IL-10 Family Receptors
Related Symbol Search List
Immunology Background
Available Resources for IL-10 Family Receptors Research
Creative BioMart is thrilled to introduce our extensive range of products related to IL-10 family receptors. Our offerings include top-quality recombinant proteins, magnetic beads pre-coupled with proteins, and cell and tissue lysates, providing researchers with indispensable tools for their studies. We understand the unique requirements of each research project, which is why our customizable services are designed to cater to your specific needs, ensuring that you receive the most suitable product tailored to your research goals.
In addition to our comprehensive product line, we are dedicated to providing a wealth of information on IL-10 family receptors. Our resources cover a broad range of topics, including pathways, protein function, interacting proteins, related articles, and research areas. These invaluable resources serve as a knowledge hub, helping researchers expand their understanding of IL-10 family receptors and their critical roles in physiological processes. By offering not only products but also knowledge, we are committed to supporting researchers and contributing to advancements in this exciting field of research.
Our Featured Products
| Cat.# | Product name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IFNAR1-3262H | Recombinant Human IFNAR1 protein, His-tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
| IFNAR2-14078H | Recombinant Human IFNAR2, GST-tagged | Human | E.coli | GST |
| IFNGR1-2250H | Active Recombinant Human IFNGR1 protein, His-tagged | Human | HEK293 | His |
| IFNGR2-14083H | Recombinant Human IFNGR2, GST-tagged | Human | E.coli | GST |
| IL10RA-212H | Active Recombinant Human IL10RA, HIgG1 Fc-tagged | Human | CHO | Fc |
| IL10RB-14142H | Recombinant Human IL10RB, His-tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
| IL20RA-779H | Recombinant Human IL20RA, His tagged | Human | HEK293 | Human |
| IL20RB-14182H | Recombinant Human IL20RB, His-tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
About IL-10 Family Receptors
The IL-10 family receptors are a group of cell surface receptors that mediate the signaling of IL-10 family cytokines. These receptors play crucial roles in transducing the signals from IL-10 family ligands and initiating specific cellular responses. Here's an introduction to some key IL-10 family receptors:
- The interleukin-10 receptor (IL-10R) is the primary receptor for IL-10. It is a heterodimeric receptor composed of two subunits: IL-10Rα (also known as IL-10RA) and IL-10Rβ (also known as IL-10RB). IL-10Rα is specific to IL-10 and binds IL-10 with high affinity, while IL-10Rβ is shared among other IL-10 family receptors. The binding of IL-10 to IL-10R triggers the activation of downstream signaling pathways, leading to the anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive effects of IL-10.
- The interleukin-20 receptor (IL-20R) is a heterodimeric receptor complex that mediates the signaling of IL-19, IL-20, and IL-24. It consists of two subunits: IL-20Rα (also known as IL-20RA) and IL-20Rβ (also known as IL-20RB). IL-20Rα is specific to IL-19, IL-20, and IL-24 and binds these cytokines with varying affinities. IL-20Rβ is shared among other IL-10 family receptors. Activation of IL-20R by its ligands leads to the activation of downstream signaling pathways involved in inflammation, tissue repair, and other cellular responses.
- The interleukin-22 receptor (IL-22R) is a heterodimeric receptor complex that mediates the signaling of IL-22. It consists of two subunits: IL-22Rα (also known as IL-22RA1) and IL-10Rβ (also known as IL-10RB). IL-22Rα is specific to IL-22 and binds IL-22 with high affinity, while IL-10Rβ is shared among other IL-10 family receptors. Activation of IL-22R by IL-22 leads to the activation of downstream signaling pathways involved in tissue homeostasis, barrier protection, and immune responses.
- Other Shared Receptors: IL-10Rβ, which is shared among several IL-10 family receptors, including IL-10R, IL-20R, and IL-22R, plays a critical role in signal transduction and amplification. It is a common signaling subunit that contributes to the activation of downstream signaling pathways upon ligand binding. IL-10Rβ interacts with specific cytokine-specific receptor subunits to form functional receptor complexes.
These are some of the key IL-10 family receptors involved in mediating the signaling of IL-10 family cytokines. Each receptor complex has specific ligand binding properties and activates distinct downstream signaling pathways, leading to diverse cellular responses. The interactions between the IL-10 family ligands and their respective receptors are essential for the regulation of immune responses, inflammation, tissue repair, and host defense.
Signaling Pathways and Mechanisms of Action of IL-10 Family Receptors
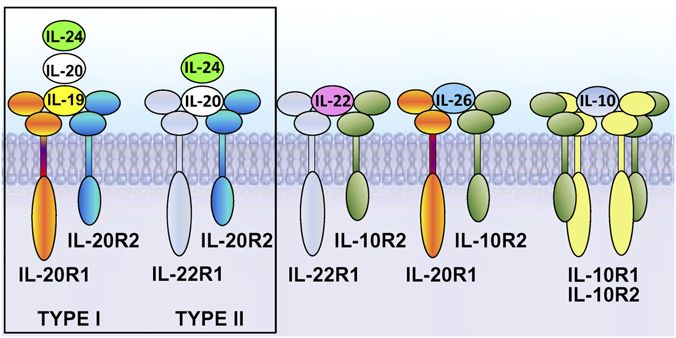 Fig.1 Schematic diagram of IL-10 family receptor complexes. (Logsdon NJ, et al., 2012)
Fig.1 Schematic diagram of IL-10 family receptor complexes. (Logsdon NJ, et al., 2012)
The signaling pathways and mechanisms of action of IL-10 family receptors involve a series of intracellular events that regulate cellular responses. Here's an overview of the signaling pathways and mechanisms associated with IL-10 family receptors:
IL-10 Receptor (IL-10R) Signaling
Upon binding of IL-10 to IL-10R, the receptor complex triggers the activation of the Janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription (JAK/STAT) signaling pathway. IL-10R-associated JAK1 and Tyk2 kinases phosphorylate specific tyrosine residues on the IL-10Rβ subunit, leading to the recruitment and phosphorylation of STAT3. Phosphorylated STAT3 forms homodimers and translocates to the nucleus, where it regulates the transcription of target genes involved in anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive responses. IL-10R signaling also activates other signaling pathways, such as the PI3K/Akt and MAPK pathways, which contribute to the biological effects of IL-10.
IL-20 Receptor (IL-20R) Signaling
IL-20 family cytokines, including IL-19, IL-20, and IL-24, signal through the IL-20R complex. Upon ligand binding, IL-20R-associated JAK1 and Tyk2 kinases phosphorylate specific tyrosine residues on the receptor subunits. This leads to the activation of downstream signaling pathways, including the JAK/STAT pathway. STAT proteins, such as STAT1, STAT3, and STAT5, are phosphorylated and translocate to the nucleus to regulate gene expression. IL-20R signaling also activates other pathways, such as the MAPK and PI3K/Akt pathways, which contribute to the modulation of inflammatory responses, tissue repair, and cell survival.
IL-22 Receptor (IL-22R) Signaling
IL-22 signals through the IL-22R complex, leading to the activation of multiple signaling pathways. Upon ligand binding, IL-22R-associated JAK1 and Tyk2 kinases phosphorylate specific tyrosine residues on the receptor subunits. This results in the activation of the JAK/STAT pathway, with STAT3 being the major transcription factor involved. Phosphorylated STAT3 translocates to the nucleus and regulates the expression of target genes involved in tissue repair, barrier function, and immune responses. IL-22R signaling also activates other pathways, such as the MAPK and PI3K/Akt pathways, which contribute to cellular proliferation, survival, and differentiation.
Shared Signaling Mechanisms
IL-10R, IL-20R, and IL-22R share the IL-10Rβ subunit, which plays a critical role in signal transduction. IL-10Rβ functions as a common signaling subunit and contributes to the activation of downstream signaling pathways upon ligand binding. It interacts with specific cytokine-specific receptor subunits (IL-10Rα, IL-20Rα, IL-22Rα) to form functional receptor complexes. The activation of shared signaling pathways, including JAK/STAT, MAPK, and PI3K/Akt, is involved in mediating the diverse cellular responses induced by IL-10 family ligands.
These signaling pathways and mechanisms of action ultimately regulate gene expression, modulate immune responses, control inflammation, promote tissue repair, and contribute to immune homeostasis. The precise downstream targets and biological effects may vary depending on the specific IL-10 family ligand and receptor combination, as well as the cellular context.
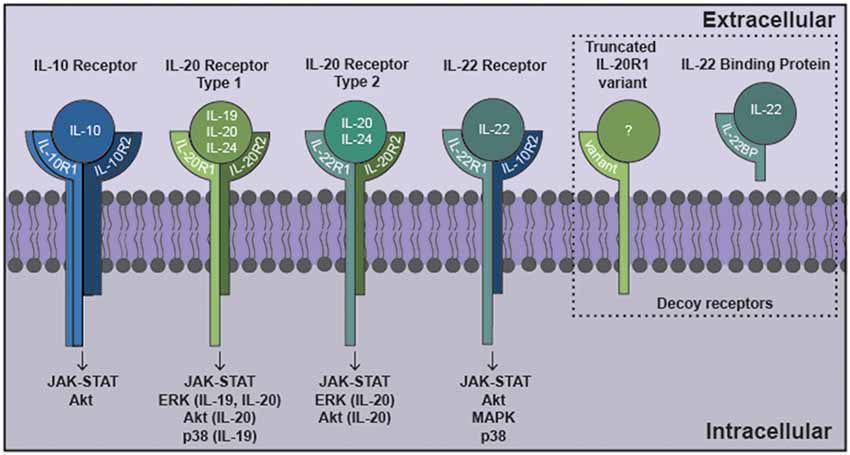 Fig.2 The interleukin-10 (IL-10) family of cytokines exert their effects via heterodimeric receptor subunits. (Burmeister AR, et al., 2018)
Fig.2 The interleukin-10 (IL-10) family of cytokines exert their effects via heterodimeric receptor subunits. (Burmeister AR, et al., 2018)
IL-10 signals through a complex of two IL-10R1 and two IL-10R2 subunits. IL-22 signals via an IL-22R1 subunit in combination with an IL-10R2 subunit. IL-19 signals through the type 1 IL-20R consisting of IL-20R1 and IL-20R2 subunits. IL-20 and IL-24 can signal via either type 1 IL-20R or the type 2 IL-20R consisting of IL-22R1 and IL-20R2 subunits. Signaling through these cognate cell surface receptors initiates the activation of canonical Janus kinase (JAK)-signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) signaling pathways. Additionally, other signaling cascades have been identified for this family that includes ERK, Akt, mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK) and p38. Potential decoy receptors for these cytokines include IL-22 binding protein (IL-22BP) and a truncated IL-20R1 variant that bind IL-22 and an undetermined ligand, respectively.
Role of IL-10 Family Receptors in Immunomodulation
IL-10 family receptors play a crucial role in immunomodulation by mediating the effects of IL-10 family ligands on immune cells and their responses. Here are the key roles of IL-10 family receptors in immunomodulation:
Anti-Inflammatory Effects
IL-10 family receptors, particularly the IL-10 receptor (IL-10R), are involved in mediating the anti-inflammatory effects of IL-10. Upon binding of IL-10 to IL-10R, downstream signaling pathways are activated, leading to the inhibition of pro-inflammatory cytokine production, such as TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6. This helps to dampen excessive immune responses and reduce inflammation. IL-10R signaling also suppresses the activation and function of immune cells, including macrophages, dendritic cells, and T cells, further contributing to the anti-inflammatory effects.
Immune Tolerance and Regulation
IL-10 family receptors, such as IL-10R and IL-22 receptor (IL-22R), are involved in immune tolerance and regulation. IL-10, through its receptor, inhibits the activation and differentiation of T cells, leading to the suppression of immune reactions against self-antigens and the prevention of autoimmune responses. IL-22, acting through IL-22R, promotes the maintenance and function of regulatory T cells (Tregs), which play a critical role in immune regulation and preventing excessive immune activation.
Modulation of Innate Immune Responses
IL-10 family receptors are involved in modulating innate immune responses. IL-10R signaling in macrophages and dendritic cells inhibits their production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and enhances their anti-inflammatory phenotype, thus attenuating innate immune activation. IL-22R signaling can stimulate the production of antimicrobial peptides and enhance barrier function in epithelial cells, contributing to the defense against pathogens and promoting tissue homeostasis.
Tissue Repair and Regeneration
IL-10 family receptors, particularly IL-22R, have important roles in tissue repair and regeneration. IL-22 signaling promotes the proliferation and migration of epithelial cells, stimulates angiogenesis, and supports tissue remodeling. This helps in wound healing, tissue recovery after injury, and maintaining tissue integrity. IL-20 family receptors, such as IL-20R, also contribute to tissue repair processes through their effects on cell proliferation and survival.
Host Defense
IL-22 receptor (IL-22R) signaling plays a crucial role in host defense against pathogens. IL-22, acting through IL-22R, promotes the production of antimicrobial peptides, enhances barrier function, and supports the defense mechanisms of epithelial surfaces, such as the skin and gut. This helps protect against bacterial and fungal infections and contributes to the maintenance of host defense mechanisms.
IL-10 family receptors activated by IL-10 family ligands regulate the function of immune cells and tissues and promote immunomodulation, thereby helping to maintain immune homeostasis and preventing immune overactivation.
If you have any questions, requirements, or cooperation intentions, please feel free to contact us. We very much look forward to working with you and helping you achieve research and commercial success.
Related References:
- Logsdon NJ, Deshpande A, Harris BD, Rajashankar KR, Walter MR. Structural basis for receptor sharing and activation by interleukin-20 receptor-2 (IL-20R2) binding cytokines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012;109(31):12704-12709. doi:10.1073/pnas.1117551109
- Burmeister AR, Marriott I. The Interleukin-10 Family of Cytokines and Their Role in the CNS. Front Cell Neurosci. 2018;12:458. Published 2018 Nov 27. doi:10.3389/fncel.2018.00458

