APP
-
Official Full Name
amyloid beta (A4) precursor protein -
Overview
This gene encodes a cell surface receptor and transmembrane precursor protein that is cleaved by secretases to form a number of peptides. Some of these peptides are secreted and can bind to the acetyltransferase complex APBB1/TIP60 to promote transcriptional activation, while others form the protein basis of the amyloid plaques found in the brains of patients with Alzheimer disease. Mutations in this gene have been implicated in autosomal dominant Alzheimer disease and cerebroarterial amyloidosis (cerebral amyloid angiopathy). Multiple transcript variants encoding several different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] -
Synonyms
APP;amyloid beta (A4) precursor protein;AAA;AD1;PN2;ABPP;APPI;CVAP;ABETA;PN-II;CTFgamma;amyloid beta A4 protein;preA4;protease nexin-II;peptidase nexin-II;beta-amyloid peptide;alzheimer disease amyloid protein;cerebral vascular amyloid peptide
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Chicken
- Rat
- Tetraodon fluviatilis (Green pufferfish) (Chelonodon fluviatilis)
- Sus scrofa (Pig)
- Takifugu rubripes (Japanese pufferfish) (Fugu rubripes)
- Macaca fascicularis
- Mammalian Cells
- HEK293
- E.coli
- Synthetic
- Mouse
- Sf21 Cells
- E.Coli/Yeast
- Human Cells
- HeLa
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- Others
- His
- Fc
- GST
- Non
- DDK
- Myc
- Avi
- SUMO
Involved Pathway
APP involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways APP participated on our site, such as Serotonergic synapse,Alzheimers disease, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with APP were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Alzheimers disease | MT-ATP6,COX7A2L,CALM1,TNF,NCSTN,SDHA,CALM2,ATP5D,GRIN2C,CALM4 |
| Serotonergic synapse | GNB2,CYP2D26,GNAS,HTR3A,PTGS1,PRKACG,PLCB2,GNB4,MAP2K1,HTR7 |
Protein Function
APP has several biochemical functions, for example, DNA binding,PTB domain binding,acetylcholine receptor binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by APP itself. We selected most functions APP had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with APP. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| serine-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity | SERPINB9,A1i3,SERPINA10,APLP2,COL7A1,SPINT1B,WFDC13,PAPLNB,SPINK8,SERPINF2 |
| identical protein binding | KCNJ10,FBXW7,PDCD6,CEACAM16,DRD2,TARDBP,NELL2,CORO1B,SUN2,TPCN2 |
| receptor binding | FGF18A,CADM1,ALCAM,NPPC,MIF,P2RX4,LBP,FGF12A,CYTL1,DIAPH1 |
| protein binding | DYNLL2,FGA,LHX4,DDX11,HYLS1,CSDC2,RTN4RL1,CGA,CD1A,FEM1B |
| heparin binding | RPL22,PTCH1,ZNF207,KNG1,LPA,IMPG2,FBLN7,TENM1,CYR61,SLIT2 |
| enzyme binding | GSTM7,H2AFX,TOP2B,YWHAB,KIAA1967,CABYR,EIF4E,FOXO4,PPP3CA,MTA1 |
| PTB domain binding | NUP62,INSR,INPP5D |
| DNA binding | PHC2B,ELF2B,H1M,SETDB1B,PHC1,TFAP4,ASCL1A,ZFP423,ZBTB42,ZFP287 |
| acetylcholine receptor binding | RIC3,KCNS1,JAK2,UBXN2A,RAPSN,RER1,DLG4,NRXN1 |
Interacting Protein
APP has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with APP here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of APP.
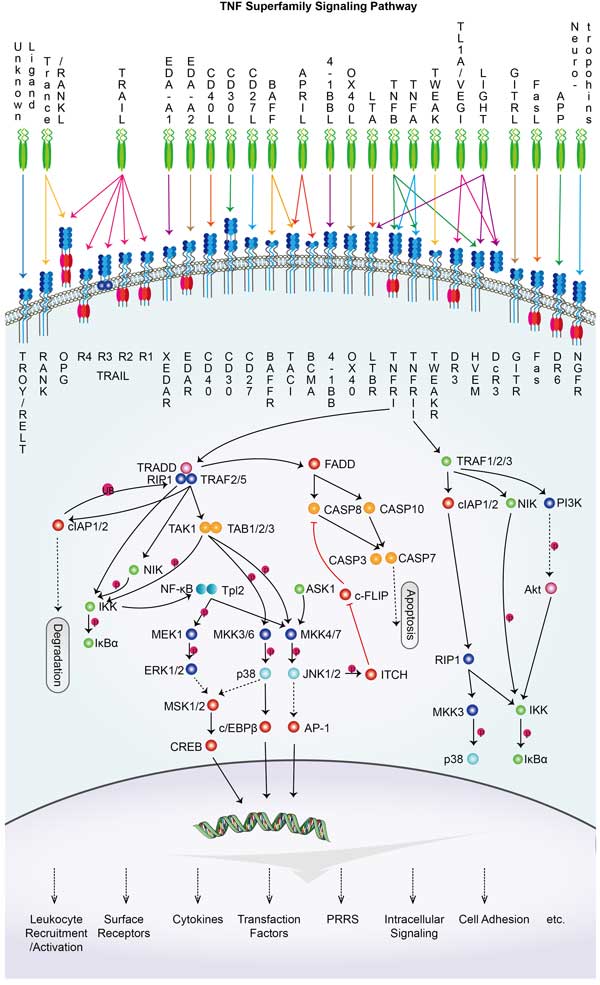
APP Related Signal Pathway
Resources
Research Area
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Chuang, YT; et al. SSCLS: A Smartphone-Supported Collaborative Learning System. TELEMATICS AND INFORMATICS 32:463-474(2015).
- Lee, HJ; Kwon, TY; et al. In Vitro Evaluation of Hydroxyapatite-Coated Titanium Implant with Atmospheric Plasma Treatment. JOURNAL OF NANOSCIENCE AND NANOTECHNOLOGY 15:5593-5596(2015).