,CCL35.1,CCL8,CCL15,CCL25B,CCL14,CCL38A.5,CCL19A.1,CCL44,CCL26 |
| CCR7 chemokine receptor binding | CCL19 |
| chemokine receptor binding | Ccl21a,CXCL12,CCL19,XCL1,CCL5,CCL25,CCRL2,CCL21B,Ccl21c,S100A14 |
| chemokine activity | CXCL10,CXCL20,CXCL12,CKLF,Ccl21a,Ccl12,IL-8,CXCL14,CCL34B.4,CCL23 |
Interacting Protein
CCL21 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with CCL21 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of CCL21.
LRRK1;LRRK2;a41_vaccw;CCR7;GOT2;q81ue9_bacan;UBQLN4
Resources
Gene Families
Research Area
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Carubbi, F; Alunno, A; et al. Is minor salivary gland biopsy more than a diagnostic tool in primary Sjogren's syndrome? Association between clinical, histopathological, and molecular features: A retrospective study. SEMINARS IN ARTHRITIS AND RHEUMATISM 44:314-324(2014).
- Chadzinska, M; Golbach, L; et al. Characterization and expression analysis of an interferon-gamma 2 induced chemokine receptor CXCR3 in common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.). DEVELOPMENTAL AND COMPARATIVE IMMUNOLOGY 47:68-76(2014).



