GDF15
-
Official Full Name
growth differentiation factor 15 -
Overview
Bone morphogenetic proteins (e.g., BMP9; MIM 605120) are members of the transforming growth factor-beta (see TGFB1; MIM 190180) superfamily and regulate tissue differentiation and maintenance. They are synthesized as precursor molecules that are processed at a dibasic cleavage site to release C-terminal domains containing a characteristic motif of 7 conserved cysteines in the mature protein.[supplied by OMIM, Oct 2009] -
Synonyms
GDF15;growth differentiation factor 15;PDF;MIC1;PLAB;MIC-1;NAG-1;PTGFB;GDF-15;growth/differentiation factor 15;NRG-1;PTGF-beta;placental TGF-beta;NSAID-activated gene 1 protein;NSAID-regulated gene 1 protein;prostate differentiation factor;macrophage inhibitory cytokine 1;placental bone morphogenetic protein;NSAID (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug)-activated protein 1
Recombinant Proteins
- Mouse
- Human
- Rat
- Cynomolgus
- Canine
- Rhesus macaque
- E.coli
- HEK293
- Mammalian Cells
- N-His
- CHO
- Wheat Germ
- Yeast
- Human
- Human Cells
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- Non
- Fc
- His
- GST
- Avi
- SUMO
Background
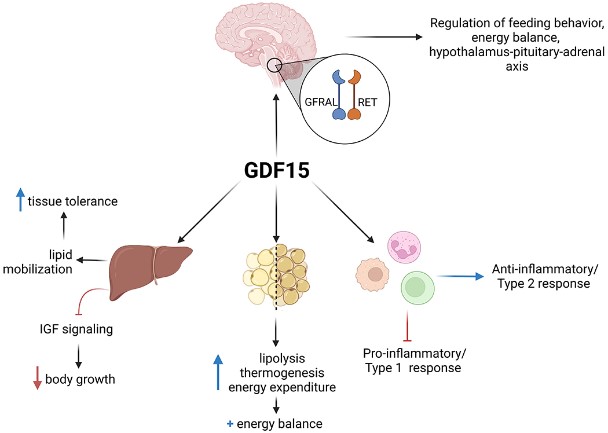
Fig1. Central and peripheral roles of GDF-15. (Jojo Reyes, 2023)
What is GDF15 protein?
GDF15 (growth differentiation factor 15) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the short arm of chromosome 19 at locus 19p13. This gene encodes a secreted ligand of the TGF-beta (transforming growth factor-beta) superfamily of proteins. Ligands of this family bind various TGF-beta receptors leading to recruitment and activation of SMAD family transcription factors that regulate gene expression. The encoded preproprotein is proteolytically processed to generate each subunit of the disulfide-linked homodimer. The protein is expressed in a broad range of cell types, acts as a pleiotropic cytokine and is involved in the stress response program of cells after cellular injury. The GDF15 protein is consisted of 308 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 34.1 kDa.
What is the function of GDF15 protein?
GDF15 promotes the proliferation of certain cell types, such as neurons and heart muscle cells, while inhibiting the proliferation of others. GDF15 showed significant anti-inflammatory properties and was able to suppress the inflammatory response. GDF15 can regulate cell migration and affect cell localization and function in tissues. GDF15 is involved in sugar and fat metabolism and can affect energy balance and weight management. GDF15 plays an important role in the protection of nervous system and heart health.
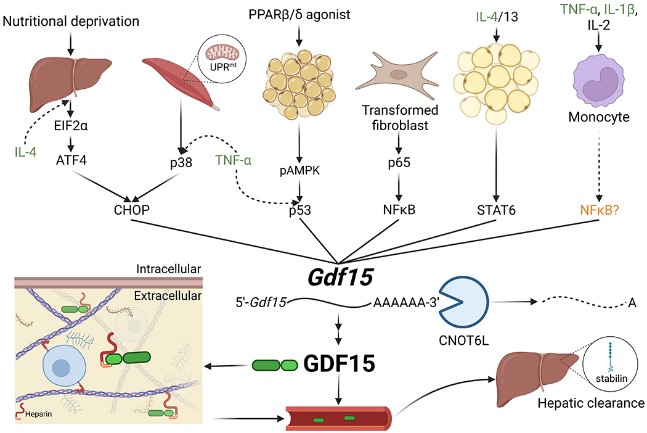
Fig2. Diverse mechanisms by which GDF-15 is regulated. (Jojo Reyes, 2023)
GDF15 Related Signaling Pathway
GDF15 binds to and activates TGF-β receptors, thereby activating the TGF-β signaling pathway, which in turn affects cell proliferation, differentiation, and migration. GDF15 can promote cell survival and anti-apoptosis through the PI3K/Akt pathway. GDF15 can activate the MAPK pathway, thereby affecting cell growth, differentiation and migration. GDF15 regulates the activity of NF-κB, which influences inflammation and immune responses. GDF15 can affect the activity of Wnt/β-catenin pathway, and thus affect cell proliferation and differentiation.
GDF15 Related Diseases
Levels of GDF15 were positively associated with the severity of cardiovascular diseases such as atherosclerosis, coronary heart disease and heart failure. GDF15 expression is increased in a variety of tumors, including gastric, lung, breast, and colorectal cancers. Increased expression of GDF15 in neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson's and Alzheimer's may be associated with the progression of the disease. It has also been linked to diabetes, kidney disease and liver disease.
Bioapplications of GDF15
GDF15 can be used as a tumor marker to facilitate the early diagnosis and prognosis assessment of tumors. GDF15 is related to the nutritional status of the body. Blood levels of GDF15 are often elevated in patients with low nutritional status. Therefore, GDF15 can be used as an indicator to evaluate the nutritional status of patients. It can also be a biomarker for related diseases.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Jyoti Asundi, 2024
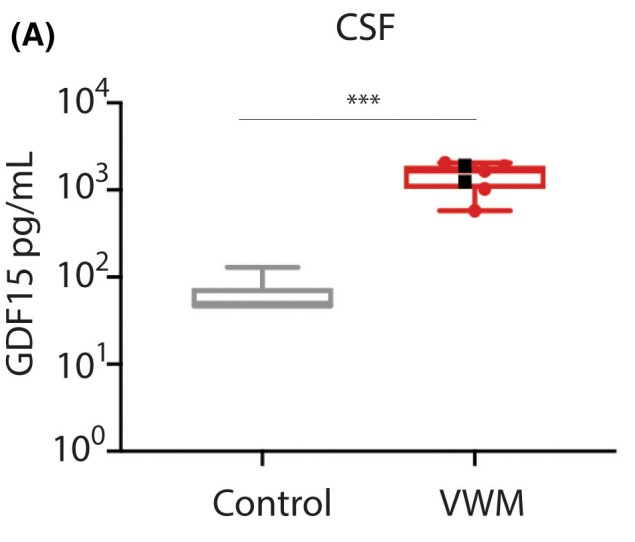
Characterize Growth Differentiation Factor 15 (GDF15) as a secreted biomarker of the integrated stress response (ISR) within the central nervous system (CNS). The researchers determined GDF15 levels utilizing in vitro and in vivo neuronal systems wherein the ISR was activated. Primarily, they used the murine model of vanishing white matter disease (VWMD), a neurological disease driven by persistent ISR in the CNS, to establish a link between levels of GDF15 in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and ISR gene expression signature in the CNS. GDF15 was also determined in the CSF of VWM patients. GDF15 expression was increased concomitant to ISR activation in stress-induced primary astrocytes as well as in retinal ganglion cells following optic nerve crush, while treatment with 2Bact, a specific eIF2B activator, suppressed both the ISR and GDF15. In the VWMD model, CSF GDF15 levels corresponded with the magnitude of the ISR and were reduced by 2BAct. In VWM patients, mean CSF GDF15 was elevated >20-fold as compared to healthy controls, whereas plasma GDF15 was undifferentiated.
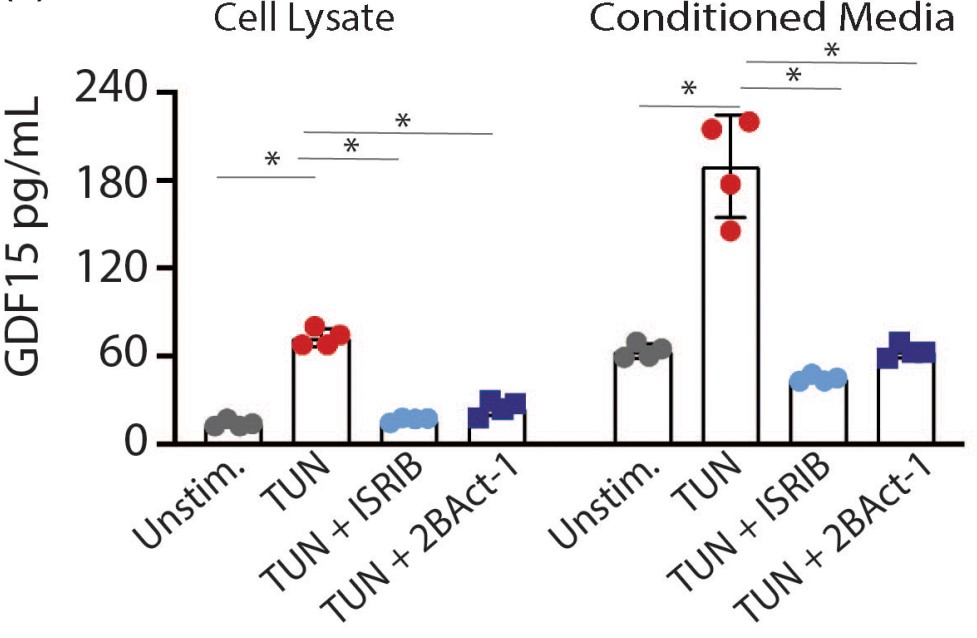
Fig1. Secretion of GDF15 protein are elevated in primary rat astrocytes.
Case Study 2: Lukas Lösch, 2023
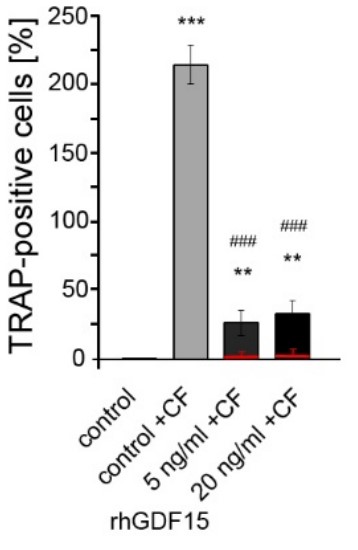
Periodontal ligament fibroblasts (PdLFs) exert important functions in oral tissue and bone remodeling following mechanical forces, which are specifically applied during orthodontic tooth movement (OTM). Located between the teeth and the alveolar bone, mechanical stress activates the mechanomodulatory functions of PdLFs including regulating local inflammation and activating further bone-remodeling cells. Previous studies suggested growth differentiation factor 15 (GDF15) as an important pro-inflammatory regulator during the PdLF mechanoresponse. GDF15 exerts its effects through both intracrine signaling and receptor binding, possibly even in an autocrine manner. The extent to which PdLFs are susceptible to extracellular GDF15 has not yet been investigated. Thus, this study aims to examine the influence of GDF15 exposure on the cellular properties of PdLFs and their mechanoresponse, which seems particularly relevant regarding disease- and aging-associated elevated GDF15 serum levels. Therefore, in addition to investigating potential GDF15 receptors, they analyzed its impact on the proliferation, survival, senescence, and differentiation of human PdLFs, demonstrating a pro-osteogenic effect upon long-term stimulation.
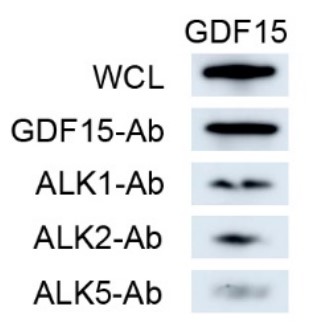
Fig3. Co-immunoprecipitation with ALK1, ALK2, and ALK5-specific antibodies (ALK1/2/5-Ab) to detect GDF15 binding by those receptors in hPdLFs stimulated with 5 ng/mL recombinant human GDF15.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
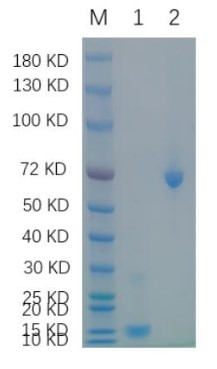
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (GDF15-338H) (PROTOCOL for western blot)
.
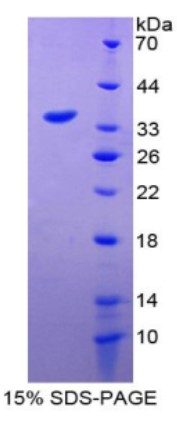
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (GDF15-284H) (PROTOCOL for western blot)
Involved Pathway
GDF15 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways GDF15 participated on our site, such as Direct p53 effectors, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with GDF15 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Direct p53 effectors | FOXA1,HIC1,EPHA2,PPM1J,CEBPZ,PCBP4,EDN2,RNF144B,GADD45A,DDB2 |
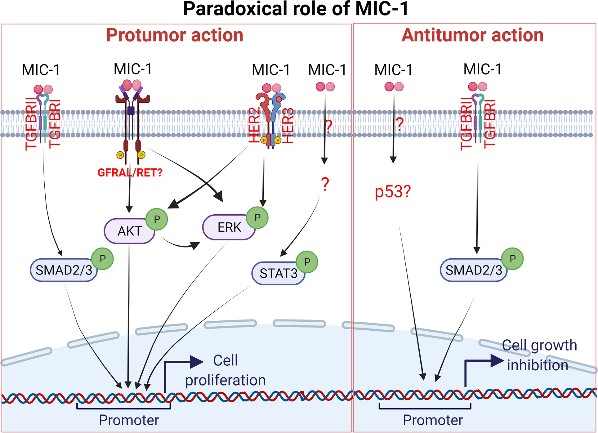
Fig1. A schematic representation of the Macrophage inhibitory cytokine-1 (MIC-1) signaling pathway in cell proliferation. (Sakthivel Muniyan, 2022)
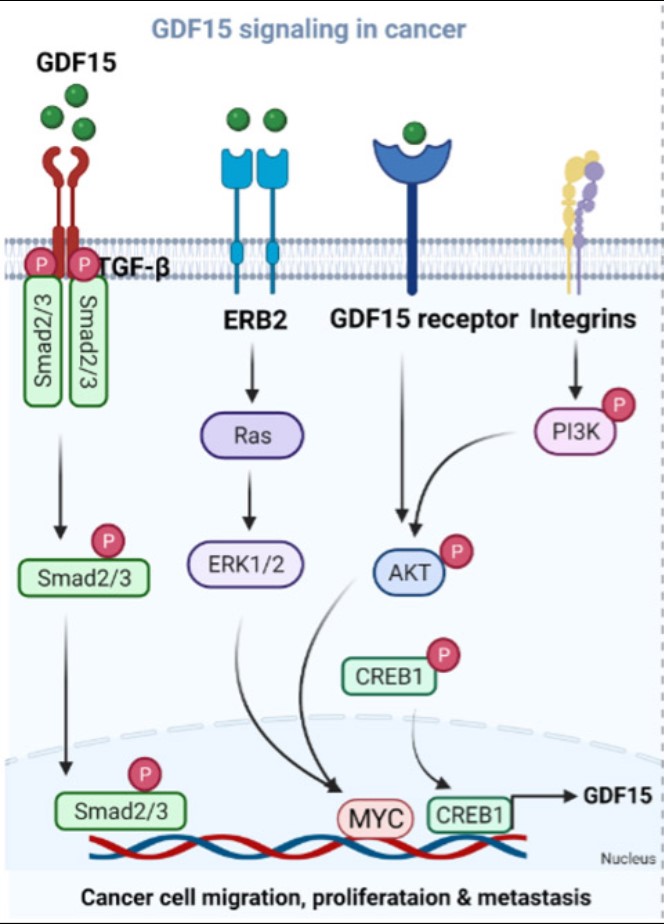
Fig2. GDF15 signaling in cancer. (Jawed Akhtar Siddiqui, 2022)
Protein Function
GDF15 has several biochemical functions, for example, cytokine activity,growth factor activity,transforming growth factor beta receptor binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by GDF15 itself. We selected most functions GDF15 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with GDF15. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| transforming growth factor beta receptor binding | BMP3,AMH,GDF6,GDF6B,TGFB1A,INHBAB,BMP10,GDF10B,INHBE,GDF7 |
| cytokine activity | KITLG,NDR1,IL4,IL36B,MIF,FAM3D,CMTM4,IL18,TNFSF13B,IL31 |
| growth factor activity | FGF3,NOV,HBEGFA,FGF1A,INHBAA,FGF18,IL5,FGF13A,TDGF1,FGF17 |
Interacting Protein
GDF15 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with GDF15 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of GDF15.
MDFI;MAPK14;Trip11;ssrna_a;STAT5A;Smn1;Cdc37;MRPL50;NUPL1;SETD4;SAE1
Resources
Gene Families
Research Area
Related Services
Related Products
References
- von der Heyde, S; Wagner, S; et al. mRNA Profiling Reveals Determinants of Trastuzumab Efficiency in HER2-Positive Breast Cancer. PLOS ONE 10:-(2015).
- Hinoi, E; et al. Regulation of Osteoclastogenesis by Osteocytes through Growth Differentiation Factor-15. YAKUGAKU ZASSHI-JOURNAL OF THE PHARMACEUTICAL SOCIETY OF JAPAN 134:1259-1263(2014).



