FAP
-
Official Full Name
fibroblast activation protein, alpha -
Overview
The protein encoded by this gene is a homodimeric integral membrane gelatinase belonging to the serine protease family. It is selectively expressed in reactive stromal fibroblasts of epithelial cancers, granulation tissue of healing wounds, and malignant cells of bone and soft tissue sarcomas. This protein is thought to be involved in the control of fibroblast growth or epithelial-mesenchymal interactions during development, tissue repair, and epithelial carcinogenesis. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2014] -
Synonyms
FAP;fibroblast activation protein, alpha;FAPA;DPPIV;seprase;integral membrane serine protease;170 kDa melanoma membrane-bound gelatinase
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Monkey
- Chicken
- Rat
- Cynomolgus
- HEK293
- Insect Cells
- NS0
- CHO
- Human
- E.coli
- Human Cells
- Insect cells
- Mammalian Cells
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- His
- Avi
- Fc
- GST
- Non
- DDK
- Myc
- Flag
- SUMO
Background
What is fap protein?
FAP stands for fibroblast activation protein, also known as FAP-α or seprase. FAP is a membrane-bound enzyme that belongs to the serine protease family. It is primarily expressed by activated fibroblasts in various tissues, including the stromal cells of many types of solid tumors.
FAP protein is a potential target for cancer imaging and treatment. Several pharmacological agents have been developed that target FAP-expressing cells like radioimmunotherapy.
What is the function of FAP protein?
The main function of FAP is to remodel the extracellular matrix (ECM), which is the network of proteins and carbohydrates surrounding cells in tissues. FAP can degrade components of the ECM, such as collagen and fibronectin, facilitating tissue remodeling, wound healing, and tissue repair. Additionally, FAP may play a role in cancer progression by promoting tumor growth, angiogenesis, and invasion.
Fap related signaling pathway
TGF-β signaling pathway: FAP can activate TGF-β signaling by cleaving latent TGF-β binding proteins, releasing active TGF-β. TGF-β then drives fibroblast activation and differentiation.
Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway: FAP interacts with Wnt co-receptor LRP6 and promotes Wnt ligand-mediated signaling. This pathway regulates processes like fibrosis and tumor growth.
PDGF signaling pathway: Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) signaling stimulates FAP expression in fibroblasts. FAP may in turn mobilize additional PDGF from the ECM via protease activity.
Notch signaling pathway: Studies suggest FAP stimulates Notch signaling in cancer-associated fibroblasts, contributing to their activation phenotype and functions in the tumor microenvironment.
Hedgehog signaling pathway: Aberrant hedgehog pathway activation has been linked to FAP expression in certain cancers. They may regulate each other's activity in the tumor stroma.
Fap Related Diseases
- Cancer: Many solid tumors show increased FAP expression in cancer-associated fibroblasts. High FAP correlates with poor prognosis in cancers of breast, lung, colon, liver, etc. It promotes tumor growth.
- Fibrosis: Diseases with excessive scar formation like idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, liver cirrhosis and cardiac fibrosis exhibit elevated FAP levels in activated fibroblasts accumulating in affected tissues.
- Liver diseases: FAP overexpression has been reported in hepatic fibrosis/cirrhosis, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
- Lung diseases: Elevated FAP levels contribute to scar formation in pulmonary fibrosis and have been detected in asthma.
- Cardiovascular diseases: FAP plays a role in myocardial infarction repair and cardiac fibrosis associated with conditions like ischemia.
- Cancer imaging and detection - Developing FAP-targeting probes can help non-invasively image and stage tumors.
- Cancer therapy - Drugs conjugated to FAP antibodies can selectively deliver chemotherapy to cancer cells. FAP is being explored as a target for immune therapies.
- Anti-fibrotic therapy - Inhibiting FAP may help reduce scar formation in conditions like pulmonary fibrosis and hepatic cirrhosis.
- Wound healing applications - Modulating FAP levels/activity can potentially improve healing outcomes by controlling excessive scarring.
- Tissue engineering - Understanding FAP's role in remodeling can help develop biomaterials to regulate repair processes.
- Drug delivery - FAP's overexpression in diseases enables targeted delivery of nanomedicines to diseased tissues.
- Cancer imaging and detection - Developing FAP-targeting probes can help non-invasively image and stage tumors.
- Cancer therapy - Drugs conjugated to FAP antibodies can selectively deliver chemotherapy to cancer cells. FAP is being explored as a target for immune therapies.
- Anti-fibrotic therapy - Inhibiting FAP may help reduce scar formation in conditions like pulmonary fibrosis and hepatic cirrhosis.
- Wound healing applications - Modulating FAP levels/activity can potentially improve healing outcomes by controlling excessive scarring.
- Tissue engineering - Understanding FAP's role in remodeling can help develop biomaterials to regulate repair processes.
- Drug delivery - FAP's overexpression in diseases enables targeted delivery of nanomedicines to diseased tissues.
Case Study
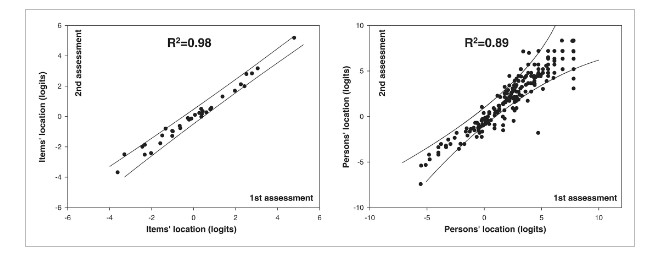
(Mariëlle H. J. Pruppers , 2015)
Fig3. Items' hierarchy and persons' location reliability studies of the familial amyloid polyneuropathy Rasch-built specific overall disability scale (FAP-RODS©). Item difficulty hierarchy of the final FAP-RODS in the first vs. the second assessment (interval 2–4 weeks). Almost all items (dots) were located within the 95% confidence interval (solid lines) reflecting ideal reliability. Patients' location in the first assessment vs. the second assessment: most person scores (dots) were located within the 95% confidence interval (solid lines).
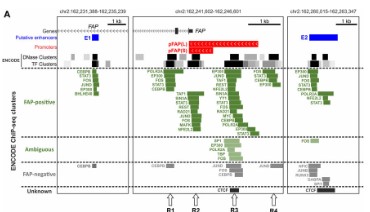
(Dina V. Antonova, 2023)
Fig4. Location of ENCODE ChIP-seq clusters/peaks near the promoter and putative enhancers of the FAP gene in FAP-positive and -negative cells.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
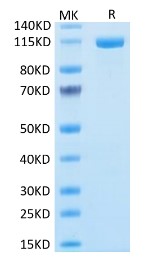
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (Cat. No.: FAP-372H)
High Bioactivity & Detection Sensitivity
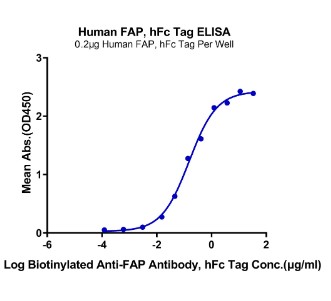
Fig2. Immobilized Human FAP, hFc Tag at 2μg/ml (100μl/Well) on the plate. Dose response curve for Biotinylated Anti-FAP Antibody, hFc Tag with the EC50 of 0.15μg/ml determined by ELISA.
Involved Pathway
FAP involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways FAP participated on our site, such as , which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with FAP were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|
Protein Function
FAP has several biochemical functions, for example, dipeptidyl-peptidase activity,endopeptidase activity,integrin binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by FAP itself. We selected most functions FAP had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with FAP. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| protein homodimerization activity | HSD17B4,LILRB1,FZD1,SNRPC,VEGFA,SLC22A1,IRAK1,CEBPA,RAP1GAP,PDGFA |
| protein dimerization activity | CLOCK,ID2,KIF9,NCF4,MTOR,DNM1,AIFM1,HIF1AB,MYCL1,MESP1 |
| peptidase activity | TMPRSS5,MALT1,CTSB,IHHA,CTSSB.2,PRSS30,BMP1A,Acr,USP12A,CTSSA |
| serine-type peptidase activity | PRSS21,SEC11C,PRSS30,DPP4,GZMB,HTRA1,GZMC,RBP3,FURINB,MCPT9 |
| protease binding | PINK1,THAP5,TIMP4,TRIP4,FADD,SERPINA5,TNF,RNF139,BCL2,CNTNAP2 |
| endopeptidase activity | PSMB11,PSMB5,ACE,FURIN,PCSK6,PSMA3,RHBDD1,SENP1,KLK1B4,ECE1 |
| metalloendopeptidase activity | ADAMTS18,ADAMTS10,PHEX,MMP23B,ADAM23,MMP11,ASTL,MMP9,MBTPS2,HE2 |
| serine-type endopeptidase activity | KLK12,PRSS54,PCSK1,HTRA4,CELA2A,F9B,TMPRSS4B,MBTPS1,IMMP2L,ST14A |
| dipeptidyl-peptidase activity | NAALAD2,DPP8,DPP4,DPP7,PRCP,DPEP3,DPEP1,DPP3,DPEP2 |
Interacting Protein
FAP has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with FAP here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of FAP.
GCG;VIP;GHRH;NPY;GIP;PYY;NPPB;ADCYAP1;TAC1;b3xyc5_sollc
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Rabenhold, M; Steiniger, F; et al. Bispecific single-chain diabody-immunoliposomes targeting endoglin (CD105) and fibroblast activation protein (FAP) simultaneously. JOURNAL OF CONTROLLED RELEASE 201:56-67(2015).
- Polites, SF; Zarroug, AE; et al. Single-Incision Laparoscopic Ileal Pouch-Anal Anastomosis in Children-How Does It Compare to a Laparoscopic-Assisted Approach?. JOURNAL OF LAPAROENDOSCOPIC & ADVANCED SURGICAL TECHNIQUES 25:167-171(2015).



