MMP3
-
Official Full Name
matrix metallopeptidase 3 (stromelysin 1, progelatinase) -
Overview
Proteins of the matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) family are involved in the breakdown of extracellular matrix in normal physiological processes, such as embryonic development, reproduction, and tissue remodeling, as well as in disease processes, such as arthritis and metastasis. Most MMPs are secreted as inactive proproteins which are activated when cleaved by extracellular proteinases. This gene encodes an enzyme which degrades fibronectin, laminin, collagens III, IV, IX, and X, and cartilage proteoglycans. The enzyme is thought to be involved in wound repair, progression of atherosclerosis, and tumor initiation. The gene is part of a cluster of MMP genes which localize to chromosome 11q22.3. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] -
Synonyms
MMP3;matrix metallopeptidase 3 (stromelysin 1, progelatinase);SL-1;STMY;STR1;CHDS6;MMP-3;STMY1;stromelysin-1;transin-1;proteoglycanase;matrix metalloproteinase-3;matrix metalloproteinase 3 (stromelysin 1, progelatinase)
Recombinant Proteins
- Rat
- Mouse
- Human
- Cattle
- Pig
- Rabbit
- Clostridium histolyticum
- E.coli
- HEK293
- Mammalian Cells
- Human
- Wheat Germ
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- His
- Avi
- Fc
- Non
- GST
- DDK
- Myc
- T7
- Flag
- SUMO
Background
What is MMP3 protein?
MMP3 (matrix metallopeptidase 3) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 11 at locus 11q22. This gene encodes an enzyme which degrades fibronectin, laminin, collagens III, IV, IX, and X, and cartilage proteoglycans. The enzyme is thought to be involved in wound repair, progression of atherosclerosis, and tumor initiation. Proteins of the matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) family are involved in the breakdown of extracellular matrix in normal physiological processes, such as embryonic development, reproduction, and tissue remodeling, as well as in disease processes, such as arthritis and metastasis. The MMP3 protein is consisted of 477 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 54.0 kDa.
What is the function of MMP3 protein?
MMP3, also known as stromelysin 1, is an enzyme that belongs to the matrix metalloproteinases family. MMP3 has a variety of biological functions, mainly involved in tissue remodeling, cell migration, inflammatory response, wound healing and tumor development. MMP3 can degrade various extracellular matrix (ECM) components, such as fibronectin, laminin and proteoglycan. By degrading ECM components, MMP3 provides pathways for cell migration, which is particularly critical in cell migration during development and in white blood cell migration in inflammatory and immune responses. MMP3 plays a role in the inflammatory process by releasing cytokines and chemokines, which attract immune cells to the site of inflammation and participate in the regulation of inflammatory response.
MMP3 Related Signaling Pathway
MMP3 degrades a variety of extracellular matrix components, such as proteoglycans, fibronectin, and collagen, which are essential for cell migration, inflammatory response, wound healing, and tumor cell invasion and metastasis.
In addition, MMP3 can activate or deactivate other MMPs family members, and through this interaction, MMP3 can regulate a broader range of biological activity. For example, it can enhance its degradation of the extracellular matrix by activating MMP-1 and other MMPs. At the same time, MMP3 can also affect signaling pathways for cell proliferation and differentiation by releasing precursor forms of growth factors and cytokines, such as transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β).
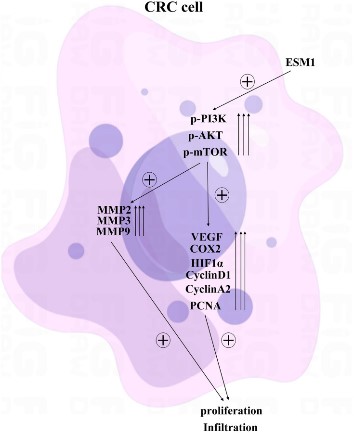
Fig1. ESM1 may affect the proliferation of CRC cells through the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. (Liqun Yang, 2023)
MMP3 Related Diseases
MMP3 is a protease capable of degrading various extracellular matrix components. It plays a role in a variety of physiological processes, such as tissue remodeling, wound healing, and embryonic development. However, abnormal expression or activity of MMP3 has also been associated with a variety of diseases, including but not limited to: elevated levels of MMP3 in osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis; MMP3 is up-regulated in a variety of cancers, and it affects tumor growth and spread by promoting tumor cell invasion and metastasis. In addition, MMP3 is also associated with liver diseases, skin diseases, cardiovascular diseases, etc. MMP3 may be involved in the reduction of bone density and the destruction of bone structure in osteoporosis.
Bioapplications of MMP3
MMP3 is considered to be an important biomarker for the early diagnosis of RA, and its concentration in the serum of RA patients is significantly higher than that of normal people. The concentration of MMP3 is closely associated with cartilage damage and bone erosion, so it can be used to monitor the progression of RA. Drug development targeting MMP3 is ongoing, particularly those aimed at inhibiting MMP3 activity to treat related diseases. These drugs may be potentially valuable in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis and other MMP3-related conditions.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Szymon W Manka, 2019
Matrix metalloproteinase-3 (MMP-3) participates in normal extracellular matrix turnover during embryonic development, organ morphogenesis and wound healing, and in tissue-destruction associated with aneurysm, cancer, arthritis and heart failure. Despite its inability to cleave triple-helical collagens, MMP-3 can still bind to them, but the mechanism, location and role of binding are not known. The researchers used the Collagen Toolkits, libraries of triple-helical peptides that embrace the entire helical domains of collagens II and III, to map MMP-3 interaction sites. The enzyme recognises five sites on collagen II and three sites on collagen III. They share a glycine-phenylalanine-hydroxyproline/alanine (GFO/A) motif that is recognised by the enzyme in a context-dependent manner. Neither MMP-3 zymogen (proMMP-3) nor the individual catalytic (Cat) and hemopexin (Hpx) domains of MMP-3 interact with the peptides, revealing cooperative binding of both domains to the triple helix.
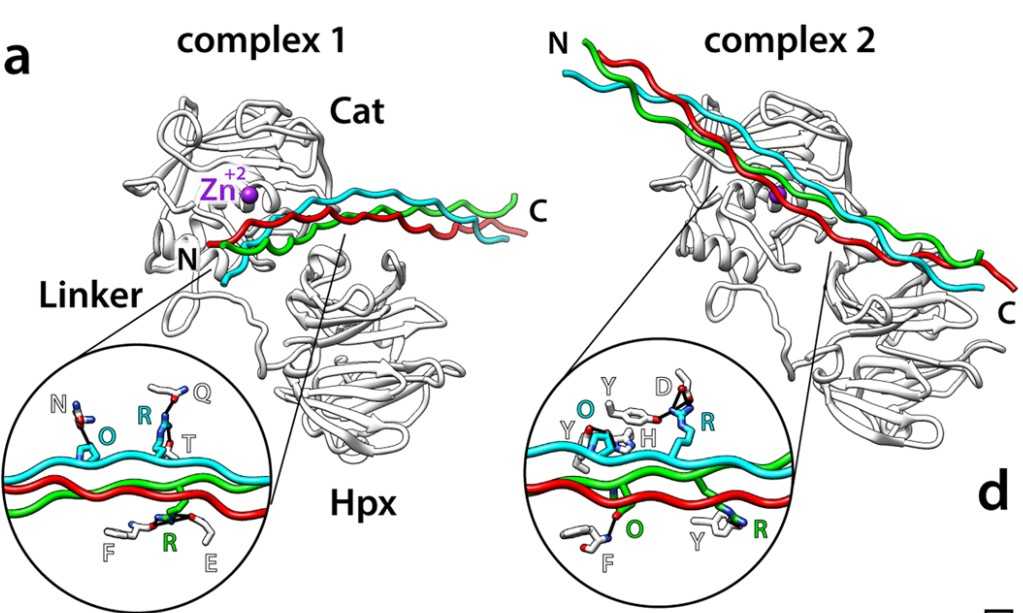
Fig1. Two modelled frontal-binding MMP-3:III-40d complexes shown as ribbons in the standard MMP-3 orientation.
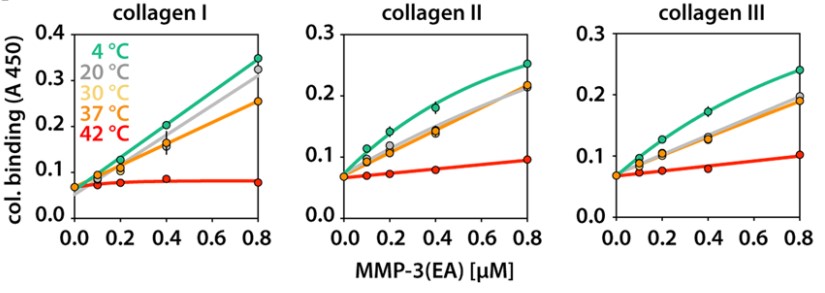
Fig2. Temperature-dependent binding of biotinylated MMP-3(EA) to collagens I, II and III.
Case Study 2: Chia-Ling Hsieh, 2017
Studies on the aberrant control of extracellular matrices (ECMs) have mainly focused on the role of malignant cells but less on that of stromal fibroblasts during cancer development. Herein, by using paired normal and prostate cancer-associated stromal fibroblasts (CAFs) derived from a coculture cell model and clinical patient samples, demonstrating that although CAFs promoted prostate cancer growth, matrix metalloproteinase-3 (MMP-3) was lower in CAFs but elevated in prostate cancer cells relative to their normal counterparts. Furthermore, hydrogen peroxide was characterized as the central modulator for altered MMP-3 expression in prostate cancer cells and CAFs, but through different regulatory mechanisms. Treatment of CAFs but not prostate cancer cells with hydrogen peroxide directly inhibited mmp-3 promoter activity with concomitant nuclear translocation of nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB), indicating that NF-κB is the downstream pathway for the transcriptional repression of MMP-3 in CAFs. Hydrogen peroxide reduced thrombospondin 2 (an MMP-3 suppressor) expression in prostate cancer cells by upregulating microRNA-128.
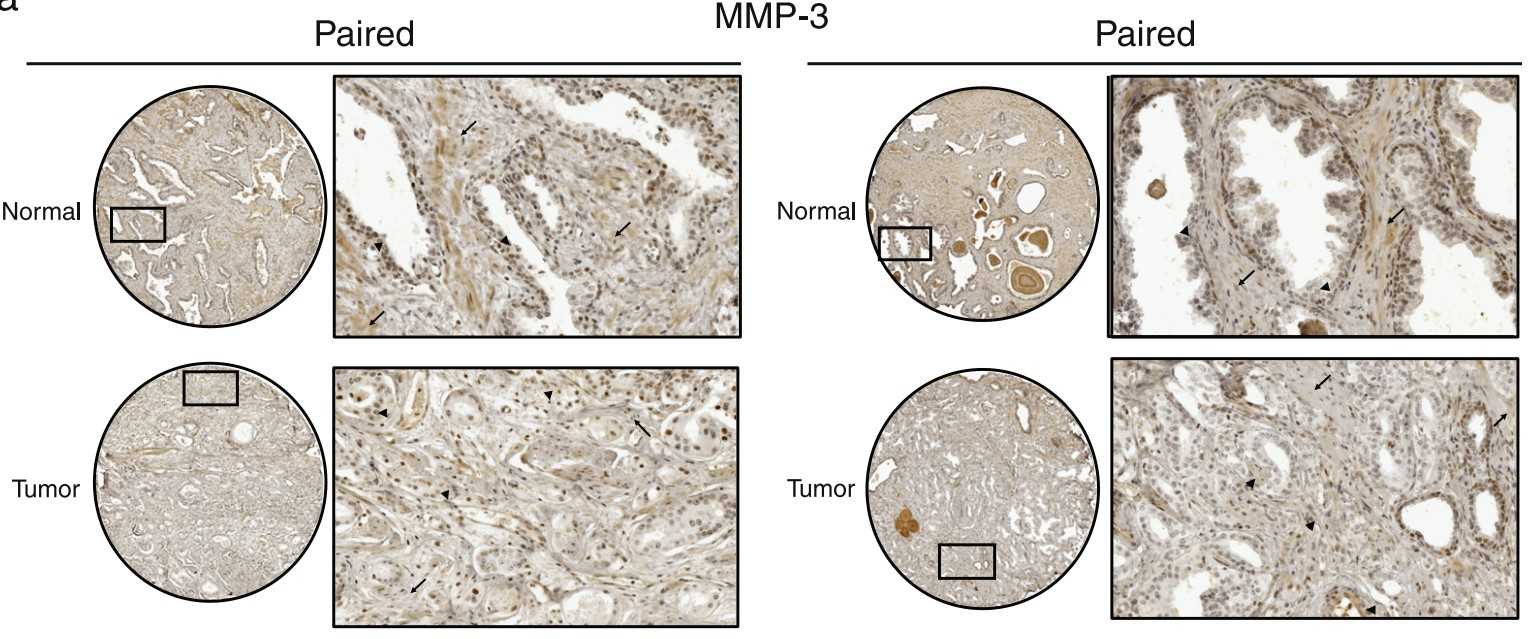
Fig3. Representative digital images of IHC staining of MMP-3.
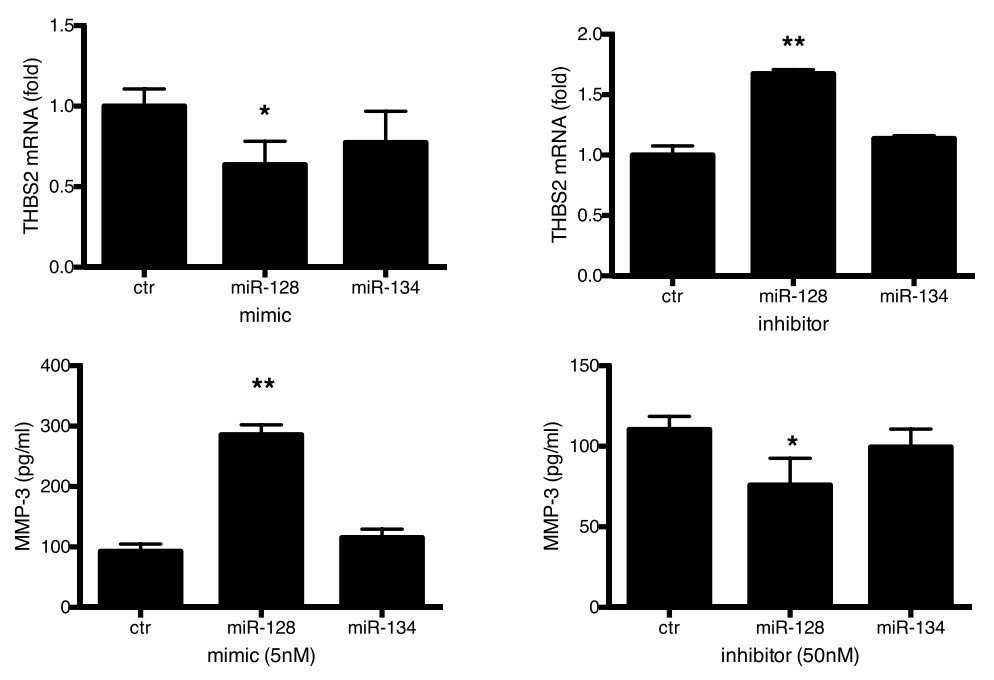
Fig4. Real-time RT-PCR of THBS2 mRNA expression level and ELISA of MMP-3 levels in conditioned media of PC3 transfected with miRNA mimics or inhibitors.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (MMP3-5433H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (MMP3-780H)
Involved Pathway
MMP3 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways MMP3 participated on our site, such as TNF signaling pathway,Transcriptional misregulation in cancer,Rheumatoid arthritis, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with MMP3 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Transcriptional misregulation in cancer | FCGR1A,MPO,RUNX1T1,Bcl2a1b,RELA,TRAF1,RUNX1,Aff1,BMI1,RARA |
| TNF signaling pathway | FAS,CXCL2,MAPK11,MAP3K14,RPS6KA4,TNFAIP3,PGAM5,MAP2K3,CREB3L1,CASP8 |
| Rheumatoid arthritis | IL23,CCL5,TGFB1,HLA-DQB1,TNFRSF11A,HLA-DPB1,HLA-DRB4,IL15,CD80,TEK |
Protein Function
MMP3 has several biochemical functions, for example, calcium ion binding,endopeptidase activity,metalloendopeptidase activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by MMP3 itself. We selected most functions MMP3 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with MMP3. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| protein binding | ATP6V0A2,TSHR,PRDM5,DNAJC7,FAM193B,MST1,ZNF511,ARHGAP1,REG3A,PIAS4 |
| zinc ion binding | PPARAB,CA15A,ZFAND2B,TRIM101,JUB,ADAMTS5,CBLB,ZCCHC11,CYLD,UNKL |
| endopeptidase activity | PSMB8F,PSMB4,NCSTN,ATG4B,RHBDD1,P4HB,PSMB7,AP1S2,SENP1,CPNE1 |
| metalloendopeptidase activity | ADAM33,UQCRC2,HE1B,TLL2,MMP7,ADAMTS9,HE2,GM12824,MMP14,ADAMTS2 |
| calcium ion binding | SLC25A23,CANT1B,CELSR3,SLC25A23B,MASP1,PKD2L1,CABP5B,ANXA1B,CSN2,PADI3 |
Interacting Protein
MMP3 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with MMP3 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of MMP3.
MEOX2;TIMP1
Resources
Gene Families
Related Services
Related Products
References




