Tnfsf11
-
Official Full Name
tumor necrosis factor (ligand) superfamily, member 11 -
Overview
This gene encodes a member of the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) cytokine family which is a ligand for osteoprotegerin and functions as a key factor for osteoclast differentiation and activation. This protein was shown to be a dentritic cell survival factor and is involved in the regulation of T cell-dependent immune response. T cell activation was reported to induce expression of this gene and lead to an increase of osteoclastogenesis and bone loss. This protein was shown to activate antiapoptotic kinase AKT/PKB through a signaling complex involving SRC kinase and tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor (TRAF) 6, which indicated this protein may have a role in the regulation of cell apoptosis. Targeted disruption of the related gene in mice led to severe osteopetrosis and a lack of osteoclasts. The deficient mice exhibited defects in early differentiation of T and B lymphocytes, and failed to form lobulo-alveolar mammary structures during pregnancy. Two alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found. -
Synonyms
TNFSF11;tumor necrosis factor (ligand) superfamily, member 11;ODF;OPGL;sOdf;CD254;OPTB2;RANKL;TRANCE;hRANKL2;tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 11;OTTHUMP00000018328;OTTHUMP00000178585;osteoprotegerin ligand;osteoclast differentiation factor;TNF-related activation-induced cytokine;receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa B ligand;receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-B ligand
Recombinant Proteins
- Monkey
- Mouse
- Human
- Rat
- Cynomolgus
- Chicken
- HEK293
- Human Cells
- Insect Cells
- E.coli
- CHO
- Mammalian Cells
- C-His
- Nicotiana Benthamiana
- Yeast
- Human
- Sf9 Cells
- Fc
- His
- Avi
- Non
- GST
- rFc
- Flag
- mFc
- T7
- DDK
- Myc
- SUMO
Background
What is TNFSF11 Protein?
TNFSF11 gene (TNF superfamily member 11) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 13 at locus 13q14. This gene encodes a member of the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) cytokine family which is a ligand for osteoprotegerin and functions as a key factor for osteoclast differentiation and activation. This protein was shown to be a dentritic cell survival factor and is involved in the regulation of T cell-dependent immune response. T cell activation was reported to induce expression of this gene and lead to an increase of osteoclastogenesis and bone loss. This protein was shown to activate antiapoptotic kinase AKT/PKB through a signaling complex involving SRC kinase and tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor (TRAF) 6, which indicated this protein may have a role in the regulation of cell apoptosis. The TNFSF11 protein is consisted of 317 amino acids and TNFSF11 molecular weight is approximately 35.5 kDa.
What is the Function of TNFSF11 Protein?
TNFSF11, also known as RANKL, is mainly involved in the differentiation and activation of osteoclasts as a key factor, and is an important regulator in the process of bone resorption. RANKL binds to its receptor RANK and activates a variety of signaling pathways, leading to osteoclast-specific gene transcription, thereby promoting osteoclast maturation and functional performance. In addition, RANKL enhances the ability of dendritic cells to stimulate naive T cell proliferation and may play an important role in the regulation of T-cell-dependent immune responses. In addition, RANKL expression is regulated by cell type-specific distal enhancers, and in T cells, this regulation is achieved by multiple distal elements
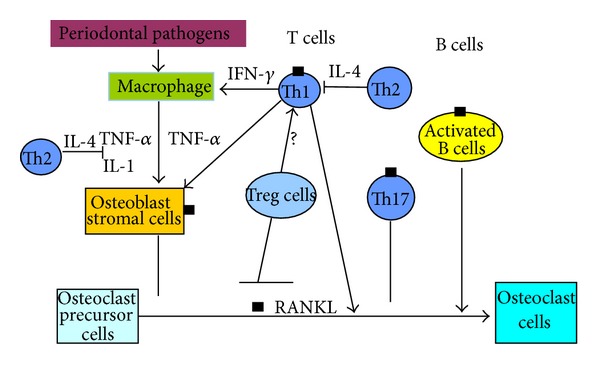
Fig1. B cells and T cells are primary RANKL expression cells in periodontal bone resorption. (Bin Chen, 2014)
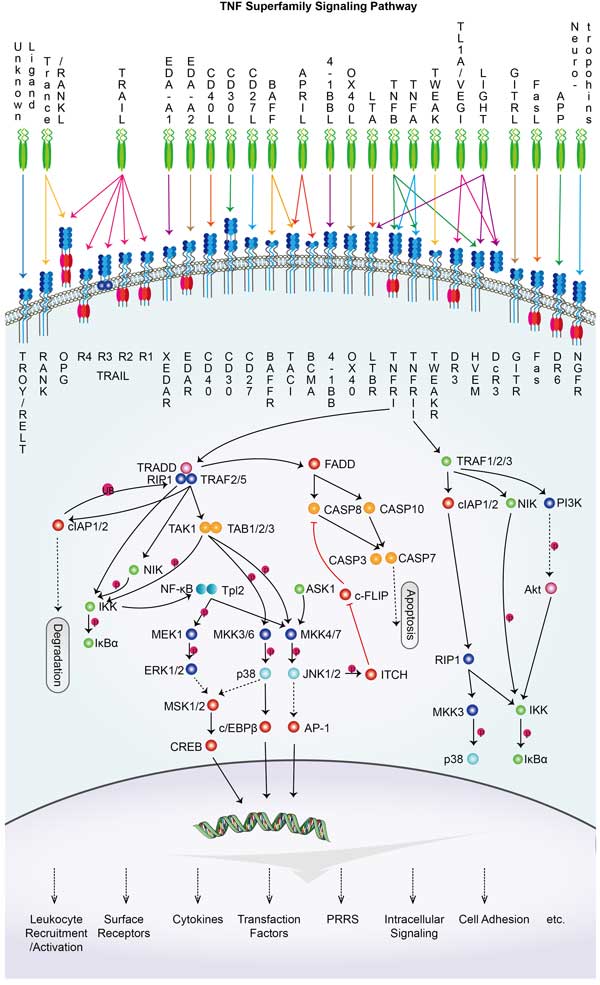
TNFSF11 Related Signaling Pathway
RANKL binds to its receptor RANK and activates the NF-κB signaling pathway. This pathway mainly controls the processes of cell proliferation, differentiation and immune response. RANKL can also influence cell survival and death by activating mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathways, such as inducing apoptosis or necrosis. RANKL is a key factor in osteoclast formation. By binding with RANK, it promotes the differentiation and maturation of osteoclasts, thus affecting bone resorption. RANKL-RANK signaling is essential for maintaining bone health and function. RANKL can also promote apoptosis and necrosis of cells, typically through the formation of cytoplasmic complex II, which involves dissociation of TRADD from complex I, and recruitment of FADD and procaspase-8, leading to caspase-8 activation and apoptosis induction.
TNFSF11 Related Diseases
Abnormal functioning of TNFSF11 (RANKL) is associated with a variety of diseases, especially bone-related diseases such as osteoporosis, which lead to increased bone resorption by affecting osteoclast differentiation and activity; Osteosclerosis, reduced bone formation due to loss of RANKL function; As well as some autoimmune diseases, in which RANKL is involved in regulating the activity of immune cells, dysregulation of which can lead to inflammatory responses and tissue damage. In addition, abnormal activation of RANKL signaling pathway is also associated with the occurrence and development of some cancers.
Bioapplications of TNFSF11
TNFSF11 (RANKL), as a key signaling molecule, has a wide range of applications in medicine and biotechnology, especially in the treatment of osteoporosis, where the use of RANKL inhibitors such as Denosumab can effectively slow bone resorption, increase bone mineral density and reduce the risk of fracture. At the same time, RANKL's role in promoting osteoblast differentiation and bone formation also makes it a potential application value in fracture healing, bone defect repair and tissue engineering. In addition, RANKL's function in immune regulation also allows it to play a role in the treatment of certain autoimmune diseases, by regulating the RANKL-RANK signaling pathway, it can control the inflammatory response and the activity of immune cells.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Mineon Park, 2021
Prostate cancer (PCa) morbidity in the majority of patients is due to metastatic events, which are a clinical obstacle. Therefore, a better understanding of the mechanism underlying metastasis is imperative if we are to develop novel therapeutic strategies. Receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-B (NF-κB) ligand (RANKL) regulates bone remodelling. Thus, agents that suppress RANKL signalling may be useful pharmacological treatments. Here, preclinical experimental models were used to investigate whether an inactive form of RANKL affects bone metastasis in RANKL-induced PCa. RANKL was associated with epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and expression of metastasis-related genes in PC3 cells. Therefore, researchers proposed a strategy to induce anti-cytokine antibodies using mutant RANKL as an immunogen. RANKL promoted migration and invasion of PC3 cells through EMT, and induced a significant increase in binding of β-catenin to TCF-4, an EMT-induced transcription factor in PCa cells, via mitogen-activated protein kinase and β-catenin/TCF-4 signalling.
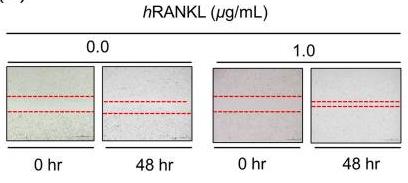
Fig1. Treatment with hRANKL led to a significant increase in the migratory capacity of PC3 cells.
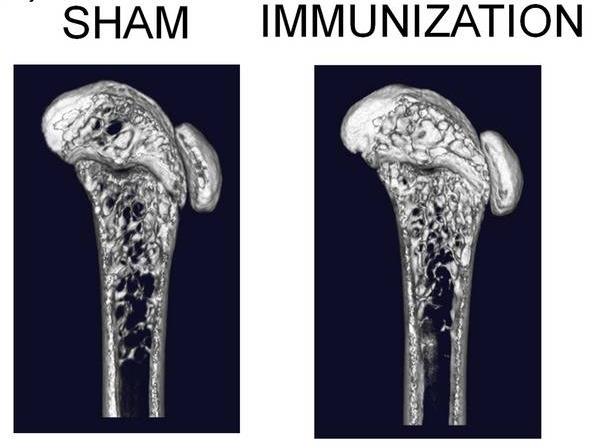
Fig2. Three-dimensional micro-CT images revealed the trabecular bone architecture of the volume of interest in SHAM and mRANKL-immunized (IMMUNIZATION) mouse femurs.
Case Study 2: Jiawei Fan, 2023
Although ILC2s have been implicated in CRSwNP, the presence and role of TNFSFs in ILC2-mediated type 2 inflammation in CRSwNP has not been elucidated. Here, researchers investigate the involvement of TNFSFs in ILC2-mediated type 2 inflammation in CRSwNP. The receptor activator of NF-κB (RANK) ligand (RANK-L (TNFSF11)) was significantly elevated in nasal polyps (NPs), and that the receptor of RANK-L, RANK, was expressed on ILC2s in human peripheral blood and NPs. An agonistic antibody against RANK induced production of type 2 cytokines in human ILC2s, and TSLP significantly enhanced this reaction. The membrane-bound RANK-L was detected mainly on CD45 + immune cells, including TH2 cells in NPs. The co-culture of NP-derived ILC2s and TH2 cells significantly enhanced production of type 2 cytokines, and anti-RANK-L monoclonal antibody suppressed this enhancement.
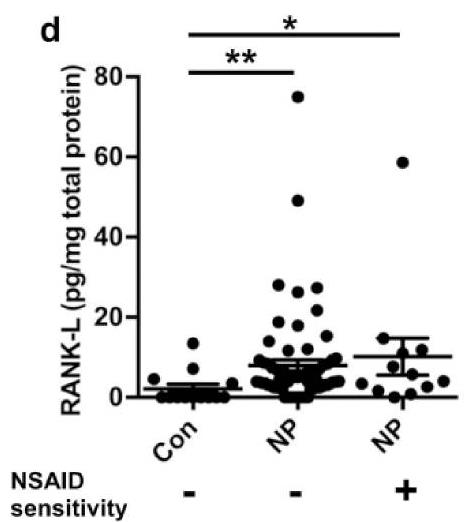
Fig3. Expression of RANK-L protein in tissue homogenates was determined by Luminex.
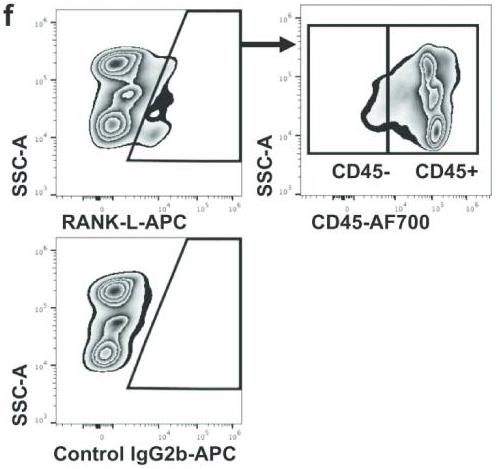
Fig4. Representative flow cytometric plots for RANK-L+ cells in NPs are shown.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (TNFSF11-395H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (TNFSF11-2650H)
Involved Pathway
Tnfsf11 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways Tnfsf11 participated on our site, such as Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction,NF-kappa B signaling pathway,Osteoclast differentiation, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with Tnfsf11 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Prolactin signaling pathway | GALT,ESR2,SOCS1,MAPK10,PIK3CD,CCND1,SOCS3,CSN2,MAPK3,CCND2 |
| Rheumatoid arthritis | HLA-DRA,CCL3L3,Ctsl,ATP6V1G1,CCL2,HLA-DRB1,ATP6V0A2,CD86,HLA-DPB1,HLA-DQA2 |
| NF-kappa B signaling pathway | BCL2,CD40LG,ATM,CD14,BCL2A1,MYD88,LAT,BIRC3,BIRC2,MAP3K14 |
| Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction | OSMR,ACVR1B,IL26,TNFRSF11A,IL17RA,CSF2RB,BMPR1A,CCR7,CCL26,IL6 |
| Osteoclast differentiation | TAB2,TNF,PIK3R3,PIK3CB,CAMK4,SIRPG,NCF1,TNFRSF1A,IFNAR2,NFKB2 |
Protein Function
Tnfsf11 has several biochemical functions, for example, cytokine activity,tumor necrosis factor receptor binding,tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by Tnfsf11 itself. We selected most functions Tnfsf11 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with Tnfsf11. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily binding | FADD,TNFSF4,TNFSF18,TNFSF9 |
| cytokine activity | IFNG,IL10,IL36G,CCL38A.5,MSTNB,SLURP1,IL17A/F2,CCL20A.3,GM13287,IL37 |
| tumor necrosis factor receptor binding | TNFSF13B,CASP8,TRADD,TNFSF4,LTB,TNFSF9,EDA,TNFSF14,TRAF6,TNFSF13 |
Interacting Protein
Tnfsf11 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with Tnfsf11 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of Tnfsf11.
MED24;SBF1;DDAH2;PLK1;LMO4;EEF1A1;MBTPS1;EZH2;SNRNP35;ZC3HC1;TRMT2A;BBS10;FAM213B;PHAX;TMOD3;CEP126
Tnfsf11 Related Signal Pathway
Resources
Gene Families
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Baldo, BA; et al. Adverse events to monoclonal antibodies used for cancer therapy Focus on hypersensitivity responses. ONCOIMMUNOLOGY 2:-(2013).
- Pise-Masison, CA; Radonovich, M; et al. Gene expression profiling of ATL patients: compilation of disease-related genes and evidence for TCF4 involvement in BIRC5 gene expression and cell viability. BLOOD 113:4016-4026(2009).