Fibrinolysis System
Related Symbol Search List
- SerpinA1
- SerpinA3
- PLAT
- Urokinase
- PRAP1
- Serpina3n
- AngIII
- KLK1
- KLK2
- KLK3
- PSA
- KLK4
- KLK5
- KLK6
- KLK7
- KLK8
- SerpinA10
- Serpina11
- Serpina12
- SERPINA1B
- SerpinA3c
- Serpina3g
- SerpinA4
- GBA3
- SERPINA7
- SERPINB1
- SERPINB10
- SerpinB11
- SerpinB12
- SerpinB2
- Serpinb3c
- SERPINB4
- SerpinB5
- SerpinB6
- Serpinb6b
- SerpinB8
- SerpinB9
- SerpinD1
- SERPINE1
- SerpinE2
- SerpinF2
- SERPING1
- SERPINI1
- Vitronectin
Immunology Background
Available Resources for Fibrinolysis System
Creative BioMart strives to be a leading force in the field of fibrinolysis system research. We are dedicated to continuously updating our product range and resources, providing cutting-edge tools and information to researchers in order to drive advancements in this vital area of knowledge.
- Our extensive portfolio includes essential items such as recombinant proteins, which play a crucial role in unraveling the functions and mechanisms of the fibrinolysis system.
- With a team of experienced experts who possess deep knowledge in fibrinolysis system research, we are committed to providing tailor-made solutions that meet the unique requirements of each researcher.
- Furthermore, we offer comprehensive resource support, including involved pathways, protein functions, interacting proteins, and other valuable information. Ultimately, our goal is to enhance the impact of their research efforts.
Our Featured Products
About Fibrinolysis System
The fibrinolysis system is a vital component of the body's hemostatic (blood clotting) mechanism. It is responsible for breaking down blood clots that have formed to prevent excessive clotting and maintain blood fluidity. Fibrinolysis involves the enzymatic degradation of fibrin, a protein that forms the structural framework of blood clots, into smaller soluble fragments. This process is regulated by a series of proteolytic enzymes and inhibitors.
The fibrinolytic system, also known as the plasminogen–plasmin system, is composed of a proteolytic enzyme plasmin (Pm) with its precursor plasminogen (Pg) (Figure 1). There are two naturally occurring activators of plasminogen, tissue-type plasminogen activator (tPA) and urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA). In addition, the conversion from Pg to Pm can be accomplished by other proteases such as streptokinase, staphylokinase and plasmin. The actions of activators are counteracted by inhibitors, plasminogen activator type 1 (PAI-1), plasminogen activator type 2 (PAI-2), protein C inhibitor (PCI), thrombin activable fibrinolysis inhibitor (TAFI), protease nexin 1 (PN-1) and neuroserpin. Pm, on the other hand, are inhibited by α2-antiplasmin, α2-macroglobulin, TAFI and serine protease inhibitors, including antithrombin and α2-antitrypsin, and by PN-1. In addition, there are receptors for plasminogen and for tPA in the form of annexin II, which is co-localized on the cell surface S-100A10, as well as a receptor for uPA, uPAR.
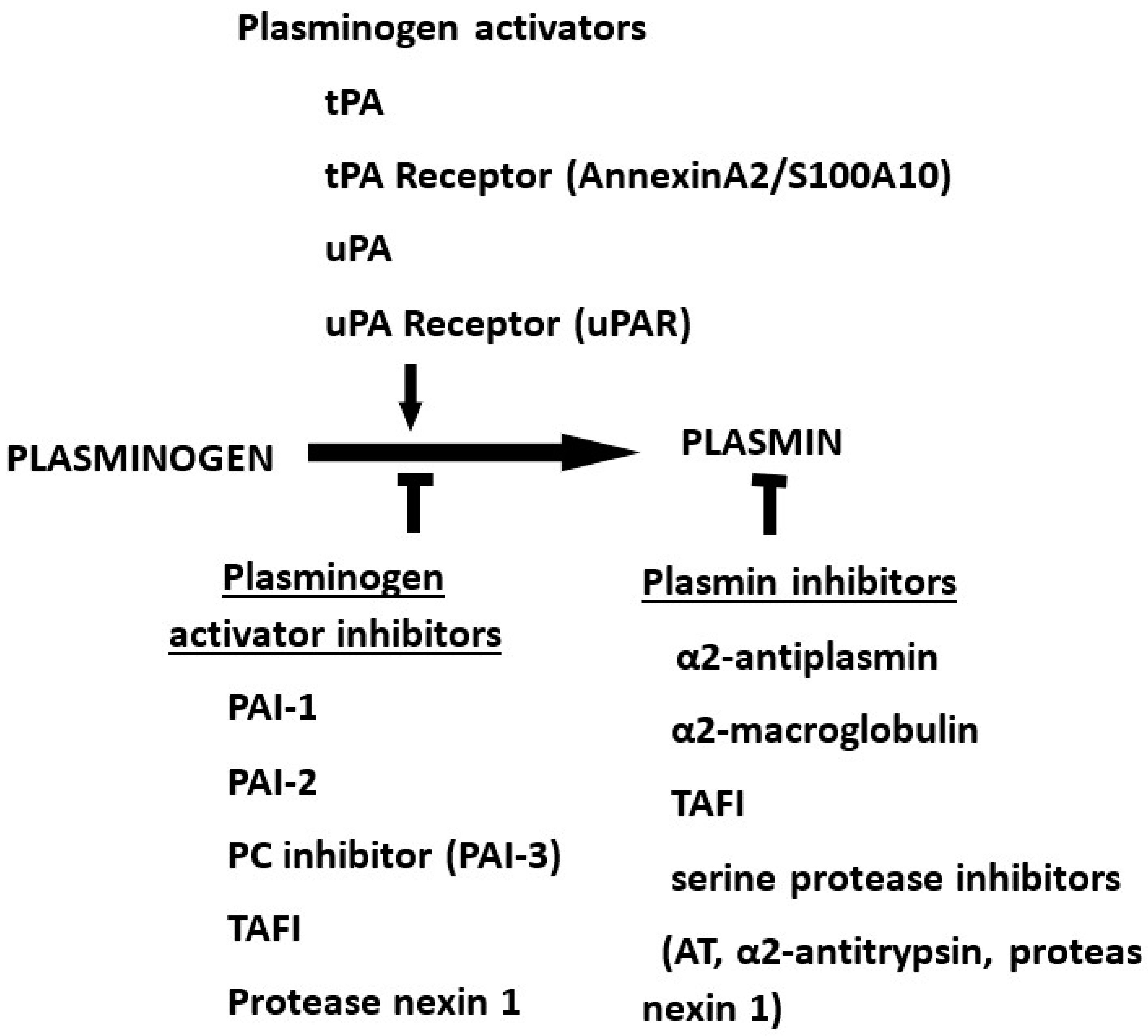 Fig.1 The fibrinolytic (plasminogen–plasmin) system. (Kwaan HC, 2022)
Fig.1 The fibrinolytic (plasminogen–plasmin) system. (Kwaan HC, 2022)
Physiological Functions of The Fibrinolytic System
- Embryogenesis Ovulation, menstruation
- Pregnancy
- Neuron growth
- Brain function
- Regulation of blood–brain barrier
- Immunity
- Wound healing
- Senescence
- Fibrosis
Role of The Fibrinolytic System in Multiple Disorders.
- Neurologic disorders
- Stroke/Hemorrhagic transformation
- Degenerative disorders
- Cancer proliferation, invasion/metastasis, angiogenesis
- Vascular diseases
- Atherosclerosis, myocardial infarction
- Metabolic syndrome
- Trauma
- Fibrosis
The fibrinolysis system is tightly regulated to ensure a delicate balance between clot formation and dissolution. It is essential for maintaining blood fluidity and preventing the formation of unwanted blood clots. Dysregulation of fibrinolysis can lead to pathological conditions, such as thrombosis (excessive blood clotting) or bleeding disorders.
Various factors can influence the fibrinolysis process, including genetic factors, medications, and underlying medical conditions. For example, certain medications, such as thrombolytic drugs, can enhance fibrinolysis to dissolve blood clots in acute conditions like myocardial infarction (heart attack) or ischemic stroke.
Understanding the fibrinolysis system and its components is crucial for the development of therapies targeting thrombotic disorders. Manipulating the system's enzymes and regulators can help regulate clot dissolution, prevent excessive bleeding, or promote clot breakdown when necessary.
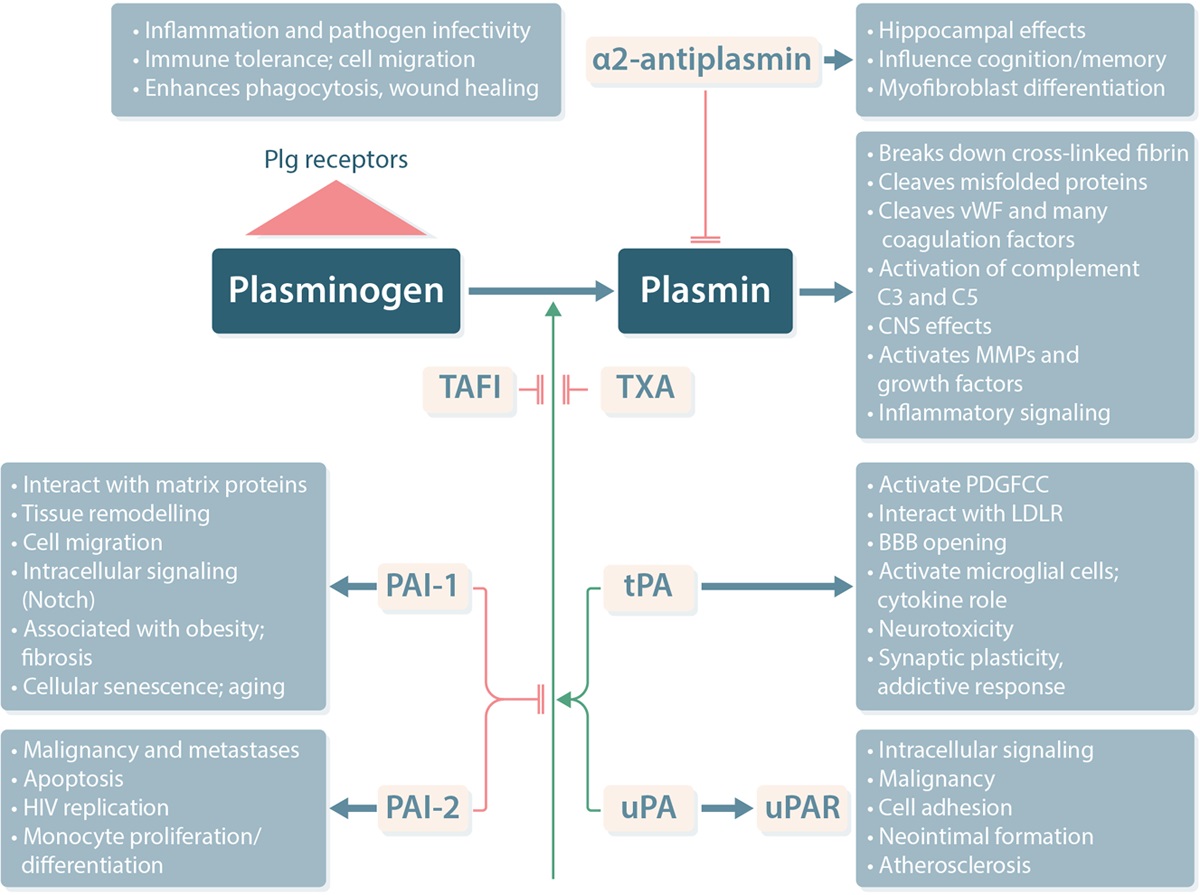 Fig.2 Schematic representation of the fibrinolytic system and the broad effects of its component parts. (Medcalf, et al., 2021)
Fig.2 Schematic representation of the fibrinolytic system and the broad effects of its component parts. (Medcalf, et al., 2021)
We are committed to helping you achieve your scientific goals and make meaningful contributions to the field of fibrinolysis system research. Contact us today to learn more about our products and resources.
References:
- Kwaan HC. The Role of Fibrinolytic System in Health and Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(9):5262. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23095262
- Medcalf RL, Keragala CB. The Fibrinolytic System: Mysteries and Opportunities. Hemasphere. 2021;5(6):e570. Published 2021 Jun 1. doi:10.1097/HS9.0000000000000570

