Active Recombinant Human Sp1 Transcription Factor, His-tagged
| Cat.No. : | SP1-1158H |
| Availability | January 27, 2026 |
| Unit | |
| Price | |
| Qty |
- Specification
- Gene Information
- Related Products
- Citation
- Download
| Species : | Human |
| Source : | Sf9 Cells |
| Tag : | His |
| Description : | The his-tagged wild type Sp1 protein (785 amino acids, 100 kDa) was expressed in a baculovirus system and purified by affinity column and FPLC.Sp1 was first detected in HeLa cells on the basis of its ability to activate the SV40 early promoter transcription. Subsequently it was shown to recognize and bind selectively to a GC-rich consensus sequence (GC-box: GGGCGG or CACCC) that presents in the promoter of several important cellular genes, including SV40 early, HIV-1, PDGF-B etc. Sp1 was the first transcription factor to be cloned and characterized. Analysis of structure and function has revealed that Sp1 can be separated into discrete functional domains. The DNAbinding domain consists of three zinc fingers that specifically bind to the GC-box element. Sp1 contains at least four separate transcriptional activation domains. Two of these domains are glutamine-rich, a wellcharacterized motif found in several other transcription factors. In addition to transcription, Sp1 function has been linked to cell growth, cancer, Huntington disease, and other disorders through transcriptional regulation or specific protein-protein interactions. The function of Sp1 can be regulated by phosphorylation and glycosylation. |
| Form : | Liquid. Supplied in 20 mM Tris-HCl pH 8.0, 100 mM KCl, 0.2 mM EDTA, 1 mM DTT, 20% glycerol. |
| Purity : | > 90% by SDS-PAGE. |
| Activity : | 30-100 ng are required for a reconstituted transcription assay and 5-25 ng are required for a gel mobility shift assay in a 20 μl reaction. |
| Application : | Sp1 can be used for in vitro transcripion activation, DNAse I activation and gel mobility shift assays. |
| Usage : | For in vitro use only. |
| Storage : | Quality guaranteed for 12 months store at -80°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. |
| Publications : |
| Gene Name | SP1 Sp1 transcription factor [ Homo sapiens ] |
| Synonyms | SP1; Sp1 transcription factor; Sp1 transcription factor; specificity protein 1; TSFP1;Transcription factor Sp1 |
| Gene ID | 6667 |
| mRNA Refseq | NM_003109 |
| Protein Refseq | NP_003100 |
| MIM | 189906 |
| UniProt ID | P08047 |
| Chromosome Location | 12q13.1 |
| Pathway | Huntington"s disease; TGF-beta signaling pathway |
| Function | RNA polymerase II transcription factor activity; double-stranded DNA binding; histone deacetylase binding; metal ion binding; promoter binding; protein C-terminus binding; protein homodimerization activity; transcription activator activity; transcription factor activity; zinc ion binding |
| ◆ Recombinant Proteins | ||
| SP1-16H | Recombinant Human SP1 protein, His-tagged | +Inquiry |
| SP1-1158H | Active Recombinant Human Sp1 Transcription Factor, His-tagged | +Inquiry |
| SP1-5677R | Recombinant Rat SP1 Protein | +Inquiry |
| SP1-98HFL | Recombinant Full Length Human SP1 Protein, N-His-tagged | +Inquiry |
| SP1-30987TH | Recombinant Human SP1, His-tagged | +Inquiry |
Differential SP1 Interactions in SV40 Chromatin from Virions and Minichromosomes
Journal: bioRxiv Data: 2020/5/19
Authors: Rowbotham Kincaid, Haugen Jacob, Milavetz Barry
Article Snippet:PrePrint: HIS-tagged SP1 binding analyses were performed using reagents present in the Millipore ChIP kit.HIS-tagged SP1 binding analyses were performed using reagents present in the Millipore ChIP kit.. SV40 chromatin (25 μl) was incubated with an equal volume of chromatin dilution buffer from the kit, 2 μl of a 10 mg/ml solution of bovine serum albumin (Sigma), and 0.25 μg of HIS-tagged SP1 (Creative BioMart) for 30 minutes at 4 0 with constant rotation.. Ni-magnetic beads (15 μl) were added to bind the HIS-tagged SP1 and the mixture was incubated for an additional one hour with rotation.Ni-magnetic beads (15 μl) were added to bind the HIS-tagged SP1 and the mixture was incubated for an additional one hour with rotation.
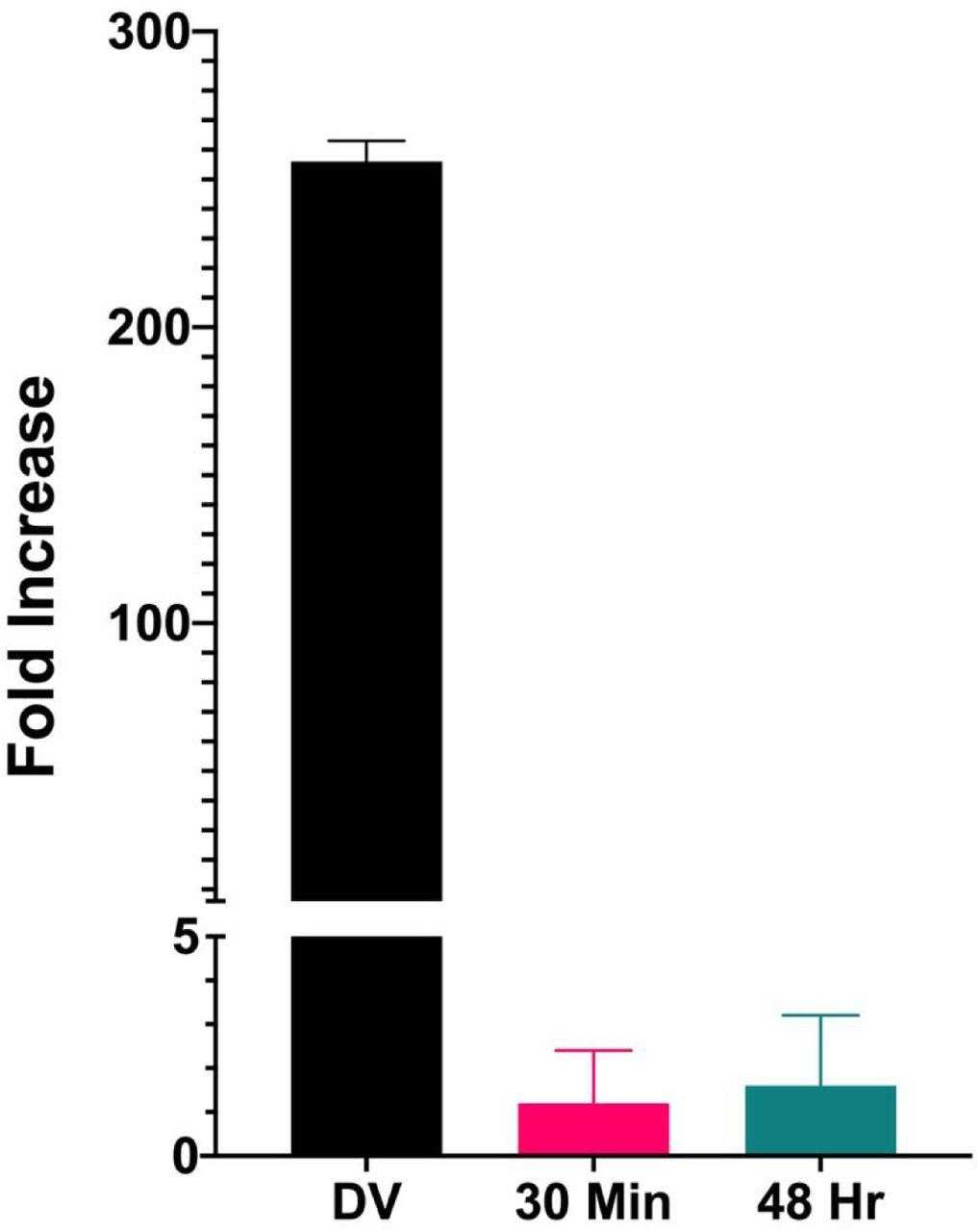
Similar amounts of chromatin from disrupted virions, minichromosomes isolated 30 minutes post infection, and minichromosomes isolated 48 hours post infection were incubated in parallel with HIS-tagged
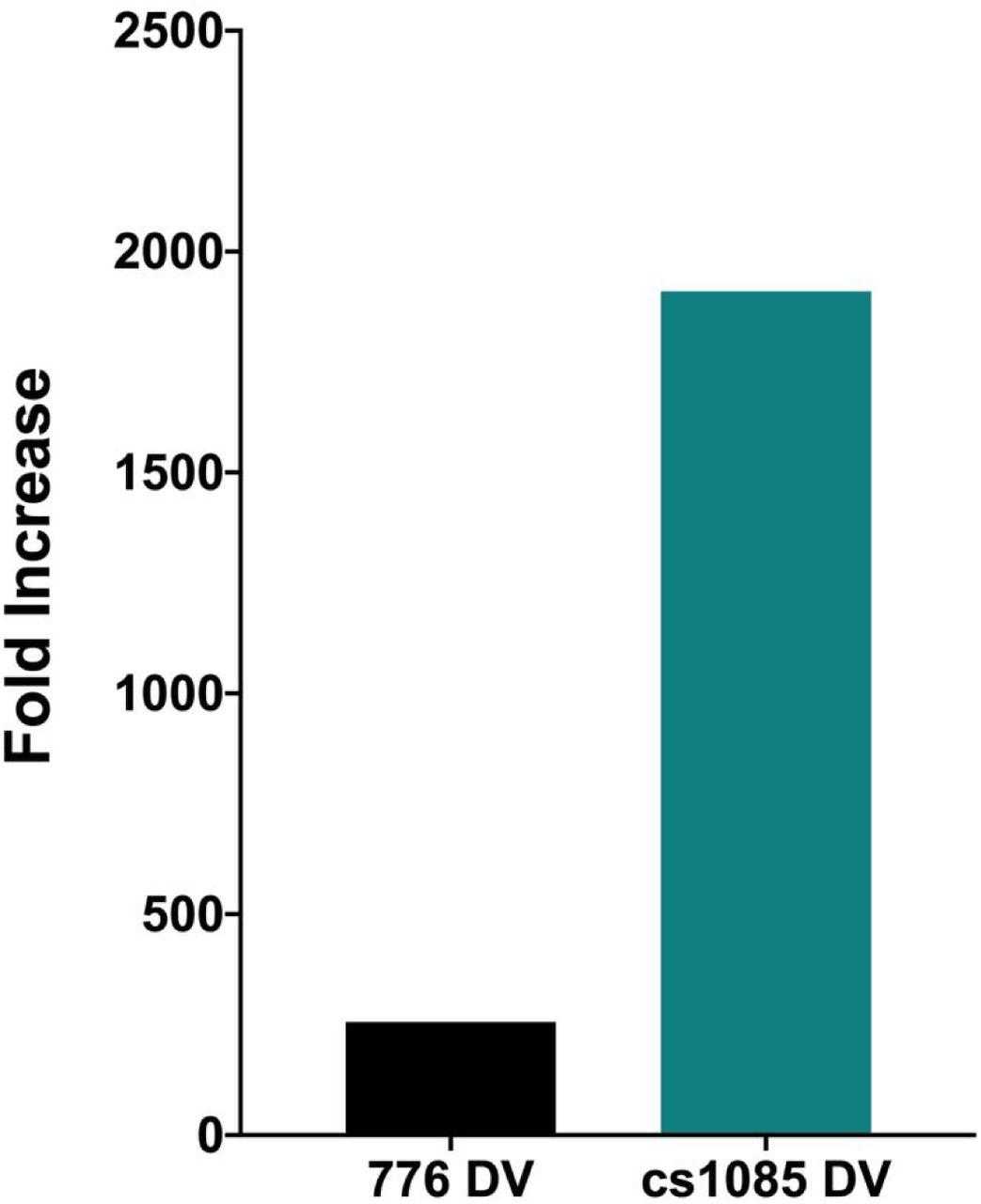
Similar amounts of chromatin from disrupted virions prepared from SV40 wild type and the mutant cs1085 virus were incubated in parallel with HIS-tagged
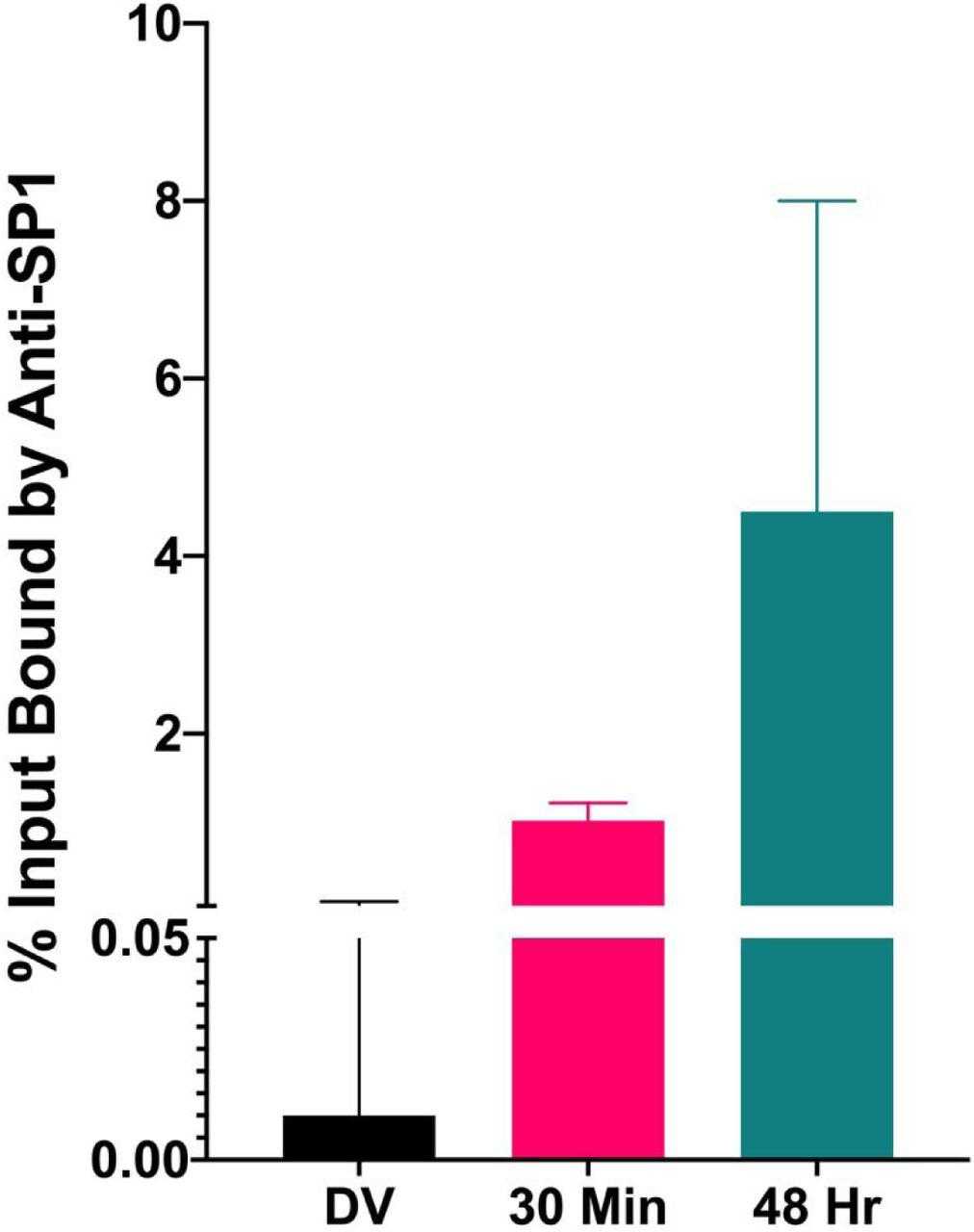
Similar amounts of chromatin from disrupted virions and minichromosomes isolated 30 minutes and 48 hours post infection were subjected to a ChIP assay with antibody to
Not For Human Consumption!
Inquiry
- Reviews (0)
- Q&As (0)
Ask a Question for All SP1 Products
Required fields are marked with *
My Review for All SP1 Products
Required fields are marked with *



