MMP2
-
Official Full Name
matrix metallopeptidase 2 (gelatinase A, 72kDa gelatinase, 72kDa type IV collagenase) -
Overview
Proteins of the matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) family are involved in the breakdown of extracellular matrix in normal physiological processes, such as embryonic development, reproduction, and tissue remodeling, as well as in disease processes, such as arthritis and metastasis. Most MMPs are secreted as inactive proproteins which are activated when cleaved by extracellular proteinases. This gene encodes an enzyme which degrades type IV collagen, the major structural component of basement membranes. The enzyme plays a role in endometrial menstrual breakdown, regulation of vascularization and the inflammatory response. Mutations in this gene have been associated with Winchester syndrome and Nodulosis-Arthropathy-Osteolysis (NAO) syndrome. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] -
Synonyms
MMP2;matrix metallopeptidase 2 (gelatinase A, 72kDa gelatinase, 72kDa type IV collagenase);CLG4;MONA;CLG4A;TBE-1;MMP-II;72 kDa type IV collagenase;MMP-2;gelatinase A;72 kDa gelatinase;collagenase type IV-A;neutrophil gelatinase;matrix metalloproteinase-2;matrix metalloproteinase-II
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Rat
- Chicken
- Zebrafish
- E.coli
- HEK293
- Yeast
- Human
- Sf9 Cells
- yeast
- Mammalian Cells
- Human Cells
- Mouse Fibroblast
- Baculovirus
- E. coli
- Human Synovial Fibroblasts
- Human Fibroblasts
- Wheat Germ
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- Non
- GST
- Avi
- Fc
- His
- DDK
- Myc
- Flag
- KSI
- SUMO
Background
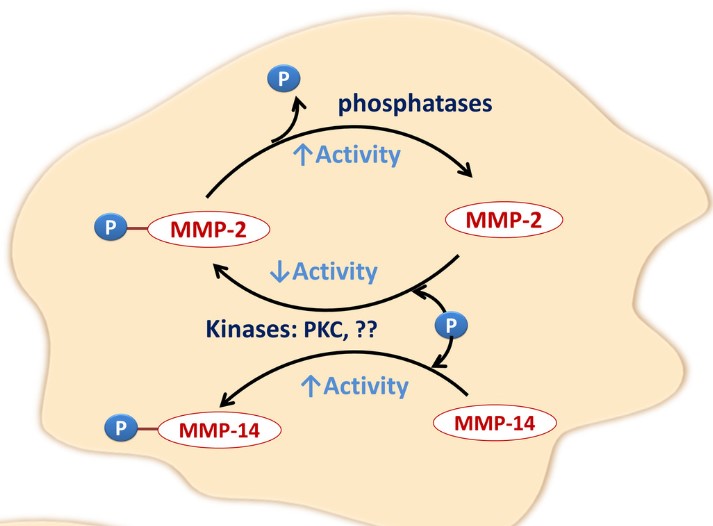
Fig1. Phosphorylation/dephosphorylation mechanism; MMP-2 activity is enhanced by dephosphorylation and diminished by phosphorylation. (Wesam Bassiouni, 2021)
What is MMP2 protein?
MMP2 (matrix metallopeptidase 2) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 16 at locus 16q12. This gene is a member of the matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) gene family, that are zinc-dependent enzymes capable of cleaving components of the extracellular matrix and molecules involved in signal transduction. The protein encoded by this gene is a gelatinase A, type IV collagenase, that contains three fibronectin type II repeats in its catalytic site that allow binding of denatured type IV and V collagen and elastin. This enzyme can be activated extracellularly by proteases, or, intracellulary by its S-glutathiolation with no requirement for proteolytical removal of the pro-domain. The MMP2 protein is consisted of 660 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 73.9 kDa.
What is the function of MMP2 protein?
The main function of MMP2 is to degrade various proteins in the extracellular matrix (ECM), such as collagen, elastin and fibronectin. Through this degradation, MMP2 plays a key role in many physiological and pathological processes, including tissue development, wound healing, angiogenesis, and tumor invasion and metastasis. In addition, MMP2 is also involved in inflammatory and immune responses, influencing cell migration and proliferation by regulating the activity of cytokines and chemokines.
MMP2 Related Signaling Pathway
MMP2 is involved in a variety of cell signaling pathways, mainly involved in extracellular matrix remodeling, cell proliferation, migration, invasion and apoptosis. During tumorigenesis, angiogenesis, tissue repair, and inflammation, MMP2 influences cellular interactions and signaling by regulating the activity of growth factors, cytokines, and receptors. In addition, MMP2 also interacts with a variety of signaling pathways, such as PI3K/Akt, MAPK/ERK, Wnt/β-catenin and TGF-β, to further regulate cell function and biological behavior.
MMP2 Related Diseases
MMP2 is upregulated in a variety of cancers, such as breast, lung, and prostate cancers, and can help cancer cells penetrate the basement membrane into the blood vessels or lymphatic system to metastasize to other sites. MMP2 plays a role in atherosclerotic plaque formation, causing plaque instability and potentially leading to myocardial infarction or stroke. In rheumatoid arthritis and other inflammatory joint diseases, MMP2 helps destroy articular cartilage. At the same time, it is associated with eye diseases, nervous system diseases and cerebrovascular diseases.
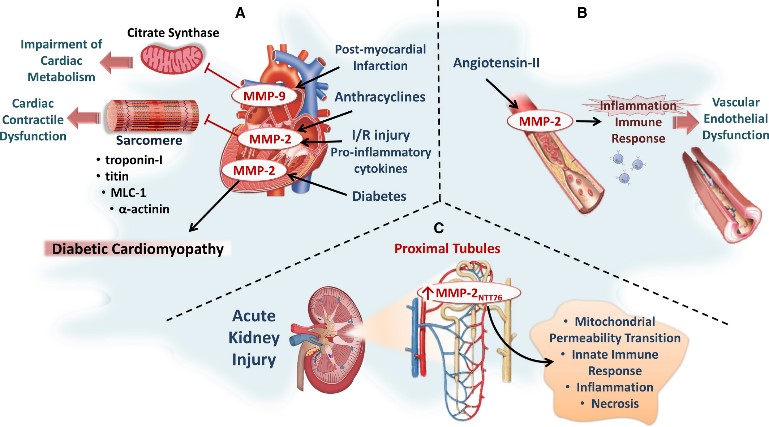
Fig2. Role of intracellular MMP-2 in selected pathological conditions. (Wesam Bassiouni, 2021)
Bioapplications of MMP2
MMP2 is widely used in cancer research as a marker of tumor aggressiveness and metastatic potential due to its ability to degrade the basement membrane and other extracellular matrix components, thereby promoting the migration and invasion of cancer cells. In addition, the detection of MMP2 activity is also used to assess the status of cardiovascular disease, arthritis, and other diseases. In some cases, MMP2 inhibitors are also being investigated as potential therapeutic agents to slow the progression of the disease, particularly in cancer treatment.
Case Study
Case study 1: Rocío Del Carmen Bravo-Miana, 2022
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) participate in cell-stroma crosstalk within the tumor microenvironment and fibroblasts (Fb) contribute to tumor promotion in thyroid cancer. However, the role of tumor-stroma derived EVs still needs to be deciphered. The researchers hypothesized that the interaction of thyroid tumor cells with Fb would liberate EVs with a specific proteomic profile, which would have an impact on EV-functionality in thyroid tumor progression-related events.
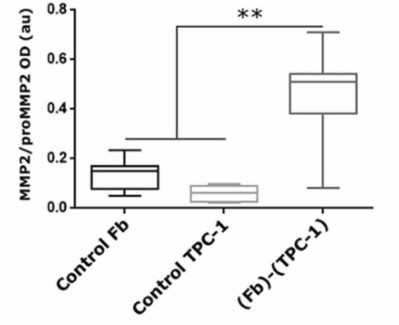
EVs, obtained by ultracentrifugation of conditioned media, were characterized by nanoparticle tracking analysis and western blotting. EV-proteomic analysis was performed by mass-spectrometry, and metalloproteinases (MMPs) were studied by zymography. EVs expressed classical exosome markers, with EVs from thyroid tumor cell-Fb co-cultures showing a proteomic profile related to extracellular matrix (ECM) remodeling. Bidirectional crosstalk between Fb and TPC-1 cells produced significantly more EVs than their isolated cells, and potentiated EV-functionality. In line with this, Fb-TPC-1 derived EVs induced MMP2 activation in NThyOri supernatants, and MMP2 activity could be evidenced in Fb and TPC-1 contact-independent co-cultures. Besides, MMP2 interactors allowed us to discriminate between EVs from thyroid tumoral and non-tumoral milieus.
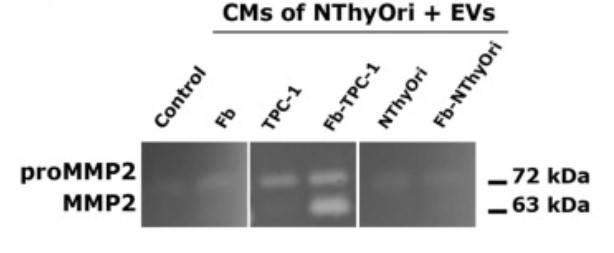
Fig1. Representative zymogram showing proMMP2 and MMP2 gelatinolytic activity in NThyOri-CM upon stimulation with medium (control) or EVs (CMs of NThyOri + EVs) from isolated Fb, TPC-1, NThyOri and Fb-TPC-1 and Fb-NThyOri co-cultured cells.
Case study 2: Luciana R Muniz-Bongers, 2021
The presence of an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment is a major obstacle in the success of cancer immunotherapies. Because extracellular matrix components can shape the microenvironment, the researchers investigated the role of matrix metalloproteinase 2 (MMP2) in melanoma tumorigenesis. They found that MMP2 signals proinflammatory pathways on antigen presenting cells, and this requires both TLR2 and TLR4. B16 melanoma cells that express MMP2 at baseline have slower kinetics in Tlr2-/- Tlr4-/- mice, implicating MMP2 in promoting tumor growth. Indeed, Mmp2 overexpression in B16 cells potentiated rapid tumor growth, which was accompanied by reduced intratumoral cytolytic cells and increased M2 macrophages. In contrast, knockdown of Mmp2 slowed tumor growth and enhanced T cell proliferation and NK cell recruitment. Finally, they found that these effects of MMP2 are mediated through dysfunctional DC-T cell cross-talk as they are lost in Batf3-/- and Rag2-/- mice.
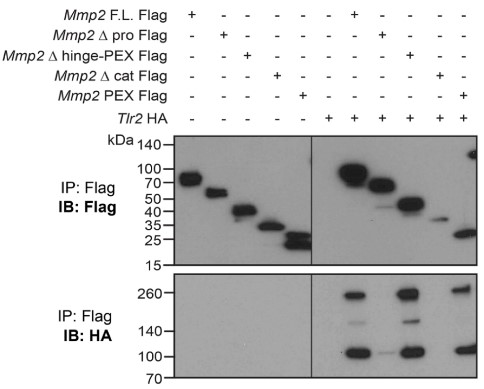
Fig3. Different MMP2 domains were deleted or expressed alone and tested for co-IP with Tlr2-HA.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
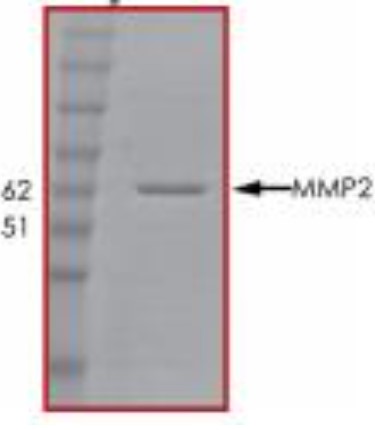
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (MMP2-201H) (PROTOCOL for western blot)
.

Fig2. SDS-PAGE (MMP2-890H) (PROTOCOL for western blot)
Involved Pathway
MMP2 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways MMP2 participated on our site, such as Leukocyte transendothelial migration,GnRH signaling pathway,Estrogen signaling pathway, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with MMP2 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Proteoglycans in cancer | CAMK2B,WNT7A,WNT7B,Fasl,PLCE1,FZD7,FZD6,SLC9A1,PLCG1,RPS6 |
| Pathways in cancer | NFKBIA,RASGRP3,MMP9,PIK3R5,TPR,VHL,RASSF1,AHA-1,AKT1,TRAF1 |
| Bladder cancer | IL-8,RAF1,MMP1A,MAP2K1,MYC,DAPK2,DAPK3,RB1,TP53,THBS1 |
| Leukocyte transendothelial migration | GNAI1,ROCK1,VCL,VAV2,MYL9,PECAM1,MYL7,ITGB2,OCLN,PTPN11 |
| Estrogen signaling pathway | SHC4,PIK3R1,GNAI1,HRAS,KRAS,ESR1,HSP90AA1,GPR30,MAPK1,SOS1 |
| GnRH signaling pathway | PLD1,CALM1,PTK2B,MAP2K4,MAP2K1,PRKACBA,GNRHR2,MAPK12A,MAP2K2B,CALM3A |
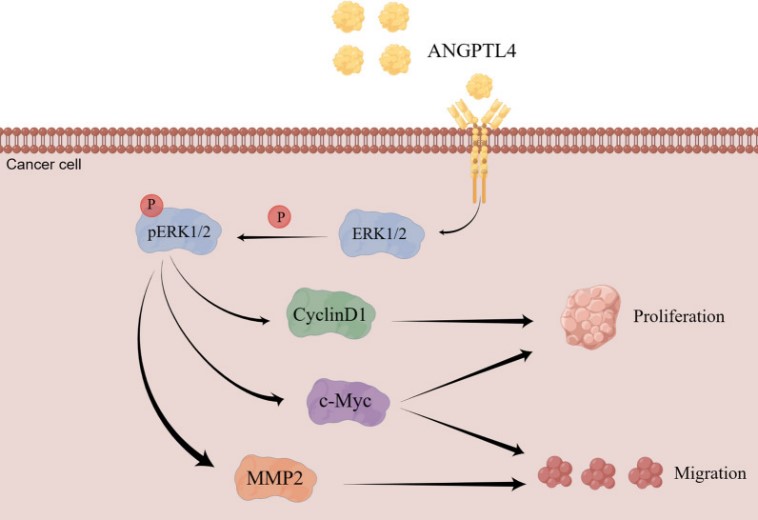
Fig1. Schematic depiction of potential mechanisms by which ANGPTL4-ERK1/2 signaling regulates OC progression. (Jiaqi Xu, 2024)
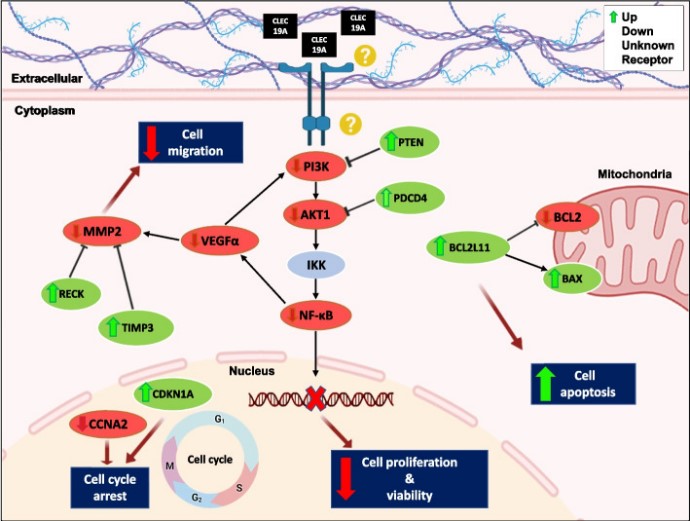
Fig2. Schematic representation of different pathways regulation by CLEC19A overexpression. CLEC19A regulates cell migration in this model by targeting VEGFα, RECK, TIMP3, and MMP2. (Fatemeh Mohajerani, 2024)
Protein Function
MMP2 has several biochemical functions, for example, metalloendopeptidase activity,metallopeptidase activity,protein binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by MMP2 itself. We selected most functions MMP2 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with MMP2. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| metallopeptidase activity | ADAM10,ADAM20,ERAP2,PSMD14,MMP30,ADAM12,GM5136,AQPEP,ADAMTS5,PAPLNB |
| metalloendopeptidase activity | MMP14,MMP7,MMP13A,ADAM23,BMP1A,ADAM21,UQCRC2B,ADAMTS15A,MEP1B,MMP13 |
| zinc ion binding | RGN,PHC2A,USP13,SF1,ZCCHC9,RNF125,MEX3B,TRIM35-39,UQCRC1,ZNF2 |
| serine-type endopeptidase activity | CMA1,PARL,ST14,HGFA,PRSS46,MBTPS1,KLK15,C1RA,FURINA,RHBDD3 |
| protein binding | KHDRBS3,CCDC88A,SUPV3L1,NR5A1,PDCD2,RALGAPA1,ENTPD1,PRKD1,KLRC1,SMR3B |
Interacting Protein
MMP2 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with MMP2 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of MMP2.
collagen_i_human;PCSK9;collagen_i_pig;TIMP2;Pcsk9;SCUBE3;USP12;A2M;LDLR;TGFB1;HSP90AA1;BACE1
Resources
-
-cover.jpg)
Exploring the Vast Potential of Targeted Antibody-Drug Conjugates (ADCs)
-

Exploring the Vast Potential of Targeted Antibody-Drug Conjugates (ADCs)
Gene Families
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Ghosh, A; Pechota, A; et al. Cigarette smoke-induced MMP2 and MMP9 secretion from aortic vascular smooth cells is mediated via the Jak/Stat pathway. HUMAN PATHOLOGY 46:284-294(2015).
- Ding, XF; Yang, DR; et al. Targeting TR4 nuclear receptor suppresses prostate cancer invasion via reduction of infiltrating macrophages with alteration of the TIMP-1/MMP2/MMP9 signals. MOLECULAR CANCER 14:-(2015).



