SPARC
-
Official Full Name
secreted protein, acidic, cysteine-rich (osteonectin) -
Overview
SPARC, an acronym for “secreted protein, acidic and rich in cysteine”, is also known as osteonectin or BM-40. It is the founding member of a family of secreted matricellular proteins with similar domain structure. The 303 amino acid, 43 kDa protein contains a 17 aa signal sequence, an N-terminal acidic region that binds calcium, a follistatin domain containing Kazal-like sequences, and a C-terminal extracellular calcium (EC) binding domain with two EF-hand motifs . SPARC is produced by fibroblasts, capillary endothelial cells, platelets and macrophages,especially in areas of tissue morphogenesis and remodeling. SPARC shows context-specific effects, but generally inhibits adhesion, spreading and proliferation, and promotes collagen matrix formation. For endothelial cells,SPARC disrupts focal adhesions and binds and sequesters PDGF and VEGF. SPARC is abundantly expressed in bone, where it promotes osteoblast differentiation and inhibits adipogenesis. -
Synonyms
ON;BM-40;Osteonectin;Basement-membrane protein 40;Osteonectin (secreted protein, acidic, cysteine-rich);SPARC precursor;Secreted protein acidic and rich in cysteine;cysteine-rich protein;secreted protein, acidic, cysteine-rich (osteonectin);SPRC_HUMAN;SPARC [Precursor];SPARC
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Cynomolgus
- Rat
- Zebrafish
- Chicken
- Rabbit
- Human
- Bovine
- E.coli
- HEK293
- Mammalian Cells
- C-His
- CHO
- Human Cells
- Insect Cells
- Bone
- Human thrombin activated platelets
- GST
- His
- Avi
- Fc
- Non
- MBP
- T7
- DDK
- Myc
Background
What is SPARC protein?
SPARC (Secreted Protein Acidic and Rich in Cysteine), also known as osteonectin, is a protein that is expressed in various tissues and has diverse biological functions. It belongs to the matricellular protein family, which influences cell-matrix interactions and tissue remodeling.
The SPARC protein is primarily found in the extracellular matrix, where it regulates cell adhesion, migration, proliferation, and tissue development. It interacts with different types of cells, including fibroblasts, endothelial cells, and immune cells, and plays a role in tissue remodeling during embryonic development, wound healing, and tissue repair.
What is the function of SPARC protein?
Modulates cell-matrix interactions: It binds collagen and other ECM components to regulate how cells interact with and respond to the surrounding microenvironment.
Inhibits cell adhesion: SPARC promotes cell detachment from the ECM by interfering with adhesion receptors like integrins. This affects cell spreading, migration, proliferation.
Remodels extracellular matrix: It regulates deposition and rearrangement of ECM components like collagen and their crosslinking by involving in ECM turnover processes.
Regulates growth factors: SPARC binds various growth factors like VEGF, PDGF, FGFs and alters their ECM retention and presentation to cells, thus modulating their downstream signaling.
SPARC related signaling pathway
MAPK/ERK pathway: SPARC binds to components like FGF to activate ERK signaling, regulating processes like cell proliferation and differentiation.
TGF-β pathway: It interacts with TGF-β1 and facilitates its signaling by retaining it in the ECM. This affects processes like fibrosis and EMT.
Wnt/β-catenin pathway: SPARC modulates Wnt ligand availability and signaling strength via interaction with FZD receptors and LRP co-receptors.
Notch pathway: It regulates cleavage and signaling of Notch receptors affecting cell-fate decisions during development and disease.
SPARC Related Diseases
- Cancers: Altered levels in many cancers like breast, brain, prostate, linked to invasiveness, metastasis, and prognosis.
- Pulmonary fibrosis: Implicated in pathogenesis by promoting collagen deposition and ECM remodeling in lungs.
- Cardiovascular diseases: Associated with atherosclerotic plaque formation and instability. Role in post-MI cardiac remodeling.
- Renal diseases: Involved in tubulointerstitial fibrosis during AKI and CKD through TGF-β modulation.
- Arthritis: Expression upregulated in osteoarthritic and rheumatoid arthritis joints contributing to cartilage degradation.
- Cancer therapy: Developing SPARC inhibitors/antagonists as anti-cancer drugs to target tumors dependent on SPARC function.
- Anti-fibrotics: Investigating SPARC modulation as an approach to treat fibrotic diseases of lungs, kidneys, liver by interfering with ECM deposition.
- Wound healing: Studying the role of SPARC in modulating wound repair processes like contraction, scar formation to improve outcomes.
- Tissue engineering: Using knowledge of SPARC to develop biomaterials for regenerative approaches by regulating interactions between graft and host tissues.
- Cancer therapy: Developing SPARC inhibitors/antagonists as anti-cancer drugs to target tumors dependent on SPARC function.
- Anti-fibrotics: Investigating SPARC modulation as an approach to treat fibrotic diseases of lungs, kidneys, liver by interfering with ECM deposition.
- Wound healing: Studying the role of SPARC in modulating wound repair processes like contraction, scar formation to improve outcomes.
- Tissue engineering: Using knowledge of SPARC to develop biomaterials for regenerative approaches by regulating interactions between graft and host tissues.
Case Study
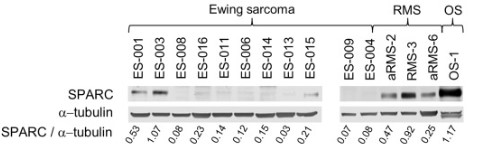
(Guillem Pascual-Pasto, 2022)
Fig2. Immunoblotting of SPARC in Ewing sarcoma, rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS) and osteosarcoma (OS) PDXs. Sample names are coded as described previously, but the codes in the figure omit the prefix HSJD for clarity purposes [22]. α-Tubulin was the loading control. Numbers below represent the signal ratio of SPARC relative to α-tubulin.
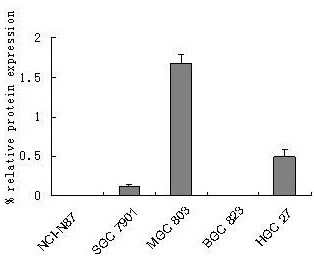
(Jie Yin, 2010)
Fig3.Relative SPARC mRNA expression levels. Autoradiographs were scanned and analyzed by densitometry followed by quantitation relative to β-actin. Results are shown as expression (in %) relative to β-actin and are means (± SD) of 3
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (Cat. No.: Sparc-7699R)
Involved Pathway
SPARC involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways SPARC participated on our site, such as Binding and Uptake of Ligands by Scavenger Receptors,ECM proteoglycans,Extracellular matrix organization, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with SPARC were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Extracellular matrix organization | BMP1B,F11R.2,MATN3B,CEACAM8,ELANE,SERPINH1,LOX,LOXL2,PCOLCEB,LTBP2 |
| Scavenging by Class H Receptors | STAB2 |
| ECM proteoglycans | VCANB,DAG1,LRP4,MUSK,DMP1,MATN3B,COL9A3,ACAN,ITGB3A,FMOD |
| Response to elevated platelet cytosolic Ca2+ | BRPF3,CAP1,STXBP3A,CLU,F13A1A.1,STXBP3,TFA,SCG3,SERPINF2B,CALU |
| Hemostasis | KIF2C,SLC16A8,PRKCHB,SERPINF2B,DOK2,ANGPT2A,MFN1,PLEK,APOA1B,GAS6 |
| Platelet degranulation | BRPF3,GAS6,MMRN2A,IGF2B,CD9B,F13A1A.1,SRGN,CLU,F13A1B,CAP1 |
| Platelet activation, signaling and aggregation | MMRN2A,AASS,GAS6,PDPN,IGF2B,ABHD6B,FCER1GL,TRPC6A,CD9A,MMRN1 |
| Binding and Uptake of Ligands by Scavenger Receptors | COL3A1,NFX1,IGKC,STAB2,LOC479668,HSPH1,APOBB.1,AMBP,COL1A1,CD163 |
Protein Function
SPARC has several biochemical functions, for example, calcium ion binding,collagen binding,extracellular matrix binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by SPARC itself. We selected most functions SPARC had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with SPARC. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| collagen binding | SERPINH2,SERPINH1A,PDGFA,C1QTNF1,NID1,USH2A,LUM,ITGA3,GP5,CTSB |
| protein binding | NINJ2,CPNE3,CASKIN1,SREK1IP1,CLOCK,PRPF3,CORO2B,ADAM8,POP7,TNFRSF13B |
| extracellular matrix binding | CD248,GPR56,DMP1,ITGA2B,TGFBI,DCN,ITGB3,SID4,ITGAV,FBLN2 |
| calcium ion binding | CALM1,S100A16,LRP4,S100A10A,S100G,PCDH11Y,MYL2B,PCDHB7,PCDH2G9,VIL1 |
Interacting Protein
SPARC has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with SPARC here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of SPARC.
faf;XRCC6;fusA;ZNF579
Resources
Research Area
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Onoz, M; Basaran, R; et al. Correlation between SPARC (Osteonectin) expression with immunophenotypical and invasion characteristics of pituitary adenomas. APMIS 123:199-204(2015).
- Peixoto, E; Atorrasagasti, C; et al. SPARC (secreted protein acidic and rich in cysteine) knockdown protects mice from acute liver injury by reducing vascular endothelial cell damage. GENE THERAPY 22:9-19(2015).



