GPC3
-
Official Full Name
glypican 3 -
Overview
Glypican-3 (GPC3) is a glycosylphospatidyl inositol-anchored membrane protein, which may also be found in a secreted form. Recently, GPC3 was identified to be useful tumor marker for the diagnosis of HCC, hepatoblastoma, melanoma, testicular germ cell tum -
Synonyms
GPC3;glypican 3;SDYS;glypican-3;DGSX;glypican proteoglycan 3;OCI 5;SGB;SGBS;SGBS1;secreted glypican-3;intestinal protein OCI-5;heparan sulphate proteoglycan;MXR7;OCI-5;GTR2-2
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Cynomolgus
- Rat
- Rhesus macaque
- Chimpanzee
- HEK293
- Insect Cells
- Human Cells
- Mammalian Cells
- CHO
- E.coli
- Wheat Germ
- Yeast
- Fc
- His
- Avi
- lFc
- Non
- GST
- T7
- Myc
- mFc
Background
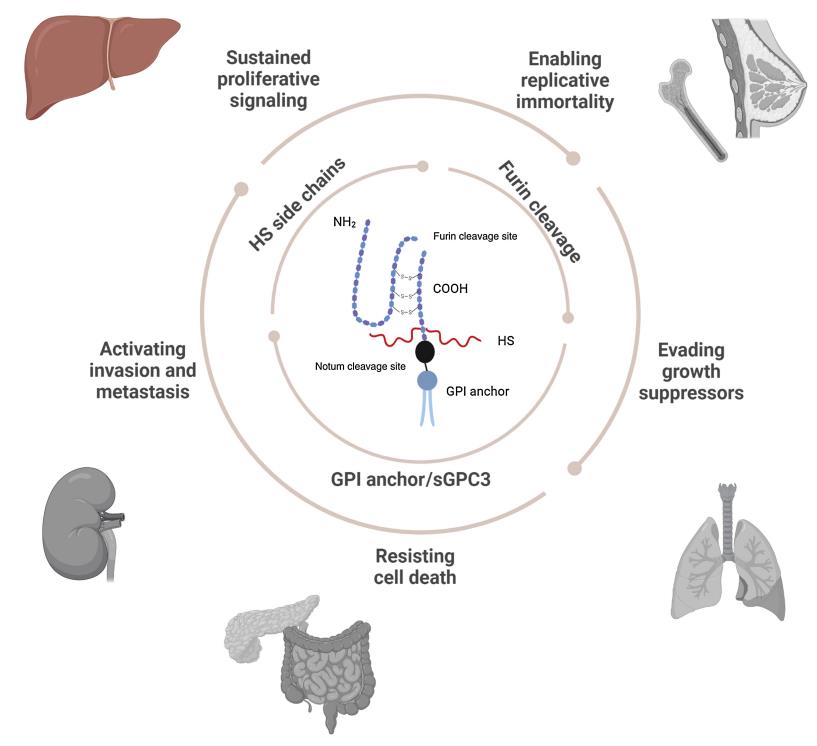
Fig1. Schematic representing GPC3 structural and functional role in disease. (Emily J Schepers, 2023)
What is GPC3 protein?
GPC3 (glypican 3) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the chromosome X at locus Xq26. Cell surface heparan sulfate proteoglycans are composed of a membrane-associated protein core substituted with a variable number of heparan sulfate chains. Members of the glypican-related integral membrane proteoglycan family (GRIPS) contain a core protein anchored to the cytoplasmic membrane via a glycosyl phosphatidylinositol linkage. These proteins may play a role in the control of cell division and growth regulation. The protein encoded by this gene can bind to and inhibit the dipeptidyl peptidase activity of CD26, and it can induce apoptosis in certain cell types. The GPC3 protein is consisted of 580 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 65.6 kDa.
What is the function of GPC3 protein?
Glypican-3 (GPC3) is a cell-surface glycoprotein that is frequently overexpressed in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and has been identified as a specific biomarker for the diagnosis of HCC as well as a potential target for targeted therapy of this disease. It undergoes extensive posttranslational modifications (PTMs), including cleavage and glycosylation, which are crucial for its function in liver cancer. The structure and function of GPC3 are intricately linked to its role in various signaling pathways. GPC3 expression in HCC has been linked to long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) and microRNAs (miRNAs). GPC3 is expressed during early development in fetal organs and has been associated with Simpson Golabi Behmel syndrome (SGBS), an X-linked overgrowth disorder, due to loss of function mutations.
GPC3 Related Signaling Pathway
GPC3 is involved in the regulation of the Wnt signaling pathway, which is a critical pathway in cell proliferation and tumor growth. It can act as a co-receptor for Wnt proteins. GPC3 has been shown to interact with Yes-associated protein (YAP), which is a component of the Hippo signaling pathway. This interaction is implicated in the progression of HCC. GPC3 can bind to various growth factors, such as insulin-like growth factor II (IGF-II), and is involved in their signaling pathways, contributing to the promotion of cell proliferation and inhibition of apoptosis in HCC. GPC3 also plays a role in the regulation of the Hedgehog signaling pathway.
GPC3 Related Diseases
Glypican-3 (GPC3) is a cell membrane proteoglycan whose abnormal expression in a variety of cancers makes it an important biomarker and therapeutic target. It is associated with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), in which overexpression of GPC3 is key to diagnosis and targeted therapy; Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), which plays a role in tumor invasion and metastasis; Melanoma, whose overexpression is associated with disease progression; Ovarian cancer, which may promote tumor growth; Stomach cancer, associated with disease progression; Squamous cell carcinoma of the lung, whose expression may indicate disease severity; Liposarcoma, a soft tissue sarcoma in which overexpression of GPC3 is associated with tumor development; Embryonic tumors, GPC3 as a marker for some embryonic tumors; And Simpson-Gorabi-Bem disease (SGBS), an inherited overgrowth and developmental dysplasia syndrome characterized by a loss-of-function mutation in GPC3.
Bioapplications of GPC3
Glypican-3 (GPC3), as a biomarker with high specific expression in a variety of cancers, is mainly applied in the following aspects: First, as a diagnostic marker for malignant tumors such as hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), it helps to improve the accuracy of early diagnosis; Secondly, in the field of targeted therapy, GPC3 is an important target for the development of monoclonal antibodies, antibody drug conjugate (ADC), immunotoxins, tumor vaccines, chimeric antigen receptor T cell (CAR-T) therapy and other therapeutic strategies. In addition, the expression level of GPC3 can also be used for prognostic assessment and monitoring of treatment effect. Finally, GPC3, as an important molecule in the study of cell signaling, cell proliferation, differentiation and migration in basic research, contributes to the in-depth understanding of the molecular mechanism of tumorigenesis.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Yulu Cherry Liu, 2022
Glypicans consist of a globular core, an unstructured stalk modified with sulfated glycosaminoglycan chains, and a glycosylphosphatidylinositol anchor. Though these structural features are conserved, their individual contribution to glypican function remains obscure. Here, researchers investigate how glypican 3 (GPC3), which is mutated in Simpson-Golabi-Behmel tissue overgrowth syndrome, regulates Hedgehog signaling. Purified GPC3 ectodomain rescues signaling when artificially recruited to the surface of GPC3-deficient cells but has dominant-negative activity when unattached. Strikingly, the purified stalk, modified with heparan sulfate but not chondroitin sulfate, is necessary and sufficient for activity. These results demonstrate a novel function for GPC3-associated heparan sulfate and provide a framework for the functional dissection of glycosaminoglycans by in vivo biochemical complementation.
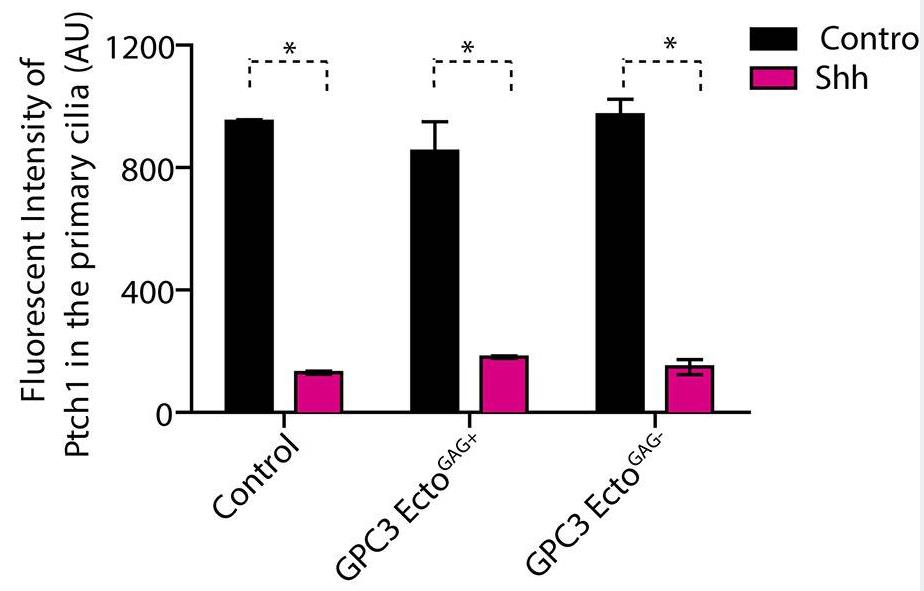
Fig1. Ciliary intensity of Ptch1 was measured by immunofluorescence microscopy after incubated with purified GPC3.
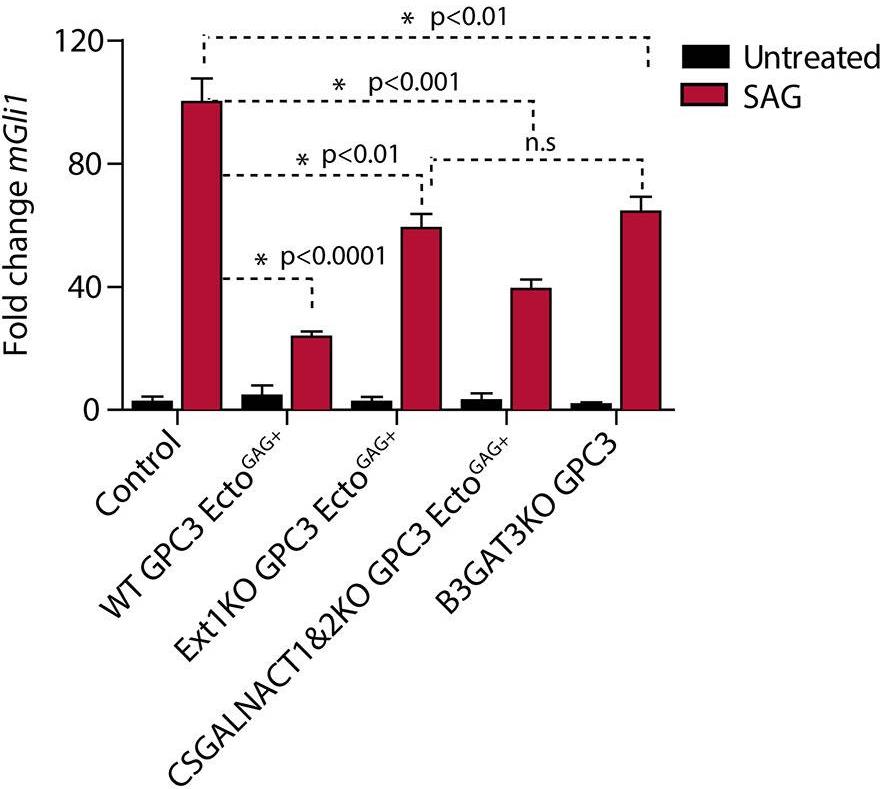
Fig2. Hh signaling was measured by qRT-PCR for Gli1 after incubated with purified GPC3.
Case Study 2: Gebing Yao, 2019
Recently, the expression of GPC3 has been reported to be inversely associated with glucose metabolism activity in LC patients, suggesting that GPC3 may play a role in the regulation of glucose metabolism in LC. However, the role of GPC3 in glucose metabolism reprogramming, as well as in LC cell growth and metastasis, is unknown. Here, by perfoming Glucose Uptake and Lactate Production Assays of LC cells with different GPC3 levels, researchers found that GPC3 significantly contributed to the reprogramming of glucose metabolism in LC cells. On the one hand, GPC3 enhanced the glycolysis of LC cells through upregulation of the glycolytic genes of Glut1, HK2, and LDH-A. On the other hand, GPC3 repressed mitochondrial respiration through downregulation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma coactivator 1-alpha (PGC-1α), which has been well known as a crucial regulator in mitochondrial biogenesis. Mechanistic investigations revealed that HIF-1α was involved in both GPC3-regulated upregulation of glycolytic genes of HK2, PKM2, and Glut1 and downregulation of mitochondrial biogenesis regulator PGC-1α in LC cells. Additionally, GPC3-regulated reprogramming of glucose metabolism played a critical role in the growth and metastasis of LC cells.
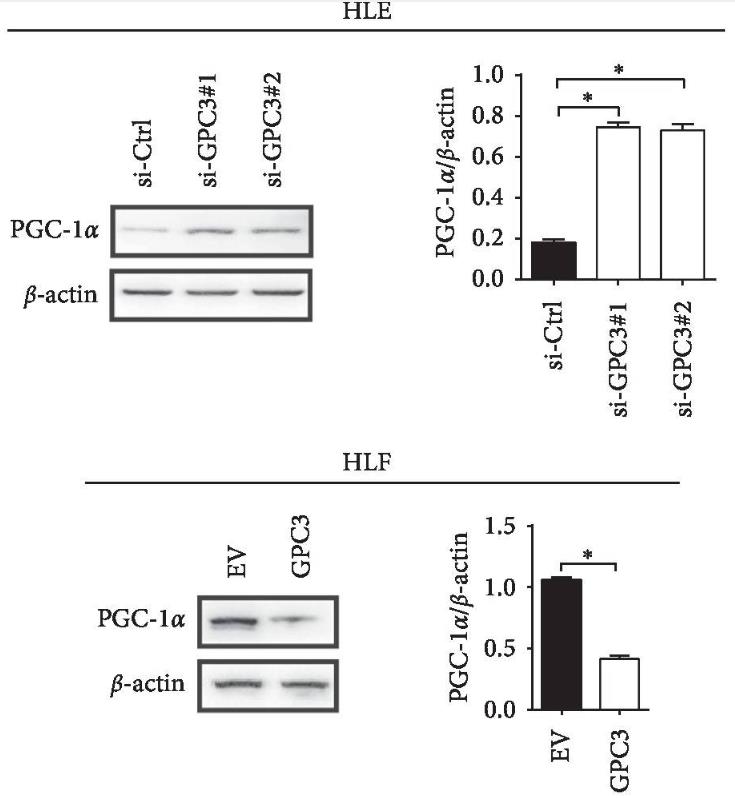
Fig3. GPC3 suppressed mitochondrial OXPHOS through downregulation of PGC-1α with WB assay.
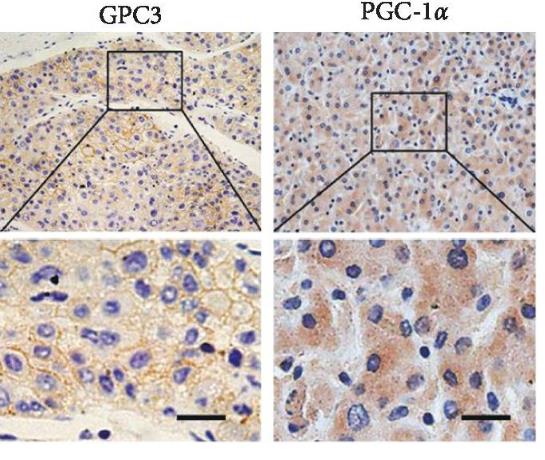
Fig4. Spearman correlation analysis between the expression levels of GPC3 and HIF-1α.
Quality Guarantee
Involved Pathway
GPC3 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways GPC3 participated on our site, such as Proteoglycans in cancer, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with GPC3 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Proteoglycans in cancer | MRAS,FASLG,WNT7B,RHOA,SMAD2,WNT3,ERBB3,RRAS2,BRAF,PXN |
Protein Function
GPC3 has several biochemical functions, for example, heparan sulfate proteoglycan binding,peptidyl-dipeptidase inhibitor activity,protein binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by GPC3 itself. We selected most functions GPC3 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with GPC3. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| protein binding | CD4,ADCYAP1,GMPPA,FBLIM1,OTX1,ITGB4,PHF23,TPD52L3,MAGI1,KIAA1267 |
| heparan sulfate proteoglycan binding | GPC6,HRG,HPSE2,PLA2G2D,GPC1A,UBE4A,Itgam&Itgb2,AGRN,Gpc2,COMP |
Interacting Protein
GPC3 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with GPC3 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of GPC3.
APPL1
Resources
Research Area
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Zaghloul, RA; El-Shishtawy, MM; et al. Evaluation of antiglypican-3 therapy as a promising target for amelioration of hepatic tissue damage in hepatocellular carcinoma. EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF PHARMACOLOGY 746:353-362(2015).
- Tretiakova, M; Zynger, DL; et al. Glypican 3 overexpression in primary and metastatic Wilms tumors. VIRCHOWS ARCHIV 466:67-76(2015).


.jpg)
.jpg)

